Article Contents ::
- 1 Vasculitis Syndrome
- 2 ›Small-vessel vasculitis:
- 3 ›Medium-vessel vasculitis:
- 4 ›Large-vessel vasculitis:
- 5 Vasculitis syndromes:
- 6 Secondary causes:
- 7 Mechanism of Vasculitis:
- 8 Vasculitis Syndrome Pathophysiology —
- 9 WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS
- 10 WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS Diagnosis
- 11 WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS Treatment
- 12 CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME
- 13 CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Symptoms
- 14 CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Lab findings
- 15 CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Treatment
- 16 POLYARTERITIS
- 17 POLYARTERITIS Clinical findings
- 18 Lab findings
- 19 POLYARTERITIS Treatment
- 20 GIANT CELL ARTERITIS
- 21 Clinical manifestations
- 22 GIANT CELL ARTERITIS Diagnosis
- 23 GIANT CELL ARTERITIS Treatment
- 24 TAKAYASU ARTERITIS
- 25 Clinical and Lab findings
- 26 Arteriography
- 27 TAKAYASU ARTERITIS Treatment
- 28 HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA
- 29 Pathology
- 30 HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA Diagnosis
- 31 HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA Treatment
- 32 IDIOPATHIC CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS
- 33 IDIOPATHIC CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS Treatment
- 34 ESSENTIAL MIXED CRYOGLOBULINEMIA
- 35 Treatment
- 36 COGAN’S SYNDROME
- 37 COGAN’S SYNDROME Treatment
- 38 KAWASAKI DISEASE
- 39 KAWASAKI DISEASE Treatment
- 40 DRUG-INDUCED VASCULITIS
- 41 Treatment
Vasculitis Syndrome
Vasculitis is a disease of blood vessels with inflammation and damage. Vasculitis may be a disease of the blood vessels itself or it may be secondarily affected due to a systemic disease. destruction of blood vessel walls, with subsequent aneurysm formation, bleeding, thrombosis, or ischemia in the various vascular beds and organs Differential Diagnosis Consists of a heterogeneous group of diseases depending on size, type, and location of the blood vessel involved.
-
›Small-vessel vasculitis:
- Wegener granulomatosis
- Viral-associated vasculitis
- Rheumatic-associated vasculitis
- Microscopic polyangiitis
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Essential cryoglobulinemic vasculitis
- Churg-Strauss arteritis
-
›Medium-vessel vasculitis:
- Isolated CNS vasculitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Polyarteritis nodosa
-
›Large-vessel vasculitis:
- Giant cell arteritis
- Takayasu arteritis
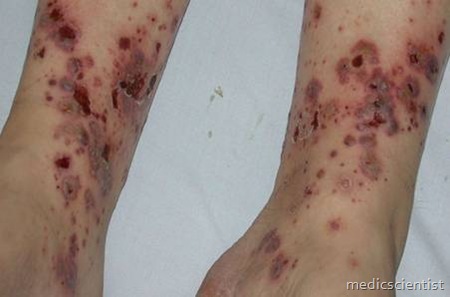
Vasculitis syndromes:
- Wegener’s granulomatosis Churg Strauss syndrome Polyarteritis nodosa
- Giant cell arteritis Takayasu arteritis
- Henoch Schonlein purpura Behcet’s syndrome
- Cogan syndrome Kawasaki disease.
Secondary causes:
- Infection
- Malignancy
- Rheumatic disease Serum sickness Drug-induced vasculitis.
Mechanism of Vasculitis:
- Immune complex formation
- Pathologic T Iymphocyte responses Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA).
Vasculitis Syndrome Pathophysiology —
- Three major immunopathogenic mechanisms have been proposed.
- Pathogenic T-lymphocyte response: Giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis
- Immune-complex formation: SLE, polyarteritis nodosa, and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs): Wegener granulomatosis, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome
WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS
- There is granulomatous vasculitis of small arteries and veins.
- Involves upper and lower respiratory tracts. There is renal involvement in the form of glomerulonephritis.
- Eye involvement can occur, like conjunctivitis, scleritis, uveitis.
- Skin may show papules, vesicles, purpura and subcutaneous nodules.
WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS Diagnosis
- · There are necrotizing granulomatous lesions in tissue biopsy.
- · Renal biopsy shows immune glomerulo-nephritis.
- · Positive anti proteinase 3 ANCA.
WEGENER’S GRANULOMATOSIS Treatment
- Glucocorticoids
- Cyclophosphamide – 2 mg/kg/day Blood counts must be monitored Prognosis of the disease is good.
CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME
- Also called allergic angiitis and granulomatosis.
- There is asthma, eosinophilia and vasculitis of several organs.
- Involves small and medium-sized blood vessels There is infiltration of tissues with eosinophils.
- Organs involved are lungs, skin, heart, kidney, peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract.
CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Symptoms
- Fever, malaise, anorexia, weight loss. There are severe asthmatic attacks. There is mononeuritis multiplex. There is allergic rhinitis and sinusitis.
CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Lab findings
- · There is severe eosinophilia
- · ANCA is positive.
