Cardiac Arrhythmias —
Ventricular Tachycardia VT –
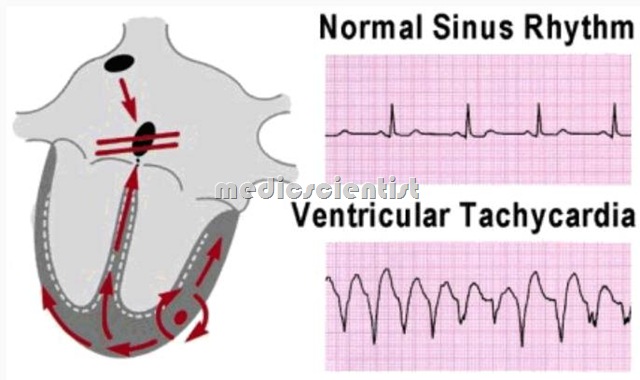
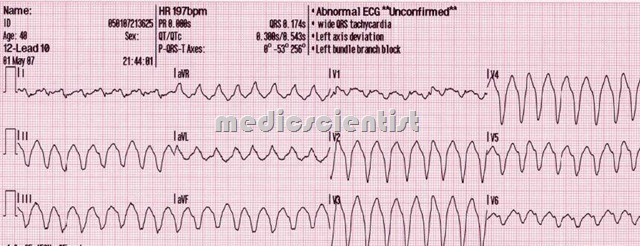
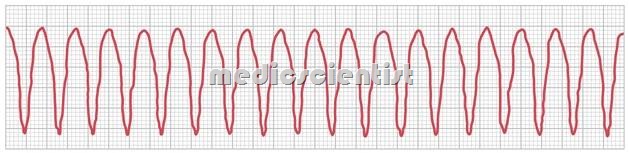
Three or more consecutive ventricular ectopic complexes (duration greater than 120 ms) occurring at a rate of 100 to 250 beats per minute.
Diagnosis of VT (ventricular tachycardia)
- At least 3 consecutive wide QRS complexes
- Rate at least 100 per minute
- Usually rhythm is regular
- Retrograde P wave seen
- Usually AV dissociation is present
- Associated with severe underlying heart disease
- Concordance of direction of wide QRS in precordial leads (all the QRS in one direction) QRS axis abnormal (-90 to -180°)
- QRS width more than 0.14 second (31/2 small squares)
- Paroxysmal VT initiated by VPC.
Causes of VT Ventricular Tachycardia —
- Although non-sustained VT may occasionally be well-tolerated,
- Non-sustained VT lasts less than 30 sec. Sustained VT lasts more than 30 sec, and is much more likely to produce loss of consciousness or other life-threatening symptoms.
- it often arises in hearts that have suffered ischemic damage or cardiomyopathic degeneration and may be a cause of sudden death.
- IHD
- Cardiomyopathies
- Drug toxicity Idiopathic.
- Metabolic disorders
- Prolonged QT syndrome
Clinical features of ventricular tachycardia —
- Cannon a waves
- Underlying heart disease
- Syncope.
- Varying first heart sounds
- Hypotension
Treatment of Ventricular tachycardia —
- The acute treatment of sustained VT is outlined in advanced life support protocols but may include the administration of lidocaine or other antiarrhythmic drugs, cardioversion, or defibrillation.
- Chronic, recurring VT may be treated with sotalol, amiodarone, or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
- Asymptomatic, nonsustained VT may not be treated.
- Congenital long QT has to be treated due to risk of sudden death.
- For sustained VT, VT with organic heart disease, hemodynamic compromise, CHF, and CNS hypoperfusion, prompt DC cardioversion is done. .
- If VT is tolerated hemodynamically (blood pressure and perfusion of organs is maintained), drug therapy is given (DC cardioversion not required)
- – Lidocaine
- Disopyramide
- Beta blockers
- Procainamide
- Flecainide