Article Contents ::
- 1 Details About Generic Salt :: Bismuth
- 2 Main Medicine Class:: Antidiarrheal
- 3 (BISS-muth sub-suh-LIS-ih-late) Bismatrol, Bismatrol Extra Strength, Pepto-Bismol Maximum Strength, Pepto-Bismol, Pink Bismuth, PMS-Bismuth Subsalicylate Liquid Class: Antidiarrheal
- 4 Drugs Class ::
- 5 Disclaimer ::
- 6 The Information available on this site is for only Informational Purpose , before any use of this information please consult your Doctor .Price of the drugs indicated above may not match to real price due to many possible reasons may , including local taxes etc.. These are only approximate indicative prices of the drug.
Details About Generic Salt :: Bismuth
Main Medicine Class:: Antidiarrheal
(BISS-muth sub-suh-LIS-ih-late)
Bismatrol, Bismatrol Extra Strength, Pepto-Bismol Maximum Strength, Pepto-Bismol,  Pink Bismuth, PMS-Bismuth Subsalicylate Liquid
Pink Bismuth, PMS-Bismuth Subsalicylate Liquid
Class: Antidiarrheal
 Pink Bismuth, PMS-Bismuth Subsalicylate Liquid
Pink Bismuth, PMS-Bismuth Subsalicylate Liquid
Drugs Class ::
 Action Produces antisecretory and antimicrobial effects; may have anti-inflammatory effect.
Action Produces antisecretory and antimicrobial effects; may have anti-inflammatory effect.
Indications for Drugs ::
 Indications Treatment of indigestion without causing constipation, nausea, abdominal cramps; diarrheal control, including traveler’s diarrhea. Unlabeled use(s): Treatment of recurrent ulcers, chronic infantile diarrhea, gastroenteritis associated with Norwalk virus; prevention of traveler’s diarrhea.
Indications Treatment of indigestion without causing constipation, nausea, abdominal cramps; diarrheal control, including traveler’s diarrhea. Unlabeled use(s): Treatment of recurrent ulcers, chronic infantile diarrhea, gastroenteritis associated with Norwalk virus; prevention of traveler’s diarrhea.
Drug Dose ::
 Route/Dosage
Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO 2 tablets (262 mg each) or 30 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN 9–12 YR: PO 1 tablet or 15 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN 6–9 YR: PO 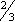 tablet or 10 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN 3–6 YR: PO
tablet or 10 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN 3–6 YR: PO 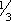 tablet or 5 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN < 3 YR: Consult physician.
tablet or 5 ml suspension q 30 to 60 min prn (maximum 8 doses/day). CHILDREN < 3 YR: Consult physician.
Contraindication ::
 Contraindications Viral illness such as chickenpox or influenza in patients < 18 yr.
Contraindications Viral illness such as chickenpox or influenza in patients < 18 yr.
Drug Precautions ::
 Precautions
Precautions
Pregnancy: Category C. Lactation: Excreted in breast milk. Children: May cause impaction. Debilitated patients: May cause impaction.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|
Drug Side Effects ::
 Adverse Reactions
Adverse Reactions
EENT: Tinnitus; discoloration of tongue. GI: Discoloration of stools; impaction.
Drug Mode of Action ::
 Action Produces antisecretory and antimicrobial effects; may have anti-inflammatory effect.
Action Produces antisecretory and antimicrobial effects; may have anti-inflammatory effect.
Drug Interactions ::
 Interactions
Interactions
Aspirin or other salicylates: May cause salicylate toxicity. Corticosteroids: May decrease effectiveness. Insulin: Drug may increase glucose-lowering effect of insulin. Methotrexate: Drug may increase effects and toxicity of methotrexate. Spironolactone: Drug may interfere with diuretic effect. Sulfinpyrazone: Drug may interfere with uricosuric effect. Tetracyclines: Bismuth subsalicylate may reduce GI absorption of tetracyclines and diminish their effectiveness. Valproic acid: Drug may increase free fraction of valproic acid, leading to toxicity.
Drug Assesment ::
 Assessment/Interventions
Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Assess patient for risk of Reye’s syndrome.
- Determine if patient is taking otc medications for colds, fever, and pain; many contain salicylates, which may produce additive toxicity.
- Observe for discoloration of stool produced by drug (may mask GI bleeding).
- Discontinue use when symptoms subside.
|
||||
Drug Storage/Management ::
 Administration/Storage
Administration/Storage
- Tablets may be crushed, chewed, or allowed to dissolve in mouth. Do not allow patient to swallow whole.
- Before administering, shake suspension well.
- Store at room temperature.
- Protect from light.
Drug Notes ::
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
- Counsel patient to maintain adequate fluid intake (2 to 3 L/day) to prevent dehydration.
- Instruct patient to notify physician if diarrhea is accompanied by high fever or continues > 2 days or if abdominal pain occurs.
- Advise patient not to use medication if concurrent viral illness is present.
- Instruct patient to consult with physician before taking drug if concurrently taking other salicylates, anticoagulants or medications for diabetes or gout.
- Instruct patient to inform physician regarding bismuth subsalicylate administration before any scheduled radiologic studies or stool examinations.
- Inform patient of possibility of salicylate toxicity and associated symptoms, and instruct patient to notify physician if these symptoms occur.
- Explain that stools may become black or gray and tongue may darken.
