MYOCARDITIS CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Diagnosis Signs and symptoms
Myocarditis is a condition resulting from inflammation of the heart muscle. usually as a consequence of infections (e.g., viruses, Lyme disease, Lyme carditis ,rheumatic fever, trypanosomes, or toxoplasmosis) However, in contrast to adults, the majority of children with myocarditis present with acute or fulminant disease.

- Myocarditis is cardiac inflammation.
- Causes are infection, drugs, radiation, chemicals or physical agents.
- It may progress to chronic dilated cardiomyopathy.
- The most common cause of acute myocarditis is viral – especially Coxsackie B virus. — —
The presentation of Myocarditis may be :
- Asymptomatic .
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias Death.
MYOCARDITIS Physical Examination:
- Tachycardia Gallop rhythm Pulsus alternans SoftSl
- S3
- MR
- Pericardial friction rub.
MYOCARDITIS CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS —
- The clinical presentation of myocarditis is variable.
- Patients with viral myocarditis, the most common etiology in children,
- frequently have a prodrome of myalgia,fever, and malaise several days prior to the onset of heart failure.
- which is associated with an acute onset and severe hemodynamic compromise
- Acute myocarditis is distinguished from fulminant myocarditis,
MYOCARDITIS Symptoms:
- Patients may be entirely asymptomatic or may seek medical attention because of the sudden onset of palpitations,
- edema,
- congestive heart failure, chest pain,
- or arrhythmias.
- shortness of breath,
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION —
- In symptomatic patients, the physical examination often reveals direct evidence of cardiac dysfunction.
- In acute fulminant myocarditis, signs of low cardiac output may be present,
- S3 and occasionally S4 gallops may be present and are important signs of impaired ventricular function,
- Signs of respiratory distress resulting from left elevated atrial pressures and pulmonary venous congestion,
- the sudden onset of palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, edema, congestive heart failure, or arrhythmias.

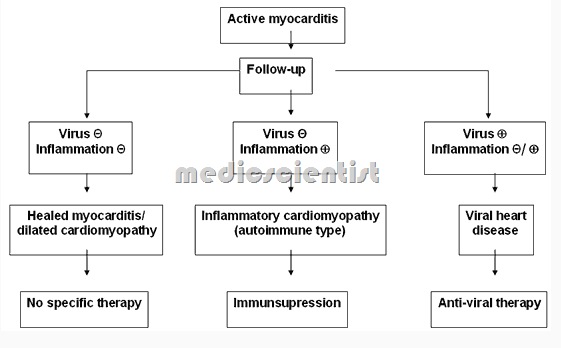
MYOCARDITIS Diagnosis:
- Isolation of virus Endomyocardial biopsy.
MYOCARDITIS Treatment:
- Any identifiable causes are corrected or treated
- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitors
- Salt restriction Antiarrhythmics
- Cardiac transplantation.
HIV Myocarditis:
- There is carditis, pericardial effusion, LV failure.
Bacterial Myocarditis:
- • It is uncommon.
- · Myocardial abscess may occur.
- DiRhtheritic myocarditis is a serious condition
- leacllng to deatb.. –
Chagas disease
- It is caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, an insect Common in South America
- · There is DCMP
- •death is due to arrythmias and CHF
- · Treatment is decongestive, antiarrhythmics, anticoagulation.
Giant cell myocarditis
- Cause is unknown
- There is infiltration with giant cells with extensive inflammation.
- May occr with SLE and thyrotoxicosi
Treatment
- immunosuppressives and cardiac transplantation.
Lyme carditis
- It is caused by Tick-borne spirochete
- There are conduction abnormalities, LV dysfunction, syncope and death.
Treatment
- is IV Ceftriaxone, amoxicillin,
- temporary pacemaker, glucocorticides.
