Article Contents ::
- 1 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
- 2 ACUTE PANCREATITIS
- 3 Water and electrolyte secretion
- 4 Enzyme secretion
- 5 ACUTE PANCREATITIS
- 6 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Etiology
- 7 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Clinical Features Symptoms –
- 8 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Physical examination
- 9 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Lab Diagnosis
- 10 Diagnosis
- 11 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Differential diagnosis
- 12 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Complications
- 13 ACUTE PANCREATITIS Treatment
- 14 Pseudocyst of pancreas
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
ACUTE PANCREATITIS
- acute inflammatory process of the pancreas. It is usually associated with severe acute upper abdominal pain and elevated blood levels of pancreatic enzymes
- The pancreas secretes 1500 to 3000 ml of pancreatic fluid with about 20 enzymes.
- The disease may be relatively mild, resolving in 3 or 4 days, or severe enough to cause multiple organ system failure, shock, and death (in about 5% of patients).
- pH is more than 8.
- Pancreatic enzymes are involved in major digestion process.
- Regulation of pancreatic secretion – Secretin is released by stimulus of gastric acid, which stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice. Release of CCK (cholecystokinin) from the duodenum and jejunum occurs.’
- The parasympathetic nervous system i.e. vagus nerve stimulates release of pancreatic juice.
- Nitric oxide is also a neuro-transmitter for pancreatic exocrine secretion.
Water and electrolyte secretion
- Bicarbonate is the chief ion in pancreatic secretion and helps to neutralize gastric acid.
Enzyme secretion
- The pancreas secretes amylolytic, lipolytic and proteolytic enzymes which are amylase, lipase, phospholipase A, cholesterol esterase; Endopeptidase-trypsin and chymotrypsin; Exopeptidases – Carboxypeptidases, Aminopeptidases, Ribonucleases, Enterokinase.
- Acetylcholine and peptides are neurotransmitters. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) causes the release of acetyl choline. •
- Autodigestion of Pancreas is prevented by presence of proteases in precursor form only (inactive form).
- Exocrine – Endocrine function
- Insulin stimulates secretion of CCK and secretin resulting in exocrine secretion.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS
- The severity of acute pancreatitis varies from edematous pancreatitis to necrotizing pancreatitis.
- Haemarrhagic pancreatitis can be found in pancreatic trauma, carcinoma, congestive heart failure, pancreatitis
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Etiology
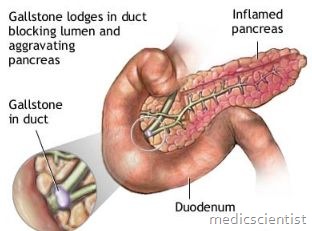
- · Gall stones
- · Alcohol
- · Hypertriglyceridemia
- · Trauma
- · Post operative
- · Drugs – Azathioprine, sulphonamides, estrogens, tetracyclines, valproic acid, anti HIV, 6 mercaptopurine
- · Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
- · Vasculitis
- · Connective tissue disorder
- · Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- · Cancer
- · Hypercalcemia
- · Hereditary pancreatitis
- · Cystic fibrosis
- · Renal failure
- · Infection – Mumps, parasites
- · Autoimmune – Sjogren’s syndrome
- · Biliary tract disease.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Clinical Features Symptoms –
- · Abdominal pain – may be mild to severe, constant and agonizing.
- · Pain is located in epigastrium, periumbilical region, radiating to back, chest, flanks, lower abdomen.
- · Pain is more in supine position; patients feel relieved with trunk flexed, knees drawn up.
- · Nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension- due to gastric and intestinal hypomotility.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Physical examination
- · Patient is anxious
- · There is low grade fever
- · Tachycardia and Hypotension are usually present.
- · There is shock due to :
- – Hypovofemia due to exudation of blood and proteins into retroperitoneum (retroperitoneal burn)
- – Vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability
- – Systemic response
- · Jaundice
- · Erythema
- · Pulmonary crepts, collapse, pleural effusion (left
- sided)
- · Abdominal tenderness
- · Muscle rigidity
- · Decreased bowel sounds
- · Pancreatic pseudo-cyst palpable
- · Cullen’s sign – blue discoloration around umbilicus
- · Turner’s sign – blue or brown discoloration of flanks.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Lab Diagnosis
- · Serum amylase increased 3 times.
