Hypertension
Hypertension is a serious disease which may be asymptomatic. According to JNC-7 normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg and a blood pressure equal to or more than 140 mmHg systolic and 90 mmHg diastolic is hypertension.
- Etiology is unknown in 90 – 95% cases.
- Greater than normal tension or tone.
2. In adults, a condition in which the blood pressure (BP) is higher than 140 mm Hg systolic or 90 mm Hg diastolic on three separate readings recorded several weeks apart.
Normal blood pressure: systolic <120 mmHg and diastolic <80 mmHg Prehypertension: systolic 120-139 mmHg or diastolic 80-89 mmHg Hypertension:
- Stage 1: systolic 140-159 mmHg or diastolic 90-99 mmHg Stage 2: systolic ≥ 160 or diastolic ≥ 100 mmHg
Optimal blood pressure: systolic <120 mmHg and diastolic <80 mmHg Normal: systolic 120-129 mmHg and/or diastolic 80-84 mmHg High normal: systolic 130-139 mmHg and/or diastolic 85-89 mmHg Hypertension:
- Grade 1: systolic 140-159 mmHg and/or diastolic 90-99 mmHg Grade 2: systolic 160-179 mmHg and/or diastolic 100-109 mmHg Grade 3: systolic ≥ 180 mmHg and/or diastolic ≥ 110 mmHg Isolated systolic hypertension: systolic ≥ 140 mmHg and <90 mmHg
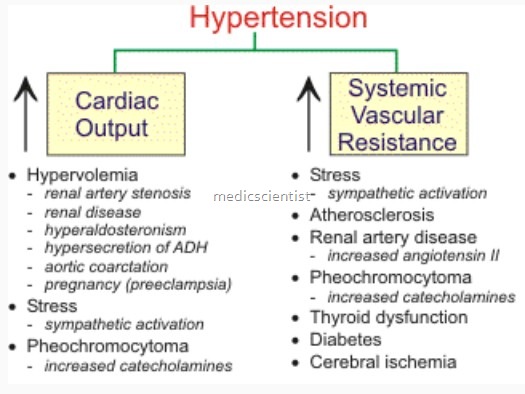
Arterial pressure is regulated by :
- Peripheral and central adrenergic systems .-
- Renal
- Hormonal
- Vascular factors
- Average prevalence is >50% in non-whites.
- Frequency of hypertension is more in men.
- In females, prevalence increases after age of 50 years.
- In the upper class of society blood pressure increases with age.
Primary or essential or idiopathic hypertension:
- Essential Hypertension is arterial hypertension with no definable cause.
Secondary hypertension :
- When a specific organ or defect is responsible for hypertension, it is called secondary hypertension. The causes are many, involving different organs.
Classification of arterial hypertension
1 Systolic hypertension with wide pulse pressure
- Arteriosclerosis
- AR
- Thyrotoxicosis Hyperkinetic circulation Fever
- AV fistula
- PDA
2. Systolic and diastolic hypertension
- Renal causes
- Chronic pyelonephritis
- Acute and chronic glomerulonephritis
- Polycystic renal disease
- Renovascular stenosis
- Arteriolar nephrosclerosis Diabetic nephropathy
- Renin producing tumors
- Endocrinalcauses ‘e
- Oral contraceptives
- Adrenocortical hyperfunction
- Cushing’s disease and syndrome
- Primary hyperaldosteronism
- Congenital or hereditary adreno genital syndromes
- Pheochromocytoma
- Myxedema
- Acromegaly
- Neurogenic causes
- Psychogenic
- b Familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome)
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Miscellaneous causes
- Coarctation of aorta
- Polyarteritis nodoses
- Hypercalcemia
- Drugs like glucocorticoids, cyclosporine
- Unknown etiology
-
- Essential hypertension
- Toxaemia of pregnancy
- Acute intermittent porphyria