Home » Drug Salts » Propylth
Article Contents ::
- 1 Details About Generic Salt :: Propylth
- 2 Main Medicine Class:: Antithyroid
- 3
(pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill)
Propyl-Thyracil
Class: Antithyroid
Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.
Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: – initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.
Lab Test Interferences None well documented.
Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).
Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS
Administration/Storage
Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.
Assessment/Interventions
Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
Monitor I&O and check for edema.
Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis
Patient/Family Education
Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
- 4 Drugs Class ::
- 5 Disclaimer ::
- 6 The Information available on this site is for only Informational Purpose , before any use of this information please consult your Doctor .Price of the drugs indicated above may not match to real price due to many possible reasons may , including local taxes etc.. These are only approximate indicative prices of the drug.
Details About Generic Salt :: Propylth
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 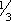 –
–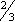 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Drugs Class ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 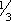 –
–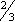 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Indications for Drugs ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 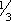 –
–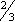 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Drug Dose ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 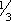 –
–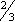 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Contraindication ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 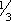 –
–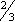 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Drug Precautions ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 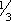 –
–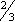 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Drug Side Effects ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.

Contraindications Hypersensitivity to antithyroid drugs; lactating women.

Route/Dosage
ADULTS: PO Initial dose: 300 mg/day in 3 equal doses q 8 hr. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism or very large goiters, initial dose is usually 400 mg/day, occasionally up to 600 to 900 mg/day. Maintenance: 100 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. CHILDREN > 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 150 to 300 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: Determined by response. CHILDREN 6 to 10 YR: PO Initial dose: 50 to 150 mg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. ALTERNATE DOSING FOR CHILDREN: PO Initial dose: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 8 hr. Maintenance: 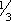 –
–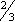 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.

Interactions
Anticoagulants: Altered anticoagulant action. Beta blockers: Increased effects of beta blockers. Digitalis glycosides: Increased digitalis levels, resulting in toxicity. Theophylline: Altered theophylline clearance in hyperthyroid or hypothyroid patients.

Lab Test Interferences None well documented.

Adverse Reactions
CNS: Paresthesias; neuritis; headache; vertigo; drowsiness; neuropathies; CNS stimulation; depression. DERM: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; erythema nodosum; skin pigmentation; exfoliative dermatitis; lupus-like syndrome (splenomegaly, hepatitis, periarteritis; hypoprothrombinemia; bleeding). EENT: Loss of taste; sialadenopathy. GI: Nausea; vomiting; epigastric distress. GU: Nephritis. HEPA: Jaundice; hepatitis. HEMA: Inhibition of myelopoiesis (eg, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia); aplastic anemia; hypoprothrombinemia; periarteritis. OTHER: Abnormal hair loss; arthralgia; myalgia; edema; lymphadenopathy; drug fever; interstitial pneumonitis; insulin autoimmune syndrome (hypoglycemia).

Precautions
Pregnancy: Category D. Lactation: Avoid nursing. However, if antithyroid drug is essential, PTU is preferred antithyroid agent while nursing. Children: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in pediatric patients. Discontinue drug immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction develop. Agranulocytosis: Potentially most serious side effect. Discontinue drug if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis occur. Hemorrhagic effects: May cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|

Administration/Storage
- Give with meals to minimize GI irritation.
- Administer q 8 hr to maintain serum drug levels.
- Encourage fluid intake of 3 to 4 L/day, unless contraindicated.
- Store in tight, light-resistant container at room temperature.

Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies.
- Obtain baseline weight, BP, body temperature and pulse rate and monitor periodically during therapy.
- Ensure that baseline thyroid function has been evaluated prior to therapy and reassess q 2 to 3 mo during therapy.
- Determine baseline WBC count and differential before administration and monitor for agranulocytosis during first 3 mo of therapy.
- Monitor I&O and check for edema.
- Before discharge, obtain dietary consult for patient regarding iodine intake; shellfish and iodine-containing foods may be restricted.
- Assess for signs of hypoprothrombinemia; monitor prothrombin time during therapy, especially during surgical procedures.
- Assess patient for development and tolerance of symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (eg, swollen lymph nodes, skin eruption or itching), notify physician. Drug may be discontinued.
| OVERDOSAGE: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| |
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritis, edema, pancytopenia; most serious effect: agranulocytosis |
|

Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to take resting pulse daily and encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Advise patient to monitor weight at least 2 to 3 times/wk or per physician instruction, obtaining weight at same time, using same scale. Encourage patient to keep recorded chart.
- Emphasize importance of following dietary restrictions regarding shellfish, iodized salt and other foods high in iodine.
- Explain that desired response may take several months if the thyroid is greatly enlarged.
- Advise patient to carry Medi-Alert identification at all times describing medications.
- Instruct patient to notify dentist or physician of drug regimen before surgical or dental procedures.
- Emphasize importance of follow-up visits to monitor effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Caution patient not to stop taking medication abruptly to avoid thyroid crisis.
- Instruct patient to report the following symptoms to physician: Sore throat, fever, rash, mouth sores; cold intolerance, mental depression; tachycardia, irritability; persistent nausea, steatorrhea or vomiting, drowsiness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes; unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness and to use caution while driving or performing other activities requiring mental alertness.
- Instruct patient not to take otc medications without consulting physician.
Drug Mode of Action ::
| (pro-puhl-thigh-oh-YOU-rah-sill) |
 Propyl-Thyracil Propyl-Thyracil |
| Class: Antithyroid |

Action Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones.

Indications Long-term therapy of hyperthyroidism; amelioration of hyperthyroidism in preparation for subtotal thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy; when thyroidectomy is contraindicated or not advisable. Unlabeled use(s): Management of alcoholic liver disease.
 Propyl-Thyracil
Propyl-Thyracil



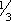 –
–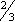 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.






 Propyl-Thyracil
Propyl-Thyracil



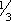 –
–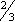 initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.
initial dose, beginning when patient is euthyroid.






 Propyl-Thyracil
Propyl-Thyracil


