Article Contents ::
- 1 All about Bacterial Infections Caused by Gram-Positive STAPHYLOCOCCAL with diagnosis Treatment Signs and symptoms
- 2 NEUMOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
- 3 STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
- 4 The diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus are:
- 5 Staphylococcus Skin and soft tissue infections
- 6 Staphylococcus Musculo skeletal infections
- 7 Staphylococcus Respiratory tract infections
- 8 Treatment:
All about Bacterial Infections Caused by Gram-Positive STAPHYLOCOCCAL with diagnosis Treatment Signs and symptoms
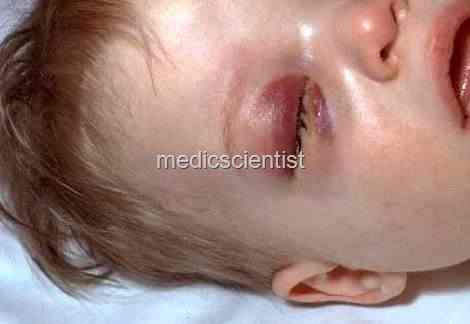 |
| Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections in eye caused by STAPHYLOCOCCAL |
NEUMOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
-
. Streptococcus pneumoniae or diplococcus pneumoniae is the major cause of pneumonia. These Gram +ve cocci grow in chains.
-
Some conditions that predispose to pneumococcal infections are overcrowding, viral respiratory infections, air pollution, smoking, COPD, multiple myeloma, extremes of ages, HIV infection, glucocorticoid treat ment, hepatic and renal insufficiency.
-
Infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae are acute sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media, meningitis, empyema, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, peritonitis, cellulitis, brain abscess.
-
The antibiotics effective against pneumococcal infec tions are amoxycillin, amoxycillin + c1avulanic acid, ceftriaxone, quinolone, penicillin, cefotaxime, imipenem, vancomycin.
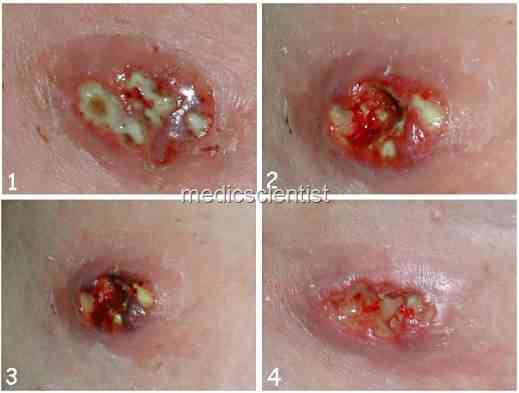 |
| STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTION |
STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
-
Staphylococcus aureus is a virulent pathogen, Gram positive cocci, which appear as grape-like clusters on Gram’s stain.
-
The other staphylococci are less virulent called co agulase-negative staphylococci.
The diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus are:
| Staphylococcus Skin and soft tissue infections |
Staphylococcus Skin and soft tissue infections
-
· Folliculitis
-
· Furuncle
-
· Cellulitis
-
· Impetigo
-
· Surgical wound infections.
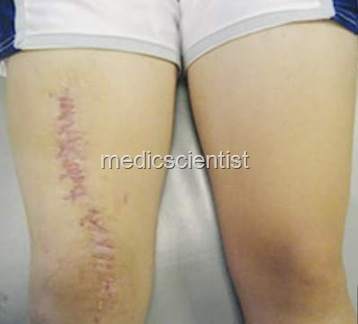 |
| Staphylococcus Musculo skeletal infections legs |
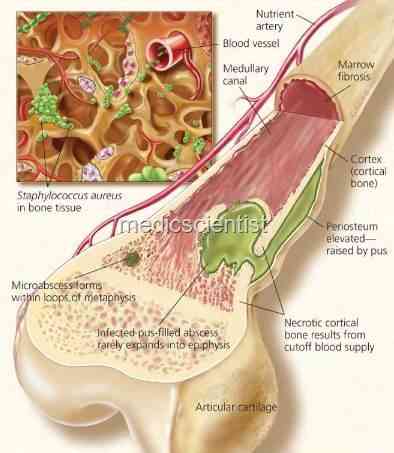 |
| Staphylococcus Musculo skeletal infections in bone |
Staphylococcus Musculo skeletal infections
-
· Septic arthritis
-
· Osteomyelitis.
| Staphylococcus Respiratory tract infections |
Staphylococcus Respiratory tract infections
-
· Ventilator-associated nosocomial pneumonia
-
· Septic pulmonary emboli
-
· Empyema.
| Staphylococcus Bacteremia |
Staphylococcus Bacteremia
-
· Sepsis and septic shock
-
· Metastatic infections of kidney, joints, bones and lungs.
| Staphylococcus Infective endocarditis |
Staphylococcus Infective endocarditis
-
· Native valve
-
· Prosthetic valve
-
· Injection drug users.
| Antimicrobial therapy for Staphylo coccus aureus infection |
Treatment:
- Antimicrobial therapy for Staphylo coccus aureus infection
-
Penicillin, Nafcillin, Cefazolin, Vancomycin
-
Trimethoprim-SuIphamethoxazole.
| Antimicrobial therapy for Staphylo coccus aureus infection |
Staphylococcus STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
-
Streptococci are Gram+ve bacteria round or ovoid shaped, which grow in chains.
-
Many streptococci which cause human infection pro duce a zone of hemolysis around the bacterial colony on blood agar called beta hemolysis.
-
The beta-hemolytic streptococci are classified into Lancefield groups ABC and D.
-
Group A consists of a single species S. pyogenes. S. pyogenes causes suppurative infections and can cause post-infectious syndromes like acute rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis.
-
Group B is represented by S. agalactiae. It is the lead ing cause of bacterial maningitis in newborns and endometritis in women.
-
Group C causes pharyngitis, cellulitis, pneumonia and bacteremia.
-
Group D is represented by enterococci and S. bovis. Viridans streptococci belong to variable group
