Article Contents ::
PRESENTATIONS OF HYPOPITUITARISM
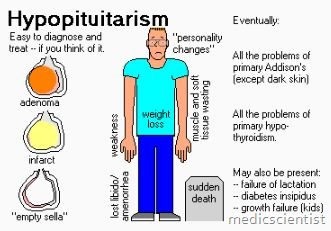
This depends on the hormones which are deficient. GH deficiency causes growth disorder and abnormal body structure. Gonadotrophin deficiency causes infertility, menstrual and sexual dysfunction and loss of secondary sexual characteristics in men. TSH and ACTH deficiency cause growth retardation, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency. Mineralocorticoid action is retained. PRL(prolactin) deficiency causes failure of lactation. If Posterior pituitary is also involved there is polyuria, polyd’Rsia due to vasopressin deficiency.
Lab investigations for Hypopituitarism
- There are low levels of trophic hormones and low level of target hormones also e.g. Iow ACTH with low cortisol, low FSH with low testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, low level of TSH with low T31 T4, low levels of GH with low IGF (insulin like growth factors).
- Provocative tests are done to assess pituitary reserve.
Hypopituitarism Risk Factors
- Infections
- Infiltrative diseases
- Irradiation
- Lymphocytic hypophysitis
- Postoperative
- Pregnancy and delivery
- Trauma
- Tumors
- Vascular aneurysms
Assessment history of pituitary function,
- Pregnancy-related hemorrhage or hypotension
- Gonadal dysfunction
- Empty sella
- Craniofacial abnormalities
- Pituitary or hypothalamic lesions
- Inflammatory or granulomatous disease
- Head trauma or head surgery
- Cranial radiation
Hypopituitarism Physical Exam
- •Pituitary failure secondary to tumors:
- ACTH: Hypotension, anorexia, pallor, weight loss
- Gonadotropins: Delayed puberty
- TSH: Weight gain, hair loss, dry skin, bradycardia, hoarseness, hypotension
- GH: Decreased muscle mass and strength, increased visceral fat, growth retardation
- •Visual field defects
- •Children:
- Congenital malformations and syndromes, especially malformations of the head and genitalia
- Growth retardation and delayed puberty
Hypopituitarism Differential Diagnosis
- Primary hypothyroidism
- Primary hypogonadism
- Kallmann syndrome
- Hypothalamic insufficiency
- Constitutional short stature
- Chronic liver disease
- Addison disease, primary adrenal insufficiency
Treatment of Hypopituitarism
- Generalized condition caused by partial or total failure of anterior pituitary gland’s hormones: adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), growth hormone (GH), and prolactin.
- Less commonly, the posterior pituitary gland’s hormones can be affected: AVP/ADH and oxytocin.
- Hormone replacement therapy like glucocorticoids, thyroid hormone, sex steroids, growth hormone, vasopressin are given.
- Shortages of ACTH, TSH, and ADH can be life-threatening.
- Synonym(s): Empty sella syndrome; Hypopituitarism; Pituitary cachexia; Simmonds syndrome; Panhypopituitarism; as a consequence of blood loss during pregnancy, Sheehan syndrome
- System(s) affected: Cardiovascular; Endocrine/Metabolic; GI; Musculoskeletal; Nervous; Reproductive; Skin/Exocrine
- Treatment of ACTH, TSH, LH, and FSH deficiencies similar to the treatment of primary hormone deficiencies of their respective target organ:
- ACTH deficiency results in cortisol deficiency:
- Treatment consists of administration of glucocorticoid hormones (hydrocortisone, dexamethasone, or prednisone) to mimic normal pattern of cortisol secretion; mineralocorticoid replacement is rarely necessary.
- Dosages and administration schedule vary according to age and sex.
- Hypoprolactinemia has no treatment.
- LH and FSH deficiency: Treatment depends on gender and whether fertility is desired.
- Men: Testerone replacement if fertility not desired; gonadotropins for fertility
- Recombinant human GH (for treating short stature in children and for treating selected adult patients)
- TSH deficiency: Goal of treatment is normal free T4 value. Treat with levothyroxine.
- Women: Estrogen–progesterone (and possibly testosterone) replacement, or pulsatile gonadotropins for fertility
- Infectious disease: Antibiotics as appropriate
- Inflammatory or granulomatous disease: Specific treatment
- Adrenal insufficiency should be excluded before thyroid hormone replacement is initiated; otherwise, thyroid hormone replacement could precipitate adrenal crisis
- Replacement of hormones secreted by target glands