CHURG-STRAUSSSYNDROME Treatment
- Glucocorticoids
- Cyclophosphamide.
POLYARTERITIS
- NODOSA Also called Classic PAN.
- Involves small and medium-sized muscular arteries.
- Involves kidneys.
POLYARTERITIS Clinical findings
- · Fever, weight loss, malaise, headache, abdominal pain, myalgias
- · Renal involvement leading to hypertension and renal failure
- · Gastrointestinal complications.
Lab findings
- · Leucocyte count is increased
- · Anaemia
- · Hypergammaglobulinemia
- · Tissue biopsy shows inflammation.
- POLYARTERITIS Angiography shows
- • Aneurysm, stenosis, occlusion of vessels.
POLYARTERITIS Treatment
- Glucocorticoids
- Cyclophosphamide Plasma exchange.
- Prognosis is poor.
GIANT CELL ARTERITIS
- Also called temporai arteritis or cranial arteritis.
- Disease of, medium and large-sized arteries.
- Occurs at age more than 50 years, more common in females.
Clinical manifestations
- · Fever
- · Anaemia
- · Increased ESR
- · Headaches
- · Malaise
- · Weight loss
- · Sweating
- · Arthralgias
- · There is polymyalgia rheumatica-stiffness and
- pain of shoulders, back and hips
- · There is claudication
- · Strokes and MI can occur
- · Loss of vision or sudden blindness due to ischemic optic neuropathy.
- · Death can occur due to cerebrovascular accidents, MI, aortic aneurysm.
GIANT CELL ARTERITIS Diagnosis
- · Increased ESR
- · Biopsy of temporal artery shows inflammation
- · Ultrasonography of temporal artery.
GIANT CELL ARTERITIS Treatment
- Prednisolone 40 – 60 mgjday.
TAKAYASU ARTERITIS
- Affects medium and large–sized arteries especially aortic arch and its branches.
- Also called aortic arch syndrome. Affects young girls and women.
- Aorta and pulmonary artery involved.
- Major branches of aorta at the origin are involved.
- There is panarteritis and infiltration with giant cells.
Clinical and Lab findings
- · There is fever, night sweats, arthralgias
- · There is decrease or absence of peripheral pulses
- · There are differences in blood pressure in different limbs
- · Arterial bruits
- · Subclavian artery is involved most commonly
- · There is hypertension
- · There are renal, cardiac, cerebral symptoms due to stenosis of arteries supplying them.
Arteriography
- · Irregular vessel walls
- · Stenosis with post stenotic dilatations
- · Aneurysm formation
- · Occlusion of arteries
- · Increased collatera I circu lation.
- Histopathology
- • Inflammation of vessels.
TAKAYASU ARTERITIS Treatment
- Death occurs due to congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular accidents, MI, rupture of aneurysm, renal failure
- Treatment includes glucocorticoid therapy 40-60 mg Prednisone per day
- Angioplasty of vessels involved
- Surgical correction
- Prosthetic grafts
- Methotrexate 25 mgjweek.
HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA
- It is a small vessel vasculitis, also called anaphylactoid purpura.
- Usually seen in children.
- There is palpable purpura on buttocks and extremities.
- Arthralgias and Gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Glomerulonephritis with proteinuria, microscopic hematuria, RBC casts in upto 50% of patients, resolves spontaneously.
Pathology
- · Antigens like drugs, upper respiratory tract infections, foods, insect bites, immunizations may cause the disease.
- · IgA antibody seen.
HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA Diagnosis
- · Skin biopsy showing vasculitis with IgA and C3 deposition
- · Renal biopsy rarely needed.
HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA Treatment
- Death is rare
- Glucocorticoids 1 mgjkgjday may be given.
IDIOPATHIC CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS
- It is a hypersensitivity vasculitis and cutaneous angiitis.
IDIOPATHIC CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS Treatment
- Glucocorticoids, Methotrexate, Azathioprine.
ESSENTIAL MIXED CRYOGLOBULINEMIA
- Cryoglobulins are cold precipitable immunoglobulins. There is palpable purpura.
- Arthralgias, Neuropathy and Glomerulonephritis.
Treatment
- Glucocorticoids
- Plasmapheresis Cytotoxic agents.
COGAN’S SYNDROME
- There is interstitial keratitis with vestibuloauditory symptoms with aortitis and aortic valve disease.
COGAN’S SYNDROME Treatment
- Glucocorticoids.
KAWASAKI DISEASE
- Also called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome.
- Acute febrile multisystem disease of children.
- Vasculitis of coronary arteries occurs.
- Aneurysm and thrombosis may occur.
- Pericarditis, Myocarditis, MI, Cardiomegaly. Prognosis is good.
KAWASAKI DISEASE Treatment
- Gamma globulins IV 2 gjkg single infusion in 10 hrs.
- Aspirin 100 mgjkgjday for 2 wks. followed by 5 mg/kg/day.
DRUG-INDUCED VASCULITIS
- Can occur with several drugs-Allopurinol, Sulphonamide, Penicillin, Thiazides etc.
- Fever, Malaise, Arthralgias and Skin involvement.
Treatment
- Stop the offending drug Glucocorticoids Cyclophosphamide.
