COMPLICATIONS OF AMI AND TREATMENT
- TRICULAR DYSFUNCTION
- RV INFARCTION
- RUPTURE OF FREE WALL
- CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
- VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT (VSD)
- MITRAL REGURGITATION (MR)
1. VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION
- Ventricular remodeling is a series of changes in shape, size and thickness of ventricular myocardium after infarction. This leads to global LV dysfunction and CHF.
Killip’s classification of L V dysfunction:
- Class I – No pulmonary or venous congestion .
- Class II – Rales at lung bases, S3′ tachypnea,
- Right heart failure .
- Class III – Pulmonary edema.
- Class IV – Shock-systolic blood pressure <90
- mmHg.
- Mortality is upto 95% in class IV .
Treatment:
- Avoidance of hypoxaemia Diuresis
- Afterload reduction Inotropic support Digitalis
- Nitrates
- Topical NTG ointment
- IV NTG and ACE inhibitors.
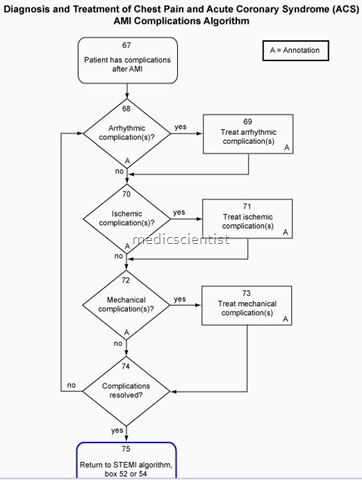
2. RV INFARCTION
- There is RV failure – JVP raised, hepatomegaly, hypotension, ST elevation of right sided precordial leads – V4 R.
Treatment:
- Volume expansion and treat LV dysfunction.
3. RUPTURE OF FREE WALL
- · Occurs specially in elderly
- · Large Q wave infarct
- · H/o hypertension
- · First time infarct
- Presents with : – Absent pulses
- – Unconsciousness
- – Cardiac tamponade.
- anagement – Surgical repair.
4. CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
- · This occurs due to severe LVF.
- · Systolic arterial pressure is <80 mmHg.
- · Cardiac index is < 1.8 It/min/m2•
- · Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure> 18
- mmHg.
- Cardiogenic shock occurs due to reduction of contractile myocardium, arrhythmias, metabolic acidosis.
Treatment:
- Intraaortic balloon counter pulsation.
- A balloon is introduced via femoral artery into the aorta and inflated in diastole to augment coronary flow.
- Vasopressors
- Isoproterenoi
- Norepinephrine – 2 to 4 IJg/min
- Dopamine 2 – 10 IJg/kg/min up to 20 – 50 IJg/ kg/min
- It has vasoconstrictor effect but at low doses dilates the renal and splanchnic blood vessels
- Dobutamine – 2.5 to 10 IJg/kg/min
- It has positive inotropic action
- Amrinone
- Milrinone – They are very potent vasodilators and positive inotropic agents
- Aortic counter pulsation
5. VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT (VSD)
- There is severe LVF, systolic thrill in left parasternal area.
Treatment:
- Nitruprusside infusion Intra aortic pulsation.
6. MITRAL REGURGITATION (MR)
- Apical systolic murmurs appear due to papillary muscle dysfunction, LV dilatation, rupture of cusp.
Treatment:
- Decongestive therapy Afterload reduction
- ABC (Aortic balloon counter pulsation) NTG infusion and Surgical treatment.
SOME more complications are — complications-of-acute-myocardial-infarction-ami-and-treatment-2
