Article Contents ::
- 1 AN OVERVIEW OF AYURVEDA FUNDAMENTALS OF AYURVEDA
- 2 AYURVEDIC TEXTS
- 3 AYURVEDA
- 4 Eight Major Clinical Specialities of Ayurveda
- 5 Methodology by which the knowledge of Ayurveda has perceived PRAMANAS
- 6 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN Ayurveda and Modern Medicine
- 7 Pancha Mahabhutas PANCHMAHABHUTAS
- 8 LOKA PURUSHA
- 9 The Theory of Tridosha
- 10 Panchamahabhuta
- 11 The Theory of Trigunas
- 12 Panchamahabhuta Gunas of Mind (Psyche)
- 13 DOSAJA PRAKRITI
- 14 SWABHAVOPARAMVAD (Self Healing)
- 15 AYURVEDIC APPROACH OF CURE
- 16 PRAKRITI AYURVEDIC CONSTITUTION
- 17 WHY IT IS ESSENTIAL TO KNOW ABOUT PRAKRITI ?
- 18 FACTORS ON WHICH THE PRAKRITI DEPENDS
- 19 Kala (Time factor)
- 20 Mother should follow the rules according to season (in relation to Prakriti)
- 21 Nature of Mahabhutas (Five basic elements)
- 22 The VATA
- 23 BASIC FACTS:
- 24 Physical Properties of Vata It is –
- 25 PITTA
- 26 Physical Properties of Pitta
- 27 NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF PITTA
- 28 KAPHA
- 29 NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF KAPHA
- 30 PHYSICAL CHARACTERS OF KAPHA
- 31 PHYSICAL CONSTITUTION (SHARIRIKA PRAKRITI)
AN OVERVIEW OF AYURVEDA FUNDAMENTALS OF AYURVEDA
- • Most ancient science of the world.
- • Considered as Upaveda (subsidiary) of Atharva Veda.
- • Vedas are oldest recorded wisdom on the earth.
- • Ayurveda survived through two sets of original authentic texts.
- • Each set consisting of three books.
- • Written in Samskrit and deals with all aspect of health, disease and treatment.

AYURVEDIC TEXTS
- VRIHATTRAYI
- ( Three big books)
- • 1. Charaka Samhita
- (600 BC)
- • 2. Sushruta Samhita
- (500 BC).
- • 3. Samhitas of Vagbhata
- (600 AD)
- LAGHUTRAYI
- ( Three small books)
- • 1.Madhav Nidana
- (900 AD)
- • 2.Sarangdhar Samhita
- (1300 AD)
- • 3. Bhav Prakash
- (1600 AD)

APPROACH OF AYURVEDA *PHILOSOPHICAL * HOLISTIC *HUMANISTIC AYURVEDA IS More Life and Health oriented than Disease and
- Treatment Ayurveda presents a total Life Science and visualizes the total health to the total human being in a holistic way.
AYURVEDA
A complete Promotive, Preventive and Curative System of Medicine
Eight Major Clinical Specialities of Ayurveda
- • 1. Kaya Chikitsa ( Medicine)
- • 2. Shalya Tantra (Surgery)
- • 3. Shalakya (Diseases of Eye & ENT)
- • 4. Kaumarbhritya (Pediatrics, Obstetrics, Gynaecology)
- • 5. Bhuta Vidya (Psychiatry)
- • 6. Agad Tantra (Toxicology)
- • 7. Rasayana Tantra (Nutrition,Rejuvenation & Geriatrics)
- • 8. Vajikarana (Sexology)
Methodology by which the knowledge of Ayurveda has perceived PRAMANAS
- 1. Pratyaksha (Direct perception)
- 2. Anuman (Logical perception)
- 3. Aptopadesh (Verbal & authentic documentary testimony)
- 4. Yukti (Experimental evidences)
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN Ayurveda and Modern Medicine
- AYURVEDA
- # Experiential Science.
- # Holistic or Totalistic.
- # Functional oriented science.
- Modern Medicine
- # Experimental Science.
- # Analytical approach.
