Renin and Hypertension Low renin and High Renin essential hypertension
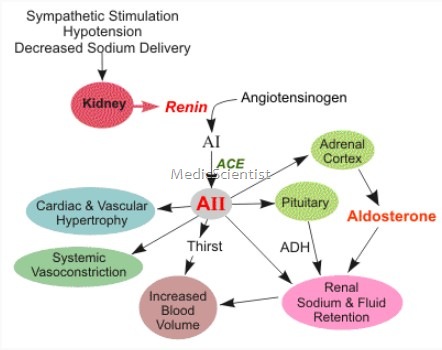
- Renin is enzyme secreted by juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney.
- Hypertensives can be low renin essential
- Hypertensives and high renin essential hypertensives.
Low renin essential hypertension :
- 20% of patients of essential hypertension have low renin essential hypertension.
- When patients with low renin essential hypertension take sodium-rich diet,
- their aldosterone suppression does not occur, leading to hyperaldosteronism causing more sodium retention, volume expansion and high BP.
- There is increased ‘mineralocorticoid production, leading to increased sodium retention, which in turn causes renin suppression.
- The adrenal cortex of low renin hypertensives have increased sensitivity to angiotensin II.
Non – modulating essential hypertension :
- The adrenal or renal vascular responses to angiotensin II is not modulated by sodium intake.
- The effect of angiotensin II does not depend on sodium intake in these patients.
- so salt intake should be low. –
- There is insulin resistance.
- Non-modulation is a genetic problem.
- 30% of hypertensives are non-modulating essential hypertensives.
- Plasma renin activity levels are normal to high.
- – Kidneys are unable to excrete sodium appropriately
Treatment –
- ACE inhibitors and salt restriction.
- High Renin Essential Hypertension (HREH) 15% of hypertensives have HREH.
- There is increased adrenergic system activity.
- Angiotensin receptor blockers may or may not be effective.
Salt intake:
- Higher the salt intake more the BP especially in primary aldosteronism, bilateral renal artery stenosis, renal parenchymal disease, low renin essential hypertension.
- Salt includes chiefly – Sodium Chloride Calcium –
Sodium, Chloride and Calcium
- NaCI increases blood pressure.
- Na without chloride does not increase blood pressure.
- Intracellular calcium can lead to hypertension .
- Calcium _entry blokers are very potent Fntihypertensives.
- Low calcium intake also results in hypertension.
Cell membrane defect:
- Abnormalities of sodium transport occur.
- There is abnormal accumulation of calcium in vascular smooth muscle leading to vasoconstriction and hypertension.
- This defect is present in of hypertensives.
Insulin resistance :
- is related to hypertension. Insulin resistance is common in obesity and NIDDM.
- Obesity and NIDDM are common in hypertensives. These together form the metabolic syndrome also called syndrome X.