PericardiaI Diseases Causes and Treatment —
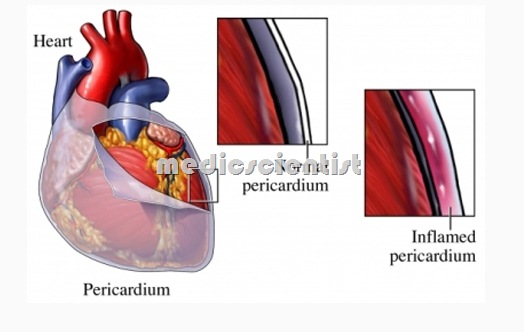
- The heart is covered by two protective membranes
- Parietal pericardium – Fibrous outer membrane.
- Visceral pericardium – Serous inner membrane.
- The pericardium is a fibroelastic sac made up of visceral and parietal layers separated by a (potential) space, the pericardial cavity.
The functions of the pericardium are:
- It prevents sudden dilatation and stretching It fixes the heart, and prevents displacement Minimizes flexion
- Prevents spread of infection.
Diseases of the pericardium present clinically in one of four ways:
- Acute fibrinous pericarditis
- Pericardial effusion without major hemodynamic compromise
- Cardiac tamponade
- Constrictive pericarditis
PericardiaI Diseases DIAGNOSTIC and CLINICAL PRESENTATION —
- ECG changes — new widespread ST elevation or PR depression
- Pericardial effusion
- Chest pain
- Pericardial friction rub
ACUTE PERICARDITIS
- Acute pericarditis is acute inflammation of the pericardium.
- Diagnosed by typical pericardial pain, pericardial friction rub, ECG changes, pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade and paradoxical pulse.
Chest pain of pericarditis
- Moderate or severe Retrosternal and left precordial
- May be a constricting pain or heaviness May be referred to back
- May be aggravated by coughing and deep inspiration
- May radiate to one or both arms
- Relieved by sitting up and leaning forwards Increased in the supine position.
Pericardial Friction Rub
- May be heard in different parts of the cardiac cycle
- It is heard mostly during expiration
- It is high-pitched, grating or scratching
- Best heard in sitting position
- Pericardial rub may appear and disappear within a day.
Causes of pericarditis (PericardiaI Diseases)
Infections —
- Viral – coxsackie virus, mumps, hepatitis, HIV
- Bacterial – Pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus,lubercular-
- Fun al – Histoplasma, candida
PericardiaI Diseases Other causes –
- syphilis, parasitic, protozoal
- Rheumatic fever
- Collagen vascular disease
- Drug induced – Procainamide, hydralazine, phenytoin
- Post cardiac injury – after MI, trauma.
- MI
- Uraemia
- Tumors – Benign, malignant
- Myxoedema
- Trauma
- Aortic dissection
- Acute idiopathic
- Sarcoidosis
ECG
- Elevation of ST se ments with concavity upwards in several leads.
- Low voltage ECG
- T inverted in several leads waves
- Q wave may be present.
PERICARDIAL EFFUSION
- Pericarditis may be associated with effusion in pericardial space called pericardial effusion.
PericardiaI Diseases Etiology: is same as pericarditis.
- In rheumatic fever there is no pericardial effusion.
- In uraemia, tuberculosis, malignancy, viral, bacterial causes there may be massive pericardial effusion.
PericardiaI Diseases Physical findings :
- Area of cardiac percussion is increased. Heart sounds are faint
- There may not be any friction rub NP is raised
- There may be ascites
- Apical cardiac impulse not palpable
- Ewart’s sign – dullness below left sca~la due t9 collapsed lung, may be prese’lt.
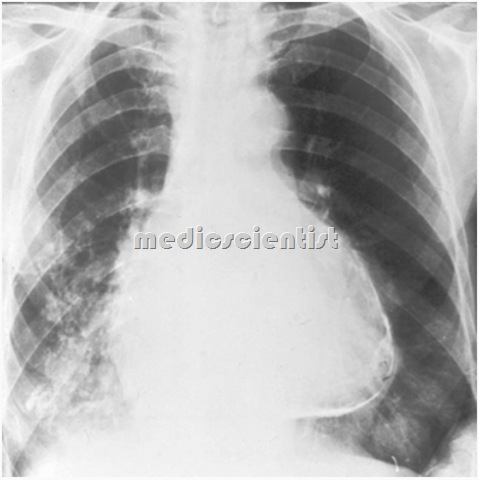
Chest X-ray
- Outline of heart is enlarged, and water bottle or flask-shaped or globular (rounded).
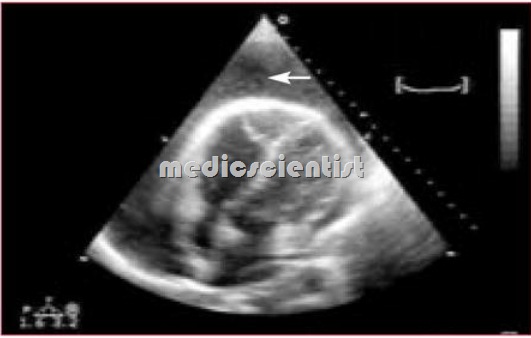
PericardiaI Diseases Echocardiography
- The best bedside tool for diagnosing pericardial effusion is echocardiography.
- Pericardial fluid can be seen as echo-free space between posterior pericardium and left ventricular free wall or between anterior right ventricle and anterior chest wall.
- Pericardial thickening can be seen. Cardiac tamponade can also be identified.
CT I MRI
- CT and MRI can detect pericardial thickening and loculated effusion.
PericardiaI Diseases Treatment
- Treat the etiology
- IV fluids to increase cardiac output Pericardiocentesis – Pericardial fluid is aspirated under echocardiographic screening
- The fluid is sent for diagnosis
- Aspiration of fluid relieves the symptoms – therapeutic aspiration
- Fluid is usually exudate
- Transudate is found in heart failure
- Bloody pericardial fluid is found in tuberculosis, uraemia, tumour, trauma.