Article Contents ::
- 1 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- 2 Risk factors of COPD
- 3 Stages of COPD GOLD staging by spirometric assessment —
- 4 Pathophysiology COPD
- 5 COPD Pathological Findings
- 6 Chronic bronchitis
- 7 Emphysema
- 8 In advanced COPD
- 9 Host Factors
- 10 Clinical features Symptoms COPD
- 11 COPD Physical findings
- 12 Diagnostic Tests & Interpretation
- 13 Lab Initial Lab Tests
- 14 Chronic bronchitis:
- 15 Emphysema:
- 16 Lab diagnosis
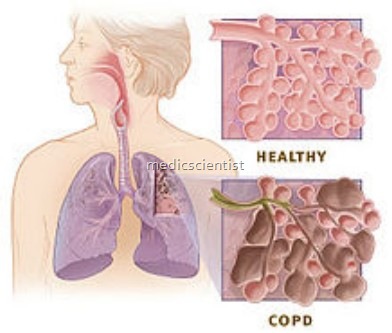
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is a disease state characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully.reversible.
- The airflow limitation is usually both progressive and associated with an abnormal inflammatory response of the lungs to noxious (toxic) particles or gases.
- The Global initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) defines COPD as a limitation of air flow which is not reversible.
- This includes emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and small airway disease. In all these, chronic airflow 05struction occurs.
- Emphysema is the destruction and enlargement of
- alveoli.
- Chronic bronchitis is a condition with chronic cough and ex ectoration.
- Small airway disease is a condition in which small broncioles are narrowed.
Risk factors of COPD
- Cigarette smoking
- Tendency for bronchoconstriction – allergic, environmental, genetic factors
- Respiratory infection
- Occupational exposures
- Air pollution
- Passive smoker.
- Smoking
- Passive smoking, especially adults whose parents smoked
- Severe viral pneumonia early in life
- Aging
- Alcohol consumption
- Airway hyperactivity
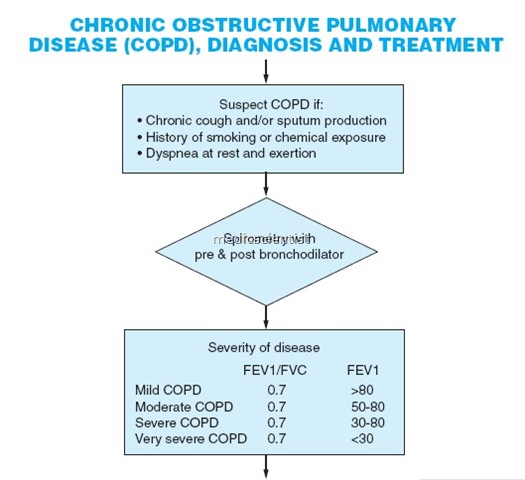
Stages of COPD GOLD staging by spirometric assessment —
- Measure the maximal volume of air forcibly exhaled from the point of maximum inhalation (FVC _ forced vital capacity).
- Measure volume of air exhaled during 1st second of the maneuver (forced expiratory volume in one second) – FEV1
- Calculate ratio of FEV1 / FVC.
- Post bronchodilator FEV1 <80% of predicted value and FEV1 / FVC <70% is an airflow limitation which is not fully reversible.
- Old
- 0 – At risk
- I – Mild
- II – Moderate
- III – Severe
- New:
- 0 –
- At risk
- Chronic symptoms
- Exposure to risk factors
- Normal spirometry
- I –
- Mild
- FEV1/ FVC <70%
- FEV1 ~80 %
- With or without symptoms
- II –
- Moderate
- FEV1/ FVC <70%
- 50%.$. FEV1 <80%
- With or without symptoms
- III –
- Severe
- FEV1/ FVC <70%
- 30%.$. FEV1 <50%
- With or without symptoms
- IV –
- Very severe
- FEV1/ FVC <70%
- FEV1 <30% or FEV1 <50% predicted plus chronic respiratory failure
- 0 –
Pathophysiology COPD
- Impaired gas (CO2 and O2) exchange
- Airway obstruction by mucus in chronic bronchitis
- Destruction of lung parenchyma in emphysema
- There is mucus hypersecretion ciliar dysfunction, airflow limitation, pulmonary hyperinflation, gas exshange abnormalities, pulmonary hypertension, and cor pulmonale.
COPD Pathological Findings
-
Chronic bronchitis
- Bronchial mucous gland enlargement
- Increased number of secretory cells in surface epithelium
- Thickened small airways from edema and inflammation
- Smooth muscle hyperplasia
- Mucus plugging
- Bacterial colonization of airways
-
Emphysema
- Entire lung affected
- Bronchi usually clear of secretions
- Anthracotic pigment
- Alveoli enlarged with loss of septa
- Cartilage atrophy
- Bullae
In advanced COPD
- QLPU momnale I.e. right heart failure may develop
- There IS hypoxaemia and later on hypercapnia. In some patients. The JVP will be raised, there will be
- Pulmonary hyperte~sion, which develops late in the edema, congested liver, right ventricular 53 ascites
- course of COPO is the ma)or cardiovascular compli- signs of pulmonary hypertension. ‘ ,
- cation of CO PO and is associated with the develop- Clubbing is not a feature of COPD.
- ment of cor pulmonale and a poor prognosis.
Host Factors
- if Hereditary deficiency of alpha 1 antitrypsin Airway hyper-responsiveness
- Lung growth
Clinical features Symptoms COPD
- Cough with expectoration
- Exertional dyspnoea and dyspnoea at rest.
- Patient uses accessory muscles of respiration therefore any activity where the arms are to be raised above shoulder level cause discomfort or are even impossible.
- There may be acute exacerbations off and on needing hospitalizption.
COPD Physical findings
- There may be nothing particular in the physical examination.
- Evidence of smoking like nicotine stains on finger tips and lips may be seen.
- There is barrel-shaped chest.
- Accessory muscles of respiration are seen to work like in the neck and abdomen.
- There is cyanosis in the lips and nails.
- On auscultation, the expiration is prolonged and there is wheezing.
- If there is predominent emphysema and no cyanosisthe patient is referred to as pink puffers.
- Pink puffers have diminished” breath sounds.
- In cigarette smokers there is centriacinar emphysema and in alphal AT deficiency there is panacinar emphysema.
- Patient with chronic bronchitis are called blue bloaters because of edema and cyanosis on face.
- There is weight loss.
- There is paradoxical inward movement of rib cage with inspiration called Hoover’s sign.
Diagnostic Tests & Interpretation
Lab Initial Lab Tests
-
Chronic bronchitis:
- Arterial blood gases (ABGs) may show hypercapnia and hypoxia.
- Hemoglobin may be increased.
-
Emphysema:
- Normal serum hemoglobin or polycythemia
- Normal PaCO2 on ABGs
Lab diagnosis
- Spirometry-FEV1, FEV/FVC Arterial blood gases-pH, PC02 X-Ray Chest for lungs
- Chronic bronchitis chest x-ray (CXR): Increased bronchovascular markings and cardiomegaly
- Emphysema CXR: Small heart, hyperinflation, flat diaphragms, and possibly bullous changes
- CT scan
- Serum alphal anntitrypsin
