Cor pulmonale Causes of Cor pulmonale Symptoms with Types and Treatment —
Cor pulmonale is enlargement of right ventricle . secondary to diseases of lungs, thorax, pulmonary ventilation or pulmonary circulation. Living for an extended period at a high altitude also may cause this condition. Cor pulmonale is the alteration of right ventricular structure or function that is due to pulmonary hypertension caused by diseases affecting the lung or its vasculature.
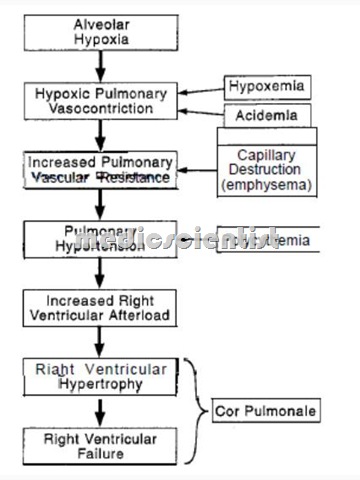
- Hypertrophy or failure of the right ventricle resulting from disorders of the lungs, pulmonary vessels, or chest wall.
- The RV enlargement can lead to RV dilatation and RV failure.
- In ulmonar vascular disease and pulmonary -.parenchymal disease, the pulmonary vascular resistance is elevated.
Causes of Cor pulmonale
- · Chronic obstructive lung disease
- · Hypoxia
- · Pulmonary hypertension due to any cause
- · Pulmonary emboli
- · Pulmonary vasculitis
- · Pulmonary venoocclusive disease
- · High altitude
- · Acidosis
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- · Restrictive lung diseases
- · Interstitial lung disease.
- · Chronic vasculitis
- · Collagen disorders
- CREST syndrome (Calcinosis, Ranaud’s phenomenon, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia).
- – Left to right shunt in congenital heart diseases like:
- – PDA patent ductus arteriosus.
- – ASD atrial septal defect
- – VSD ventricular septal defect
Types of Cor pulmonale —
- ACUTE COR PULMONALE
- CHRONIC COR PULMONALE
ACUTE COR PULMONALE
- Pulmonary thromboembolism is the main cause of acute corpurmonale –
- There is acute right heart failure due to massive or multiple emboli .
- There is fall in cardiac output due to sudden obstruction in the pulmonary vascular circulation.
- There is pallor, sweating, hypotension, rapid thready pulse .
- Neck veins are distended.
- JVP is raised, with prominent v waves.
- Pa02 is reduced.
- The embolus may be thrombus, IV drugs, parasites, tumour tissue.
- There is sudden-onset, severe dyspnoea and cardiovascular collapse.
- There is tricuspid regurgitation – v waves in JVP, systolic murmur, and 54.
- There is pulsatile liver.
- There is tender hepatomegaly.
- Death can occur within 1 hour.
Treatment COR PULMONALE
- Anticoagulation, Heparin, low molecular weight heparin
- Blood volume expanders 100% oxygen
- Embolectomy.
- Thrombolysis
CHRONIC COR PULMONALE
- There is gradual increase in pulmonary vascular rasistance, RV-hypertrophy, and increased’ pulmonary artery pressure.
Clinical features and Symptoms of COR PULMONALE
- Symptoms include chronic productive cough, exertional dyspnea, wheezing, fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, and alterations in level of consciousness.
- Dyspnoea
- Cough
- Chest pain
- Hepatomegaly – The liver is enlarged and tender, and hepatojugular reflux is present.
- Tachypnoea
- Edema
- The pulse is weak.
- Systolic murmur of TR (tricuspid regurgitation)
- Diastolic murmur of PR (pulmonary regurgitation)
- Prominent a and v waves in JVP Right ventricular failure
- A gallop rhythm, tricuspid insufficiency, or a right ventricular heave may be present.
- Cyanosis
- Right ventricular heave
- PUlmonary ejection click
- Loud P 2
- .S3RV(Right ventricular third heart sound)
- Hypoxaemia.
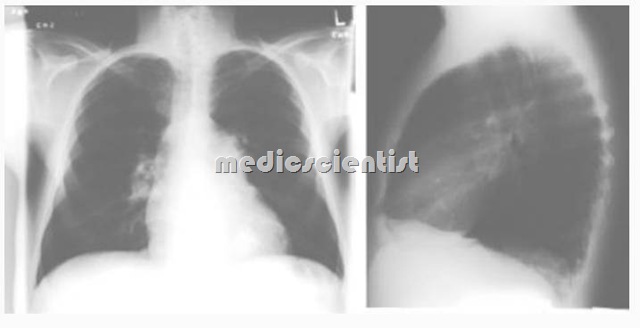
Chest X–ray :
- Right ventricular failure may result in right ventricular and right atrial dilatation on chest radiography.
- Pulmonary trunk and hilar vessels are enlarged.
- The characteristic chest radiograph in pulmonary arterial hypertension shows enlargement of the central pulmonary arteries
Vascular Doppler :
- There is deep vein thrombosis in lower extremities.
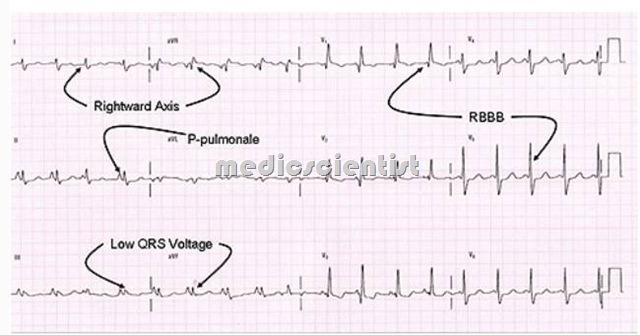
ECG :
- RVH (right ventricular hypertrophy)
- Right axis deviation and R/S ratio greater than 1 in lead V1.
- RAD (right axis deviation).
- P pulmonale – Increased P wave amplitude in lead II (P pulmonale) due to right atrial enlargement
Echocardiography :
- Pulmonary artery pressure increased RVSP- (RV systolic pressure) increased TR (tricuspid regurgitation)
- Most patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension have two-dimensional echocardiographic signs of chronic right ventricular pressure overload
- PR (pulmonary regurgitation
- RV wall thickness increased RV dilatation
- IVS( interventricular septum) displaced towards left
MRI:
- RV mass, thickness, volume increased and EF (ejection fraction) decreased.
Cardiac catheterization :
- There is increased pulmonary artery pressure Congenital heart diseases ruled out Pulmonary angiography done
- EF (ejection fraction) of RV and LV.
- RV pressure measured
Lung Biopsy for :
- Pathologic assessment of pulmonary artery hypertension requires lung biopsy.
- Pulmonary function tests should be performed in patients with the history of underlying lung disease and in those with normal cardiac function.
- Vasculites
- Collagen vascular diseases Rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment for Cor pulmonale
- The medical management of patients with cor pulmonale has centered upon attempts to improve oxygenation
- Treatment of thromboembolism
- Treat COPD – long-term oxygen therapy Bronchodilators
- Oxygen therapy relieves pulmonary vasoconstriction,
- thereby decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance;
- as a result, the right ventricle increases stroke volume and cardiac output.
- Digitalis
- Nebulizers
- Aerosols
- Antibiotics
- Diuretics
- Nitric oxide inhalation Prostacycline
- Correct acidosis and alkalosis.
