Article Contents ::
- 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Diagnosis CAGE criteria and Treatment
- 2 Alcoholic Liver Disease
- 3 Alcoholic liver disease is a very common liver disease.
- 4 Pathology
- 5 Alcoholic Liver Disease Clinical features
- 6 DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Alcoholic Liver Disease —
- 7 CAGE criteria —
- 8 Definitions of sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values
- 9 Lab diagnosis
- 10 Alcoholic Liver Disease Treatment
Alcoholic Liver Disease Diagnosis CAGE criteria and Treatment
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease is involvement of the liver due to chronic and excessive alcohol intake.
- There is a spectrum of clinical and laboratory findings in patients with alcoholic liver disease, ranging from asymptomatic fatty liver to alcoholic hepatitis to end-stage liver failure with jaundice, coagulopathy, and encephalopathy
- alcoholics first become symptomatic only when severe, life threatening liver disease is already present.
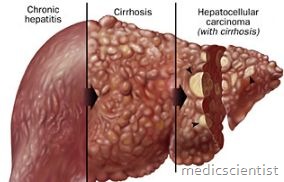
- Cirrhosis resulting from chronic liver damage by alcoholism. Approx. 20% of chronic alcoholics develop cirrhosis.
Alcoholic liver disease is a very common liver disease.
- It presents with :
- 1. Fatty liver
- 2. Alcoholic hepatitis
- 3. Cirrhosis.
- Fatty liver is present in 90% drinkers. Alcohol (Ethanol) is a direct hepatotoxin. 20% of alcoholics develop alcoholic hepatitis.
- Liver damage in alcoholics depends on quantity of alcohol taken.
- 20 – 80 g/day of ,3cohol for 10 years results in severe alcoholic liver disease.
- Chronic hepatitis C with alcoholic liver disease results in cirrhosis more commonly than in non-alcoholic.
Pathology
- There is fatty liver which may be reversible.
- There is hepatocyte injury, necrosis, fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis in 50% patients of alcoholic hepatitis.
Alcoholic Liver Disease Clinical features
- · There is hepatomegaly which may be tender.
- · There may be nausea and vomiting.
- · There may be jaundice.
- · There is fever, abdominal pain.
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Alcoholic Liver Disease —
- Good history taking is often the first step in diagnosing alcohol use
- ask the patient and family members or friends include the pattern, type of alcohol consumed, the amount of alcohol ingested, the age of first onset of drinking, and the date of the last drink
CAGE criteria —
- Denial is a major component of alcohol abuse,
- Have you felt the need to Cut down drinking?
- Have you ever felt Annoyed by criticism of drinking?
- Have you had Guilty feelings about drinking?
- Do you ever take a morning Eye opener (a drink first thing in the morning to steady your nerves or get rid of a hangover)?
Definitions of sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values
- Disease present Disease absent Test positive A B Test negative C D Sensitivity = A ÷ (A + C) Specificity = D ÷ (B + D) Positive predictive value = A ÷ (A + B) Negative predictive value = D ÷ (C + D)
Lab diagnosis
- AST (Aspartate amino-transferase), ALT (Alanine amino-transferase), GGT (Gamma glutamy.1 transpeptidase), triglycerides, bilirubin, are increased.
- AST and ALT are increased up to 7 times.
- There is hypoalbuminemia, ascites, portal vein flow reversal.
Alcoholic Liver Disease Treatment
- Early alcoholic hepatitis is reversible.
- Liver biopsy should be done to confirm diagnosis.
- Alcohol should be totally given up. Balanced diet is advised.
- Glucocorticoids are given except in cases of GI bleeding, sepsis, renal failure, pancreatitis.
- Liver transplant may be done.