- # Structure or organ oriented.
- LOKA PURUSHA SAMYA
- (Macrocosm- Microcosm continnum)
- *INDIVIDUAL * UNIVERSE
Pancha Mahabhutas PANCHMAHABHUTAS
- 1. AKASHA ( Eather / space)
- 2. VAYU (Air / motion )
- 3. TEJA ( Fire / radiant energy )
- 4. JALA (water / cohesive factor )
- 5. PRITHVI ( Earth / mass )
LOKA PURUSHA
Constant interaction To Maintain Homeostasis Life (Ayu) and Panchamahabhuta Theory
- LIFE (Ayu)
- ATMA (Conscious element)
- INDRIYA (Senses)
- SATTVA (Psyche)
- SHARIRA (Physical Body
The Theory of Tridosha
- Panchamahabhuta Biological applications of
Panchamahabhuta
- VAYU
- AKASHA
- TEJA
- JALA
- PRITHVI
- VATA (Motional energy)
- PITTA (Chemical activities) KKAPHA (Solid substratum)
The Theory of Trigunas
Panchamahabhuta Gunas of Mind (Psyche)
- VAYU
- AKASHA
- TEJA
- JALA
- PRITHVI
- SATVA GUNA (STATE OF COMPLETE BALANCE)
- RAJAS GUNA (DYNAMICITY & ACTIVITY) TAMAS GUNA (MASS ENERTIA)
- Genetically determined relative proportion of DOSHAS within the normal range
- Determine the total Personality
- (Physique, Physiology & Psyche)
DOSAJA PRAKRITI
- Doshaja Prakriti should be considered in
- • Understanding of human life.
- • Health status.
- • Disease susceptibility.
- • Preventive & promotive health care.
- • Treatment.
SWABHAVOPARAMVAD (Self Healing)
- Human body is inherently endowed with an unique power of
- SELF DEFENCE
- SPONTANEOUS HEALING (against injury and disease)
- Role of Medicine
- To assist the Nature
- BASIC CAUSES OF DISEASE
- FAILURE OF HARMONY
- BETWEEN
- MAN(Purusha) & ENVIRONMENT (Loka)
- Normally interaction between Loka and Purush takes place at the level of Three factors
- KALA
- (Time factor and its chronological influence)
- BUDDHI
- (Intellect of man as the major source of thought information)
- INDRIYARTH
- (Objects of 5 sense organs are sourse of stressfull informations
- From environment
- Ayoga
- Atiyoga
- Mithya yoga
- KALA
- BUDDHI
- INDRIYARTH
- Kal Parinam
- Pragyaparadha
- Asatmendriyarth
AYURVEDIC APPROACH OF CURE
- 1. DAIVVYAPASHRAYA CHIKITSA
- (Devine Therapy)
- 2. YUKTIVYAPASHRAYA CHIKITSA
- (Rational Treatment)
- i. Samshodhan ii. Samsaman
- (Purificatory therapy) (Curative Treatment)
- 3. SATTVAVAJAYA (Psychotherapy)
- • Samshodhana includes Panchakarma therapy, rejuvenation and apphrodisiac techniques
- • Samshamana includes uses of healing herbs and approaches to achieve optimum health
PRAKRITI AYURVEDIC CONSTITUTION
- WHY TWO PERSONS
- ARE NOT SAME ?
- PHYSICALLY & MENTALLY
- PRAKRITI
- Determine the total Personality
- (Physique, Physiology & Psyche)
- Genetically determined relative proportion of DOSHAS within the normal range.
- WHAT IS PRAKRITI ?
WHY IT IS ESSENTIAL TO KNOW ABOUT PRAKRITI ?
- • Understanding of human life.
- • Health status.
- • Disease susceptibility.
- • Preventive & promotive health care.
- • Treatment.
- PRAKRITI
- PHYSICAL (SHARIRIKA)
- MENTAL (MANASIKA)
FACTORS ON WHICH THE PRAKRITI DEPENDS
- • Nature of Sperm and Ovum of the parents.
- • Kala (Time factor)
- # Time of fertilization.
