Article Contents ::
VARICEAL BLEEDING Clinical features Diagnosis and Treatment
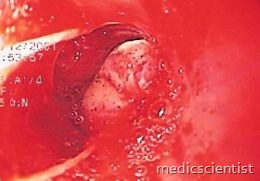
VARICEAL BLEEDING
- It results from portal systemic venous collaterals when portal hypertension is more than 12 mmHg.
Clinical features,:
- There is painless hematemesis, tachycardia and even shock.
VARICEAL BLEEDING Differential diagnosis :
- Peptic ulcer and gastritis. Endoscopy is done for proper diagnosis.
- Variceal bleeding is serious emergency
- patients with varices will develop variceal hemorrhage, a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with cirrhosis
PREDICTIVE FACTORS —
- Numerous clinical and physiologic factors are useful in predicting the risk of variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis.
- These include:
- Location of varices
- Size of varices
- Appearance of varices
- Clinical features of the patient
- Variceal pressure
Treatment
- Blood transfusion Specific interventions
- Fresh frozen plasma transfusion.
- Admission to ICU with monitoring of central venous pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, urine output, mental status.
- Endoscopy is advised.
- Vasoconstrictors – somatostatin / octreotide or vasopressin
- Vasopressin is given 0.1 to 0.4 units / min. in IV infusion.
- Bleeding often recurs after stoppage of infusion. Side effects of vasopressin are acute renal failure, hyponatremia and coronary ischemia.
- Somatostatin is splanchnic vasoconstrictor. It is given 250IJg bolus followed by 250 IJg / hour.
- Octreotide is given 50 – 100 IJg/hour. These are preferred to vasopressin.
- Nitroglycerin drip or isosorbide-di-nitrate are given to prevent side effects.
- Balloon tamponade is done to stop bleeding Endoscopic ligation or sclerotherapy of varices may be done to check and pevent bleeding.
- Endoscopic variceal Iigation (EVL)
- is the best method where circular rings are used to ligate the varices.
- Surgical treatment
- is last resort because of high mortality.
- In TIPS (Trans Jugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) a metal stent is used to create a portocaval channel. This is used in refractory bleeding only.
- Liver transplantation is being increasingly done nowadays.
- Gastric fundal bleeding is more difficult to manage.
Prevention of first haemorrhage :
- · Beta blockers
- · Banding of oesophageal varices
Prevention of recurrent haemorrhage :
- · Endoscopic band ligation
- · Beta blockers
- · Portosystemic shunt surgery
Portal hypertensive gastropathy
- · A congestive gastropathy occurs due to venous hypertension.
- · Mucosa becomes friable.
- · Beta blockers and proton pump inhibitors are given.