Article Contents ::
- 1 Peptic Ulcer
- 2 Agents which may damage the mucosa
- 3 Peptic Ulcer Types —
- 4 Gastric ulcer
- 5 Duodenal ulcer
- 6 Esophageal ulcers
- 7 Peptic Ulcer Clinical Features
- 8 Peptic Ulcer Risk Factors
- 9 Peptic Ulcer Examination Diagnosis
- 10 Peptic Ulcer Complications of Peptic ulcer disease
- 11 Peptic Ulcer Diagnosis
- 12 Peptic Ulcer Treatment
- 13 Acid suppressing drugs
- 14 Therapy of Helicobacter pylori
- 15 Surgical therapy
- 16 Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Peptic Ulcer
- Peptic Ulcer Causes Examination Diagnosis and Treatment
An ulcer is a disruption of mucosal lining of stomach and or duodenum due to active inflammation. Ulcers are usually chronic in nature. Peptic ulcer disease is a common illness, affecting about 10% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes
Agents which may damage the mucosa
- · Acid
- · Pepsin
- · Bile acids
- · Pancreatic enzymes
- · Drugs
- · Bacteria.
- Both exogen9us and endogenous substances attack the mucosa. ‘
- The mucosal’defence consists of pre-epithelial, epithelial and sub-epithelial layers.
- There is a mucoLl bicarbonate layer which protects the mucosa.
- Bicarbonate secretion is stimulated by calcium, prostaglandins, cholinergic input, and acidification.
- Peptic ulcer disease includes gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Ulcers are defined as a break in mucosal surface more than 5 mm in size.
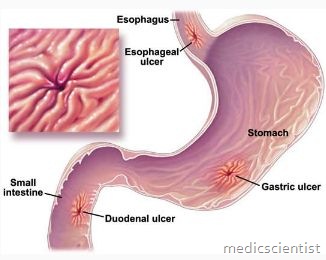
Peptic Ulcer Types —
Gastric ulcer
- Gastric ulcers occur later in life than duodenal ulcers usually around 6th decade.
- Gastric ulcers are more common in males.
- Found distal to junction between antrum and acid secreting mucosa.
- May be malignant.
- There may be H. pylori infection.
- Cause may be NSAIDs and H. pylori infection. Gastric acid may be normal or decreased. There is impairment of mucosal defence. There is delayed gastric emptying of solids.
- Less common than duodenal ulcer in absence of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Commonly located along lesser curvature of the antrum near the incisura and in the prepyloric area
- H. pylori is also called Campylobacter pyloridis.
- H. pylori can also cause lymphoma and gastric adenocarcinoma.
- In gastric ulcers discomfort is precipitated by food.
- Nausea and weight loss are seen in gastric ulcers.
Duodenal ulcer
- Duodenal ulcers are more common than gastric ulcers.
- Most common in first part of duodenum within 3 cm of pylorus.
- Usually less than 1 cm diameter. ~ Giant ulcer may be 3-6 cm.
- Sharply demarcated and sometimes deep. Base of ulcers shows eosinophilic necrosis.
- Most common form of peptic ulcer
- Usually located in the proximal duodenum
- Multiple ulcers or ulcers distal to the second portion of duodenum raise possibility of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- Common causes are H. pylori infections and NSAIDs~ Gastric acid secretion is increased.
- There is increased gastric emptying of liquids. Bicarbonate secretion is decreased.
Esophageal ulcers
- Located in the distal esophagus and usually secondary to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); also can be seen with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Peptic Ulcer Clinical Features
- · Abdominal pain.
- · In NSAIDs-induced ulcers there may be bleeding, perforation, obstruction.
- · Epigastric pain, burning, gnawing pain.
- · Hunger pains.
- · Typical pain occurs 90 minutes to 3 hours after meal.
- · Relieved by meals or antacids.
- · Pain occurs between midnight and 3 AM and is so severe that the patient wakes up.
- · Dyspepsia is a common symptom.
- · In endoscopy-ulcers, ulcer crater and gastroduodenitis are seen.
- · When complications occur there is dyspepsia.
- · Pain is not relieved by food or antacids, pain radiates to back in penetrating ulcers.
- · There may be pancreatitis.
- · There is constant nausea and vomiting.
- · Perforation is suggested by generalized and sudden onset severe abdominal pain.
- There may be bleeding from the ulcers giving rise to’ • tarry stools or coffee-ground vomitings.
Peptic Ulcer Risk Factors
- H. pylori infection
- NSAID use
- Smoking cigarettes
- Family history of ulcers
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Medications: Corticosteroids (high-dose and/or prolonged therapy),
Peptic Ulcer Examination Diagnosis
- • Epigastric tenderness.
- Pain to the right of midline.
- Tachycardia, dehydration, orthostatic hypotension due to vomiting or blood loss.
- Tender board-like (rigid) abdomen due to perforation.
- Gastric outlet obstruction is indicated by presence of succussion splash (splashing sound from the abdomen on shaking the body).
Peptic Ulcer Complications of Peptic ulcer disease
- 1. Gastrointestinal bleeding – Common in elderly and due to use of NSAIDs.
- 2. Perforation – Common in elderly, and use of NSAIDs.
- Duodenal ulcer penetrates into pancreas leading to pancreatitis.
- Gastric ulcers penetrate into left liver lobe.
- 3. Gastric outlet obstruction – Occurs in prepyloric region. There is loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pain after meals and weight loss.
Peptic Ulcer Diagnosis
- · Barium study
- · Endoscopy
- · Detection of H. pylori
- · Serum gastrin and gastric acid analysis.
- Test for detection of H. pylori
- Rapid urease, histology, culture, serology, urea breath test, stool antigen.
Peptic Ulcer Treatment
Acid suppressing drugs
- Antacids – 100 meq/L given 1 and 3 hours after meals and at bed time.
- H2 receptor antagonists:
- Cimetidine – 400 mg BD
- Ranitidine – 300 mg HS
- Famotidine – 40 mg HS
- JProton pump inhibitors:
- Omeprazole 20 mg/day
- Lansoprazole 30 mg/day
- Rabeprazole – 20 mg/day
- Pantoprazole – 40 mg/day
- ucosal protective agents:
- Sucralfate 19m QID
- Prostaglandin analogue (misoprostol 200IJg QID) Bismuth-containing compounds
- H2 receptor antagonists.
Therapy of Helicobacter pylori
- Multiple drugs are used in combination therapy because single agent is not effective.
- Different regimens are:
- Bismuth subsalicylate + Metronidazole
- Tetracycline
- Ranitidine bismuth citrate +
- Tetracycline
- Metronidazole ..7 Omeprazole
- Clarithromycin
- Metronidazole/ Amoxici lIin
- 500 mg qid 400 mg bd
- 500 mg bd 20 mg bd
Surgical therapy
- For refractive ulcer, GI bleeding, perforation, and gastric outlet obstruction.
- For duodenal ulcers, operations performed are vagotomy, pyloroplasty and gastrojejunostomy .
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
- There is severe peptic ulcer diathesis due to gastric acid hypersecretion. This is due to gastrinoma which is a non-betacell endocrine tumor.