- # Season of fertilization.
- • Nature of Garbhashaya (Uterus).
- • Ahara (Diet) and Vihara (Mode of Life) of mother.
- • Nature of Mahabhutas (Five basic elements).
- Nature of Sperm and Ovum of the parents.
- • Sperm and Ovum having definite proportion of Doshas.
- • Dominancy of Doshas show their impact in formation of Prakriti.
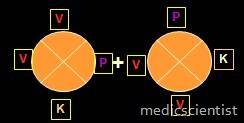
V=4, P=2, K=2 VATA Prakriti
Kala (Time factor)
- • # Time of fertilization. * Dominancy of Dosha at the time of fertilization (day/night hours).
- • # Season of fertilization.
- * Adana Kala (Late winter, Spring, Summer)
- – Fetal development may be affected.
- * Visarga Kala ( Rainy, Autumn, Early winter)
- -Endows strength for mother and child, both
Mother should follow the rules according to season (in relation to Prakriti)
- Nature of Garbhashaya (Uterus).
- • Normally developed.
- • Normal physiological functions.
- • Position of Placenta.
- Ahara (Diet) and Vihara (Mode of Life) of mother.
- • The diet of pregnant woman should be according to her Prakriti.
- • Improper diet and mode of life
- Vitiation of Doshas
- EFFECT ON THE STATUS & CONSTITUTION OF FETUS
Nature of Mahabhutas (Five basic elements)
- • Nature of Mahabhut comprised the fetus.
- • Five basic elements:
- * Akasha (Ether/ space).
- * Vayu (Air).
- * Agni (Fire).
- * Jala (Water).
- * Prithvi (Earth).
- • These elements combine in different proportion to form biological entities-
- *VATA
- *PITTA
- *KAPHA
The VATA
BASIC FACTS:
- • Made up of Akasha (space) & Vayu (air).
- • Vata is self originated, subtle and all pervasive.
- • It sustains the body.
Physical Properties of Vata It is –
- • dry( ruksha),
- • cold (shita),
- • subtle (sukshama),
- • light (laghu),
- • unstable (chala) and
- • rough (khara).
PITTA
- • RESPONSIBLE FOR ALL TYPES OF TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE BODY
Physical Properties of Pitta
- • Liquid.
- • Light.
- • Viscous.
- • Acrid.
- • Sour.
NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF PITTA
- • Intellectual functions.
- • Imparts colour.
- • Production of heat.
- • Promotes digestion.
- • Vision.
KAPHA
- • CONSISTS OF PREDOMINETLY BY JALA (WATER) & EARTH (PRITHVI) ELEMENTS.
- • MORE STABLE THAN OTHER TWO DOSHAS.
- • POTENTIAL SOURCE OF STRENGTH AND RESISTANCE AGAINST DISEASES (BALA)
NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF KAPHA
- • BINDER OF VARIOUS BODY STRUCTURES ESPECIALLY JOINTS.
- • RESPONSIBLE FOR STABILITY & STURDINESS OF THE BODY.
- • BODY RESISTENCE AGAINST DISEASE & DECAY.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERS OF KAPHA
- • VISCOUS
- • SMOOTH
- • SOFT
- • FIRM
- • DENSE
- • MOIST
- • HEAVY
- • COOL
- • SLIMY
- • CLEAR
- • THE BODY BULK, COMPACTNESS & THE PHYSICAL STRENGTH.
- • HEALING PROCESS.
- • LUBRICATION OF JOINTS & OTHER BODY PARTS.
- • MENTAL QUALITIES: Forbearance, fortitude, greedless ness,intelligence.
PHYSICAL CONSTITUTION (SHARIRIKA PRAKRITI)
- PHYSICAL CONSTITUTION IS OF SEVEN TYPES
- 1. VATIKA
- 2. PAITTIKA
- 3. KAPHAJA
- 4. VATA-PITTAJA
- 5. VATA-KAPHAJA
- 6. PITTA-KAPHAJA
- 7. SAMADOSHAJA
This is an Overview about the Basics of Ayurveda…….