Tricuspid Stenosis and Tricuspid Regurgitation
Symptoms of Tricuspid Stenosis and Tricuspid Regurgitation with Physical findings Treatment
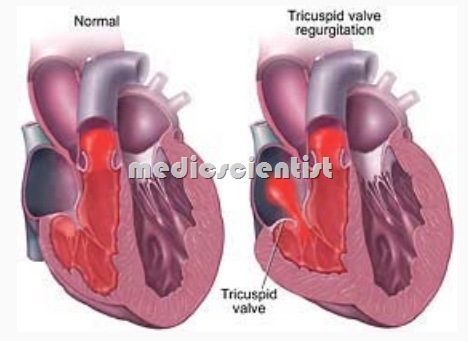
Tricuspid stenosis is an uncommon valvular abnormality that most commonly occurs in association with other valvular lesions. Regurgitation caused not by valvular disorder but by dilatation of ventricles, the great vessels, or valve rings. Tricuspid Regurgitation A backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
TRICUSPID STENOSIS is a narrowing of the tricuspid valve.
- It is a rare disease. Etiology is usually rheumatic. It is more common In females. It always occurs with mitral stenosis. –
- There is usually tricuspid regurgitation associated with TS.
Symptoms
- There are features of mitral stenosis like dyspnoea, hemoptysis etc.
- When TS develops in a patient of mitral stenosis, there is lessening of symptoms like dyspnoea. Relief of symptoms occurs because, due to development ofTS the RV output decreases, and therefore pulmonary congestion is lesser.
- ~Hepatomegaly, ascites and edema develop.
- There is severe fatigue.
Symptoms of Tricuspid Stenosis Echocardiography and Tricuspid Regurgitation with Physical findings Treatment
Tricuspid Stenosis Physical findings
- There is he atic con estion, cardiac cirrhosis, jaundice, malnutrition, anasarca, ascites, splenomegary.
- JVP is raised, with iant ‘a’ waves, and slow ‘y’ descent.
- The murmur of aortic stenosis is best heard by placing the stethoscope over the base of the heart.
- In sinus rhythm there may be pres stolic liver ulsa-
- Auscultation : OS opening snap) of tricuspid valve may be heard after P . P2 is normal, nofToud.–
- The diastolic murmur ofTS is mid-diastolic and heard along left lower sternal margin and the xi 01 process.–Setween the diastolic murmur ofTS and that of rOr5;there is a gap as the stethoscope is moved laterally from the xiphoid process.
- ~The murmur of TS increases durin ins irationLdecreases during expiratio~nd Valsalva maneuve~
Investigations of Tricuspid Stenosis
- ECG : RAE (Right atrial enlargement) is seen as tall,
- eaked P waves in lead II and u right P waves in lead V1 There is no RVH in ECG even in patients of right neart failure.
Chest x-ray:
- RAE and superior vena cava enlargement are seen.
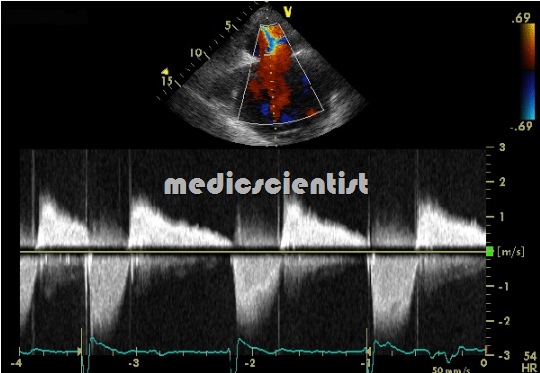
Echocardiography
- stenosed Tricuspid valve is thickened and
Tricuspid Stenosis Treatment
- Salt restriction, diuretics. Surgical repair of the tricuspid valve. Tricuspid valve replacement with prosthetic valve
DIAGNOSIS —
- Aside from systemic venous congestion, the symptoms and findings on physical and laboratory examination largely depend upon the presence and severity of associated aortic and/or mitral valve disease.
- In the absence of mitral valve disease, such findings are generally well out of proportion to dyspnea;
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY —
- As a result of valvular stenosis, there is a persistent diastolic pressure gradient between the right atrium and right ventricle.
ETIOLOGY —
- Tricuspid stenosis is most commonly of rheumatic etiology; the majority of cases present with tricuspid regurgitation or a combination of regurgitation and stenosis
- This may result from embryonic maldevelopment,or excessive development of fibrous tissue hypertrophy and thickening of a sphincter muscle, inflammatory disorders, .
- Congenital atresia or stenosis of the valve .
- Right atrial or metastatic tumors.
TRICUSPID REGURGITATION is a leak of blood back into the right atrium during right ventricular systole.
Functional TR
- TR is most commonly functional due to dilatation of the tricuspid annulus as in mitral stenosis and inferior wall infarction.
- It may also be seen in severe ulmonary hyertension, ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, p-pulmonale.
Organic TR :
- is always associated with tricuspid stenosis. Other causes of organic TR not associated with TS are RV papillary muscle infarcts, tricuspid valve prolapse, carcinoid disease, infective endocarditis, Ebstein’s anomaly.
Clinical features
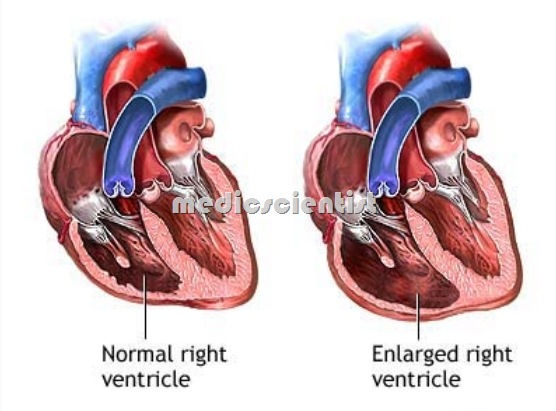
- there is systemic venous congestion, reduced cardiac output, right-sideneart failur
- When TR develops in patients of pulmonary hypertension symptoms of pulmonary congestion reduce, but right heart failure develops.
- JVP is raised with prominent ‘v’ waves .
- There is marked hepatomegaly, ascites, pleural effusion, edema, systolic pulsations of the liver, positive he atoju ular reflux.
- There is parasternal heave (prominent RV pulsation in left parasternal re ion), blowing holosystolic murmur along the lower left sterna margin Increase in inspiration, and reduced uring expiration, and Vafsa va maneuver.
- There is atrial fibrillation.
Investigations
ECG :
- There is RVH.
Symptoms of Tricuspid Stenosis and Tricuspid Regurgitation Echocardiography with Physical findings Treatment
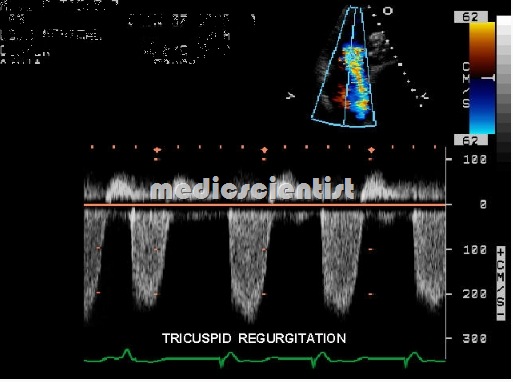
Echocardiography :
- TR and its etiology may be seen. Pulmonary artery pressure is estimated which may be high.
Tricuspid Regurgitation Treatment .
- Treat the underlying cause.
- Tricuspid valve repair and replacement are usually not required.