Article Contents ::
Aldosteronism Clinical features Causes and Treatment
definition
- Aldosteronism is a syndrome with hypersecretion of mineralocorticoid aldosterone.
- Primary aldosteronism is excessive aldosterone production due to disease of adrenal glands. It is also called nodular hyperplasia or idiopathic hyperaldosteronism.
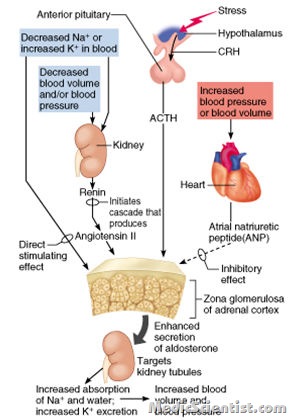
- Nonsuppressible (primary) hypersecretion of aldosterone is a underdiagnosed cause of hypertension.
- There is hypokalemia, diastolic hypertension, extra cellular volume expansion, muscle weakness, fatigue, headache, polyuria, polydipsia.
- Secondary aldosteronism is excessive aldosterone production due to extra-adrenal causes. There is aldosterone secretion in response to activation of renin angiotensin system.
- Aldosterone-producing adenomas Bilateral idiopathic hyperaldosteronism (bilateral adrenal hyperplasia)
- It occurs in accelerated phase of hypertension. Secondary aldosteronism is present in many forms of edema e.g. cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, CHF. Arterial hypovolaemia stimulates aldosterone secretions resulting in edema.
- Familial hyperaldosteronism type I (glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism) and type II (the familial occurrence of aldosterone-producing adenoma or bilateral idiopathic hyperplasia or both).
- HYPOFUNCTION OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX
- Addison’s disease or primary adrenocortical deficiency
- It is due to the progressive destruction of adrenals. It may be due to tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, idiopathic atrophy due to autoimmune causes, HIV, bilateral haemorrhage etc.
Clinical features:
- · Weakness
- · Brown pigmentation of skin especially creases
- · Weight loss
- · Anorexia
- · Nausea and vomiting
- · Hypotension
- · Pigmentatio(1 of mucus membrane
- · Pain in abdomen
- · Diarrhoea
- · Constipation
- · Syncope
- · Vitiligo
- · Craving for salt.
Diagnosis:
- • ACTH stimulation test.
Treatment:
- If potassium losses are severe, muscular weakness, cramps, tetany, or cardiac arrhythmias may occur
- Specific hormone replacement to correct both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid deficiencies.
- Hydrocortisone is given 20 – 30 mg / day. 2/3rd of dose is taken in morning and 1/3rd in afternoon.
- 0.1 mg Fludrocortisone (Mineralocorticoid) is given orally.
- 3-4 g / day of sodium.
- Measurement of blood pressure and serum electrolytes is done.
- Female patients may require 50 mg of DHEA orally daily.