- · After 2 – 3 days serum amylase value may return to normal.
- · Patients with acidemia, arterial pH less than 7.3
- may have false elevation of serum amylase.
- · Serum lipase increased in acute pancreatitis.
- · Leucocytosis more than 15,000/ I-lI
- · Hematocrit more than 50%
- · Hyperglycemia
- · Hypocalcemia
- · Hyperbilirubinemia (>4 mg / dl)
- Serum bilirubin returns to normal in one week
- · Serum alkaline phosphatase is increased
- · LDH is increased
- · Serum albumin is decreased
- · Hypertriglyceridemia
- ·Hypoxemia – specially with ARDS. ECG – ST-T abnormalities.
- X–ray
- Ultrasound
- CT – scan
- Radio–nuclide scan
Diagnosis
- Patient with acute pain in abdomen or back with nausea, fever, tachycardia, leucocytosis hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia increased serum amylase suggests pancreatitis.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Differential diagnosis
- Perforation – peptic ulcer – diagnosed by free intraperitoneal air.
- Acute cholecystitis – Right sided pain.
- Biliary colic – Ileus absent, stone seen on sonography. Acute intestinal obstruction – colicky pain, physical examination and X-ray are suggestive.
- Mesenteric vascular occlusion – bloody diarrhoea, arteriography for diagnosis.
- Renal colic – typical pain of renal colic.
- Myocardial infarction – typical findings – ECG, elevated troponin.
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm – hypertension and chest pain.
- Vasculitis and Pneumonia.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis – Serum lipase and amylase not elevated.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Complications
- High risk patients are elderly, age more than 70 years, patients with hypotension, tachycardia, CO2 < 60 mmHg, oliguria «50 ml/hour), GI bleeding, obesity, hematocrit >44%, CRP > 150 mg / I.
- Complications are
- · Necrosis
- · Ascites
- · Pancreatic abscess
- · Pseudo cyst – rupture, haemorrhage, infection
- · Intestinal obstruction
- · Bowel infarction
- · Obstructive jaundice
- · Pleural effusion
- · Atelectasis
- · Pneumonia
- · Mediastinal abscess
- · ARDS (Acute respiratory distress syndrome)
- · Hypotension
- · Shock
- · Sudden death
- · Pericardial effusion
- · DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)
- · Gastrointestinal haemorrhage
- · Peptic ulcer
- · Portal vein thrombosis
- · Esophageal varices
- · Renal failure
- · Acute tubular necrosis
- · Encephalopathy
- · Blindness – Purtscher’s retinopathy
- · Fat emboli.
- Pancreatitis is more common in patients of AIDS due to infection’ with cytomegalovirus, mycobacterium avium, use of drugs like pentamidine and trimethoprim sulphamethoxazole.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS Treatment
- Usually self-limiting in 7 days Analgesics for pain
- IV fluids and colloids
- Nil orally
- Nasogastric suction to prevent gastric contents entering duodenum
- Antibiotics – Imipenem – cilastatin 500 mg T03 for 2 weeks
- Glucocorticoids, calcitonin, NSAIDs, somatostatin, octreotide
- Fungicides for Candida infection
- CT scans help to decide severity and prognosis IV fluids – liquid diets
- Supportive care
- Surgical pancreatic debridement- necrosectomy Laparotomy with drainage and removal of necrotic tissue.
- For hypertriglyceridemia – weight loss, fat free diet, exercise, avoid alcohol and drugs like estrogen, vitamin A, thiazides and beta blockers, control of diabetes.
Infected Pancreatic Necrosis, Abscess and Pseudocyst
- It may occur from 2 – 4 wks after pancreatitis
- There is secondary infection
- Diagnosed by CT – guided needle aspiration Pseudocyt should be aspirated
- For nectrotic pancreas management as above
Pseudocyst of pancreas
- are collection of tissue, fluid, pancreatic enzyme and blood in 1 to 4 wks after acute pancreatitis. There is no epithelial lining therefore it is called pseudocyst. There may be ascites, abdominal pain, palpable tender mass in middle or left upper abdomen, increased serum amylase.
- In X-ray, pseudocyst displaces a part of GIT In ultrasound it can be seen.
- It may resolve spontaneously
- Complication of psudocyst – pain, rupture, haemorrhage, abscess, shock, death
- Surgery may be required
- Pseudoaneurysm may occur in 10%.
