Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve Ebstein’s anomaly Physical examination with Clinical features
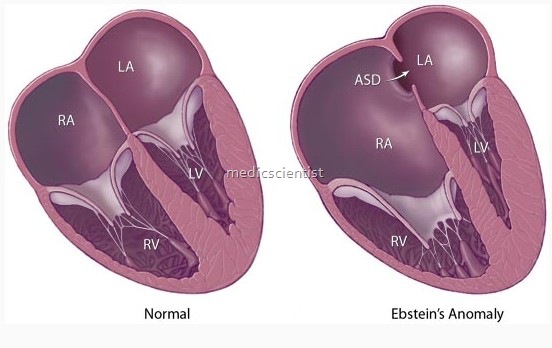
- Ebsetin’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve is a congenital heart disease in which the tricuspid valve is placed at a lower level so that there is atrialization of the rigFit ventricle.
- A congenital heart condition resulting from downward displacement of the tricuspid valve from the anulus fibrosus. It causes fatigue, palpitations, and dyspnea.
- Abnormal downward placement of tricuspid valve within the RV; tricuspid regurgitation, hypoplasia of RV, and a right-to-left shunt are common
- There is a downward displacement of the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle due to anomalous at. achment of tricuspid leaflets.
Clinical features of Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve
- Ebsetin’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve cyanosis ay or may not be present.
- ulmonary vascularity is normal or reduced. left ventricle is dominant.
- here may be transient neonatal cyanosis with recur-ence years later.
- cyanosis is present in the neonatal age infant is achypneic and prognosis is bad.
- there is earl systolic decrescendo murmur of TR best eard in the tricuspid area.
- 3rd and 4th heart sounds are present resulting in a triple or quadruple rhythm.
- left ventricular impulse is seen
- VP is normal
- jrst heart sound is widely split and TI is loud
- there is short mid-diastolic, presystolic murmur.
Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve Ebstein’s anomaly Physical examination with Clinical features
Ebstein’s anomaly Physical examination —
- The last finding represents passive hepatic congestion resulting from tricuspid regurgitation and elevated right atrial pressure.
- The physical findings vary with the severity of pathology and the magnitude of right-to-left interatrial shunting.
- A systolic murmur from tricuspid regurgitation is a common finding
- When tricuspid regurgitation is severe, jugular venous distension and a prominent “v” wave may be seen
ECG
- shows tall, broad, right atrial P waves in V1, increased PR interval, right bundle block branch dee
- aves in L2, 3, aVF and Vl V2.
X-ray
- decreased pulmonary vascularity, small aortic t and pulmonary trunk and large right atrium.
- In severe cases, the chest radiograph reveals massive cardiomegaly (often termed a “wall to wall” heart) with diminished pulmonary vascularity
- In a neonate the cardiac silhouette occupies the entire chest.
- The chest radiograph may be normal in patients with less severe disease.
2D echo
- Echocardiography shows apical displacement of tricuspid septal leaflet, abnormal RV size, and quantitates degree of tricuspid regurgitation.
- Shows leaflet abnormalities, atrialized right ventricle, paradoxical septal motion, tricuspid regurgitation, enlarged left ventricle and right-to- left shunt via atrial septal defect.
Treatment of Ebstein’s anomaly
- Prosthetic tricuspid valve may be surgically implanted.

