AV CONDUCTION DISORDERS
- When AV nodal block occurs the His bundle can generate a heart rate of 40 – 60 beats per minute with normal QRS complexes.
- If the distal His Purkinje system takes over then the heart rate generated is 25 – 45 beats per minute with wide QRS complexes.
- This rhythm is unstable and can degenerate into VT,-VF or cardiac standstill.
Etiology
- · Myocardial infarction
- · Digitalis
- · CCB
- · Coronary spasm
- · Beta blockers
- · Myocarditis
- · Infectious mononucleiosis
- · Sarcoidosis
- · Rheumatic fever
- · Lyme disease
- · Mesotheliomas.
- Lev’s disease (calcification and sclerosis of conduction system). Lenegre’s disease (sclera degenerative disease).
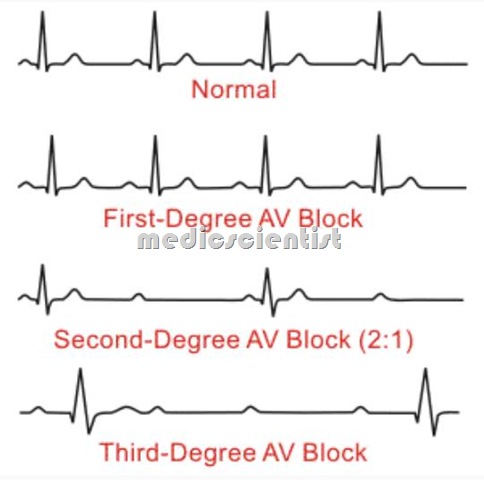
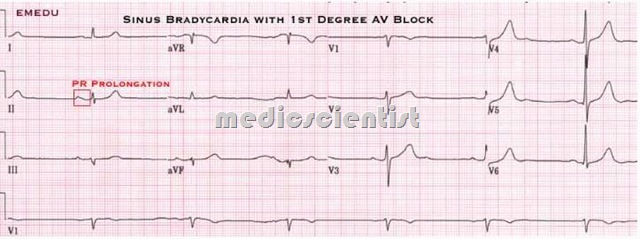
First degree AV block
- AV conduction is prolonged.
- It is recognized on the electrocardiogram by a prolonged P-R interval.
- PR interval is more than 0.20 seconds.
- A heart block in which the conduction of impulses through the atrioventricular node is delayed but all atrial beats are followed by ventricular beats.
Second degree AV block
- There is intermittent AV block and some atrial impulses do not conduct to ventricles.
- A form of atrioventricular block in which only some atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles. Two variants exist: Mobitz I (Wenckebach) and Mobitz II.
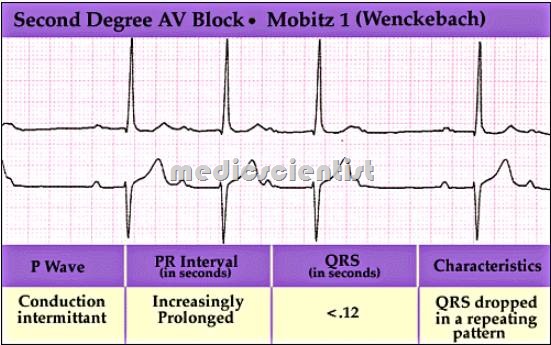
Mobitz type I – second degree A V block
- In Mobitz I, the PR intervals become progressively longer until a QRS complex is dropped.
- Because of the dropped beats, the QRS complexes appear to be clustered (a phenomenon called “grouped beating”) on the electrocardiogram.
- This is also called AV Wenckebach block.
- There is progressive increase of PR interv I till there is a blocking of an atrial impulse resulting in absence of QRST following the P wave ,
- The block is in the AV node and so the QRS is normal.
- It is seen in inferior wall MI, drug intake like digitalis, beta blockers, and CCBs.
- It does not need aggressive treatment.
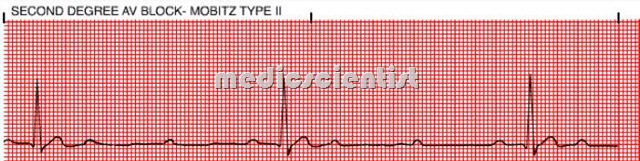
Mobitz type Il – second degree A V block
- The PR intervals are constant and suddenly there is failure of conduction due to disease of His Purkinjy system.
- In Mobitz II, PR intervals have a constant length, but QRS complexes are dropped periodically, usually every second, third, or fourth beat
- The QRS is wide.
- After a PQRST sequence suddenly there is a P wave which does not conduct to the ventricles and so there is no QRST following the P.
- Pacemaker implantation is usually necessary. ~It usually occurs with anterior wall infarction.
- Treatment is a cardiac pacemaker implantation.
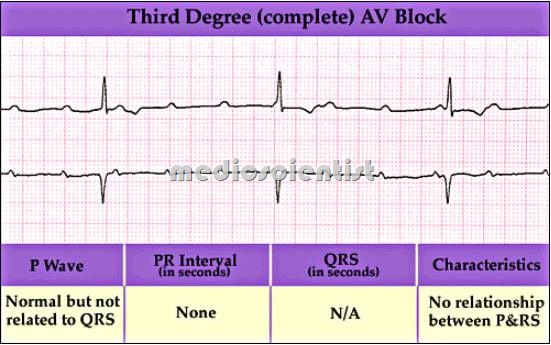
Third degree AV block —
- No atrial impulse propagates to the ventricles in third degree AV block.
- The atria and ventricles beat independently at different rates.
- The atria beats at around 72 beats per minute whereas the ventricles beat at rate of 40-50 per minute.
- In congenital AV block the heart rate increases with exercise.
- The QRS complexes representing ventricular beats which come at 40-55 beats per minute, increase with atropine or exercise, originate in the AV node.
- This may not be very serious and pacemaker may not be required.
- If the QRS is wide and the rate is less than 40 beats per minute, the block is in or distal to His bundle and treatment is pacemaker implantation.
- It is recognized in the ECG by P waves and QRS coming at different times, having no relation with each other.
- The P waves comes at around 72 beats per minute and the QRS comes at about 40-50 beats per minute.
- So there are more Ps than QRS and the ventricular rate is slow.
Treatment of AV block
- 1. Atropine – 0.5 -2 mg IV
- 2. Isoproterenol – 1 -4 mg IV
- 3. Mineralocorticoids
- 4. Ephedrine
- 5. Orciprenaline
- 6. Theophylline
- 7. Serotonin uptake inhibitors
- 8. Pacemakers.