CARDIAC TAMPONADE Causes Physical findings and Treatment
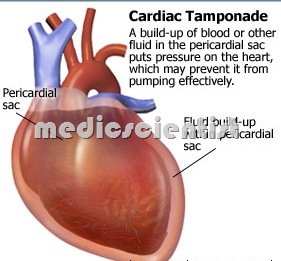
CARDIAC TAMPONADE may result from injuries to the heart or from cardiac rupture, great vessels,or CARDIAC TAMPONADE may accur from other conditions that produce large pericardial effusions Cardiac tamponade is characterized by the accumulation of pericardial fluid under pressure and may be acute or subacute A life-threatening condition in which elevated intrapericardial pressures impair the filling of the heart during diastole.
CARDIAC TAMPONADE Causes —
- ericardial effusion which roduces serious obstrucion of inflow of blood to the ventricles iscalled ca-rdiac tamponade.
- his occurs in tumours, idiopathic pericarditis, uraemia, tuberculosis, and trauma.
- There is increased pressure in the chambers of heart.
- There is reduction of cardiac output.
- apidly accumulated small amount of fluid or slowly accumulating large amount of fluid may cause pericardial tamponade.
CARDIAC TAMPONADE Physical findings :
- Low blood pressure
- Raised JVP – There is a prominent x descent and absent or small y descent
- In constrictive pericarditis the y descent is prominent
- Faint heart sounds Dyspnoea and Orthopnea Hepatomegaly.
ECG
- There is electrical alternans i.e. alternate low voltage and normal complexes.
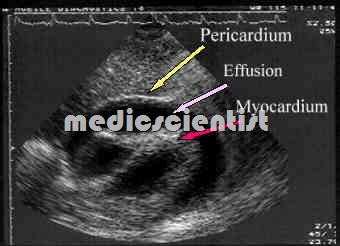
Echo I X-ray I CT I MRI echo —
- Pericardial effusion seen with ventricular collapse in cardiac tamponade.
Paradoxical pulse
- The arterial pulse disappears during inspiration. There is a significant fall (more than 10 mmHg) of systolic arterial pressure during inspiration.
- This is called pulsus paradoxus.
- Normally also there is a fall in blood pressure during inspiration but if this exceeds 10 mm then it is a sign of cardiac tamponade.
- Pulsus paradoxus is found in cardiac tamponade constrictive l2ericarditis (l/3rd of patients), COPD, RV infarction.
CARDIAC TAMPONADE Treatment :
- Pericardiocentesis, Surgical drainage and Thoracotomy.