Article Contents ::
Acute Peritonitis Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
Peritonitis
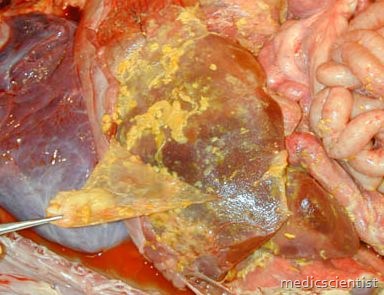
Peritonitis is inflammation of peritoneum. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is defined as an ascitic fluid infection without an evident intraabdominal surgically-treatable source
ACUTE PERITONITIS
- Peritonitis is inflammation of peritoneum.
- May be localized or diffuse, acute or chronic, infectious or aseptic.
- Acute peritonitis is usually infectious and related with perforation.
- There is decreased motility of intestines, with gas and fluid in lumen.
- There is intravascular volume depletion.
Causes of peritonitis are
- · Perforation of viscus
- · Foreign body
- · Peritoneal dialysis
- · Hernia
- · Gangrene
- · Volvulus
- · Bowel infarction
- · Cancer
- · Intestinal obstruction
- · Inflammatory bowel disease.
Clinical features Symptoms
- · Acute abdominal pain
- · Fever
- · Tenderness
- · Rigidity
- · Absent bowel sounds
- · Tachycardia
- · Hypotension
- · Dehydration
- · Acidosis
- · Leucocytosis
- · Edema of bowel wall
- Ascites prevents the development of a rigid abdomen by separating the visceral from the parietal peritoneal surfaces
- · Ascites
- · Free air under diaphragm seen with X-ray, CT, USG (Ultra sonography).
- The signs and symptoms of both SBP and surgical peritonitis in the presence of ascites can be surprisingly subtle
Risk factors —
- The vast majority of patients with SBP have advanced cirrhosis
- . Other risk factors (most of which are associated with cirrhosis) include
- Ascitic fluid total protein concentration less than 1 g/dL (<10 g/L)
- Prior episode of SBP Serum total bilirubin concentration above 2.5 mg/dL
- Variceal hemorrhage Possibly malnutrition
- Possibly use of proton pump inhibitors
Acute Peritonitis Diagnosis –
- diagnosis is established by a positive ascitic fluid bacterial culture and an elevated ascitic fluid absolute polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) count (≥ 250 cells/mm3)
- The prevalence of bacterial overgrowth was higher in the patients with a history of SBP (70 versus 20 percent); these patients also exhibited more severe small intestinal motility disturbances.
- bacterial translocation is increased in patients with advanced cirrhosis
- Total protein concentration >1 g/dL (10 g/L)
- Glucose concentration <50 mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L)
- Lactate dehydrogenase greater than the upper limit of normal for serum
Acute Peritonitis Treatment
- Correct hydration, electrolytes Surgical correction
- Antibiotics
- Management of complications.