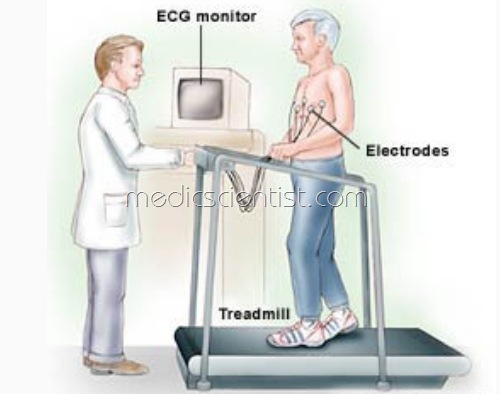
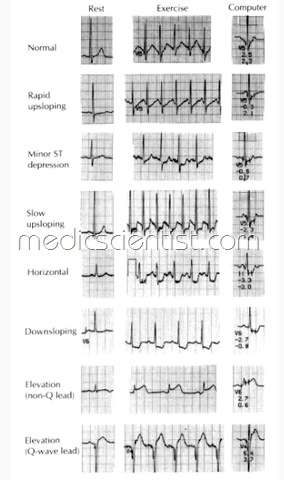
Stress Testing (TMT – Treadmill stress test)
- It is the best test for angina.
- 12 – lead ECG is recorded before, during, and after exercise on a bicycle or treadmill ergometer.
- Patient’s ECG, arm blood pressure, heart rate, symptoms are monitored and the work load is gradually increased.
- Exercise ECG testing is a preferred component of stress testing in most patients.
- Stress testing is an important modality for the evaluation of patients with known or suspected coronary heart disease (CHD),
- The emphasis will be on stable patients with known CHD
- The test is stopped if patients gets chest discomfort, dyspnoea, fatigue, dizziness and ST-T changes (ST depression >2 mm), systolic blood pressure falls more than 10 mmHg, patient gets ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
- The percentage of irreversibly scarred myocardium
- Compare symptoms, especially chest discomfort or pain with ECG changes.
- The amount and distribution of viable but jeopardized left ventricular myocardium
Stress test / Treadmill stress test positive
- The degree of ischemia can be graded semiquantitatively by each of these methods.
- If ST depression >0.1 mv below baseline for more fhan 0.08 seconds or 2 small squares.
- Exercise or pharmacologic stress (mostly using dobutamine) echocardiography;
- ownsloping ST is significant
The measure of induced ischemia —
- Abnormally low peak systolic blood pressure (<130 mmHg) or a fall in systolic blood pressure below baseline during exercise
- Poor exercise capacity (<5 METs) (show figure 1)
- Exercise-induced angina, particularly at a low workload
- Chronotropic incompetence
- Evidence of ischemia may be assessed in several ways,
- T wave changes, conduction abnormalities, veDtricular and atrial arrhythmias ma not sig.o.jfy CAD.
- Target heart rate -i.e. 85% maximum heart rcrre fo r ag e a nd sex, if Qot achi eve_d, testLs non-di~gnostic.
- ensitivity of TMT is only 75% ( Treadmill stress test)
- Complications and risks ofTMT (Treadmill stress test) One death can occur per 10,000 cases so equipments for resuscitation must be present.
Contraindications :
- Acute MI (within 4-5 days)
- Rest angina <48 hrs Unstable rhythm
- Severe aortic stenosis Myocarditis
- Heart failure
- Acute infective endocarditis
- Severe IHD is signified by .’
- >0.2 mv ST segment depression at low ~orkload (before stage II).
- ST segment depression> 5 minutes after termination of exercise.
- adionuclide studies
- This shows the m ocardium and hence infarcted areas of the myocardium i.e. its viability can be seen.
Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging:
- IV Thallium 201 or Technetium 99 m is given and then imaging is done immediately and after 4 hours to detect regions of infarction.
- With thallium, infarcted areas do not take up the dye (cold spots). With technetium, infarcted areas take up the dye (hot spots).
The Duke treadmill score uses three exercise parameters:
- Duke prognostic treadmill score = Exercise time (minutes based on the Bruce protocol) – (5 x maximum ST segment deviation in mm) – (4 x exercise angina [0=none, 1=nonlimiting, and 2=exercise limiting])
- Patients are classified as low, moderate, or high risk according to the score:
- Low-risk — score ≥ +5
- Moderate-risk — score from -10 to +4
- High-risk — score ≤ -11
- 16 percent had single vessel disease, and 9 percent had three vessel or left main disease; five-year survival was above 97 percent.
- Among the 9 percent of patients categorized as high-risk, 74 percent had three vessel or left main disease and five-year survival was 65 percent.
- Among the 36 percent of patients categorized as low-risk, 60 percent had no coronary stenosis ≥ 75 percent,