Article Contents ::
Intestinal Obstruction
Intestinal obstruction may be mechanical or non mechanical
- Mechanical obstruction may be adhesions, hernias, diverticulitis, carcinoma, regional enteritis, gall stone obstruction, intussusception.
- Non-mechanical may be neuromuscular disturbances leading to ileus.
- Obstruction may occur in small intestine or large intestine.
- Small intestine obstructions are due to adhesions and hernias.
- Large intestine or colonic obstruction is due to carcinoma, diverticulitis, volvulus.
- Pseudo-obstruction is a motility disorder without mechanical obstruction.
- Adynamic ileus (atonic or paralytic ileus) is the most common cause of obstruction.
- It is due to peritoneal injury with hydrochloric acid, colonic contents, pancreatic enzymes, blood and urine.
- Retroperitoneal causes of adynamic ileus are retroperitoneal hematoma, ureteral calculus, pyelonephritis.
- Dynamic ileus or spastic ileus is uncommon ant!- is due to heavy metal poisoning, uremia, porphyria, intestinal ulcerations.
Pathophysiology
- Obstruction gives rise to increased intra luminal pressure.
- Accumulation of gas and fluid occurs in the obstructed segment.
- There is impairment of blood supply. Bacterial invasion occurs.
- Peritonitis may occur.
- Ventilation becomes restricted due to elevation of diaphragm and distention of abdomen.
- There may be atelectasis of lung (collapse of lung). Venous return is hampered.
- There is loss of fluid and electrolytes.
- There is hypokalemia, and dehydration because of vomitings.
- There is hemoconcentration, hypovolaemia, renal failure.
- All this can lead to shock and death.
Symptoms of Intestinal Obstruction
- · Mid-abdominal pain
- · Paraoxysmal pain, cramps, colics
- · Audible borborygmi
- · In strangulation, pain is localized
- · There is vomiting of bile and mucus
- · Low ileal obstruction gives rise to feculent vomitus, very foul smelling
- · Hiccups or singultus
- · Obstipation (gas)
- · Diarrhea due to partial obstruction
- · Blood in the stool in intussusception
- · Altered bowel habit
- · Constipation.
Physical findings
- · Abdominal distension, more in colonic obstruction ‘
- · Tenderness, rigidity
- · Fever more than 100°F
- · Shock in strangulation
- · Rigidity, tenderness, fever in peritonitis
- · Hernias
- · Palpable mass
- · Loud high-pitched borborygmi.
Lab findings
- · Leucocytosis
- · Increased serum amylase.
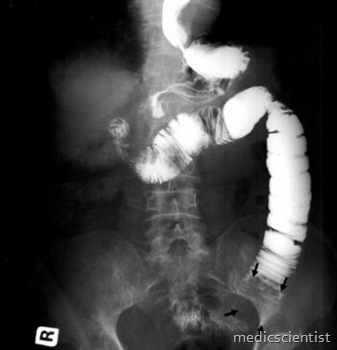
X-ray
- Shows distended and gas filled loops of small intestine in step-ladder pattern with air fluid levels and no colonic gas shadows.
- In strangulation, coffee-bean shaped mass seen. In adynamic ileus, colonic distension seen.
Sigmoidoscopy
- It shows volvulus and other diseases.
Barium study
- Barium study may be done by mouth for obstruction in small intestine. Oral barium should never be given in colonic obstruction.
Treatment of Intestinal Obstruction
- In obstruction, always operative treatment is the best choice.
- For strangulation – urgent surgery. Conservative management in incomplete obstruction and in complete obstruction, along with surgery.
- IV fluids, IV potassium, nasogastric tube for suction, antibiotics, and sometimes neostigmine in colonic ileus.
- The degree of volume depletion and metabolic derangement
- The severity, cause, extent and location of the obstruction
- Whether nonoperative management can be considered
- The need for and timing of operative intervention