Article Contents ::
- 1 Sepsis & Septic Shock
- 2 Systemic responses to infection:
- 3 Sepsis DEFINITIONS
- 4 Bacteremia –
- 5 Septicemia –
- 6 SIRS
- 7 The different stages are :
- 8 SIRS:
- 9 Etiology :
- 10 Spread :
- 11 DIAGNOSIS of Sepsis
- 12 Differential Diagnosis Septic Shock
- 13 Gram-negative bacteremia occurs in :
- 14 Gram-positive bacteremia occurs in :
- 15 Fungemia occurs in :
- 16 Increased risk
- 17 Sepsis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- 18 Microbial signals
- 19 Host response
Sepsis & Septic Shock
- Sepsis is a clinical syndrome characterized by systemic inflammation due to infection.
- Whenever there is infection there is a reaction from host involving various responses.
Systemic responses to infection:
- · Fever
- · Hypothermia
- · Tachypnea
- · Tachycardia.
Sepsis DEFINITIONS
There is a continuum of severity ranging from sepsis to severe sepsis and septic shock. A systemic inflammatory response to infection, in which there is fever or hypothermia, tachycardia, tachypnea, and evidence of inadequate blood flow to internal organs
Bacteremia –
- Presence of bacteria in blood.
Septicemia –
- Presence of organisms or their toxins in blood.
SIRS
- (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) Presents with 2 or more of the following:
- • Fever
- · Tachypnoea
- · Tachycardia
- · Leucocytosis
- · Leucopenia.
- Sepsis is microbial infection with SIRS.
- Severe sepsis or sepsis syndrome – Sepsis with organ dysfunction.
- Septic Shock – Sepsis with hypotension.
- Refractory septic shock – Septic shock for more than 1 hour.
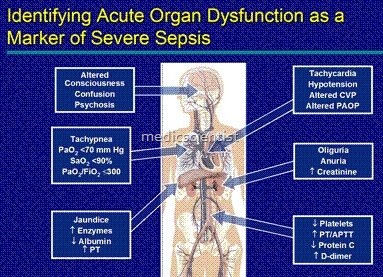
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)
- Dysfunction of more than 1 organ, requiring intervention.
- When the defence mechanism fails, there is dysfunction of major organs.
The different stages are :
- Septic shock Hypotension Organ dysfunction Death.
- Sepsis is reversible but septic shock is usually not.
SIRS:
- SIRS is an inflammatory reaction to various clinical insults (e.g., severe trauma or burn) manifested by 2 or more of the following:
- Temperature >38°C or <36°C
- Heart rate >90/min
- Respiratory rate >20/min or PaCO2 <32 mm Hg
- White blood cell (WBC) count >12,000/mm3, <4,000/mm3, or >10% immature forms (bands)
- is systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- It may be infectious or a non-infectious syndrome. If there is infection, it is called sepsis.
Etiology :
- Genitourinary system
- Hepatobiliary tract
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Lungs
- Indwelling catheter
- Surgical wound
- Decubitus ulcer
Spread :
- By blood stream, local spread, systemic spread of signal molecules or toxins.
- Blood cultures yield bacteria or fungi in severe sepsis and septic shock. 70% are gram negative or positive bacteria.
DIAGNOSIS of Sepsis
- By blood culture.
- Microscopic examination of infected material from local site.
- Culture of micro-organisms from infected material from local site.
Differential Diagnosis Septic Shock
- Hyponatremia due to other causes, e.g., SIADH, cirrhosis, vomiting
- Abdominal pain due to other causes
- Other types of shock, e.g., septic, cardiogenic, hypovolemic, anaphylactic
- Hyperkalemia due to other causes, e.g., renal failure, rhabdomyolysis
Gram-negative bacteremia occurs in :
- Diabetes mellitus Lymphoproliferative diseases
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Burns
- Invasive procedures, devices
- Treatment with drugs which cause neutropenia.
Gram-positive bacteremia occurs in :
- Vascular catheterization Indwelling mechanical devices Burns
- IV drug use.
Fungemia occurs in :
- Immunosuppressed patients Neutropenia
- After broad-spectrum treatment.
Increased risk
- Age more than 50 years.
- Primary site pulmonary, abdominal or.
- Age extremes (very old and very young)
- Impaired host (see Associated Conditions)
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- Critically ill patients
- Indwelling catheters: Intravascular, urinary, biliary
- neuromeningeal.
- (From urinary tract or catheter there is less severe sepsis).
Sepsis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- In sepsis, an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators at the site of infection results in widespread systemic inflammation that damages distant uninvolved tissues.
- · Local spread – GIT, skin, blood
- Dysregulated nitric oxide production and activation of the coagulation system are the main contributors to maldistribution of organ blood flow.
- · Direct into blood stream (IV catheters)
- Widespread endothelial damage and microvascular dysfunction leads to maldistribution of blood flow, causing impaired tissue oxygenation and resultant organ dysfunction.
- · Low immune response (any microbe anywhere can cause septicemia)
- · Endotoxins (act as super antigens).
- The initial, overexuberant inflammatory response can progress to significant immunosuppression in the later stages of sepsis.
-
Microbial signals
- When microorganisms invade body, certain signals are recognized by the individual like : LPS Lipopolysachharide or endotoxins, LPS-binding protein-LBP which transfers LPS to CD14 on the surface of monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils. This causes release of TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) and signals amplify and spread.
-
Host response
- Involves microbial signal molecules-Ieucocytes, humoral mediators, vascular endothelium, cytokines, phospholipid derived mediator, coagulation factors, complement, vascular endothelium.
- Mediator for septic shock is probably inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS).