Article Contents ::
- 1 Acidosis & Alkalosis Diagnosis And treatment–
- 2 Respiratory failure may be —
- 3 The pH of blood is maintained by —
- 4 Acid Base balance —
- 5 RULES OF COMPENSATION IN ACID-BASE BALANCE —
- 6 1. Metabolic acidosis: expected PaCOz decreases by 1 mmHg for every 1 meq/L decrease in HCO-3•
- 7 2. Metabolic alkalosis :
- 8 3. Respiratory acidosis :
- 9 4. Respiratory alkalosis :
- 10 Stepwise approach In acidosis & alkalosis —
Acidosis & Alkalosis Diagnosis And treatment–
 |
| Acidosis & Alkalosis |
The arterial blood gases provide information about-
- 1. Ventilation
- 2. Oxygenation
- 3.Acid base status This maintains the pH.
- Arterial blood gases (ABG) help to diagnose respiratory failure.
Respiratory failure may be —
- 1. Primary oxygenation failure
- 2. Ventilatory failure
1–. Primary oxygenation failure is indicated by —
- a. low PaCOz
- b. low PaOz
- c. alkaline pH
2– Ventilatory failure is indicated by —
- a. high PaCOz
- b. moderately low PaOz
- c. acidic pH.
Arterial Blood Gas analysis tells about —
- 1. Oxygenation
- 2. Ventilatory status
- 3. Acid base status.
The pH of blood is maintained by —
- 1. Alveolar ventilation
- 2. Oxygenation
- 3. Acid base balance.
1– Alveolar ventilation
- PaCOz is the best index for alveolar ventilation.
- High PaCOz > 45 mmHg indicates alveolar hypo ventilation.
- – Low PaCOz < 35 mmHg indicates alveolar hyperventilation.
2– Oxygenation:
- Depends on —
- arterial oxygen tension written as PaOz
- – oxygen concentration of inspired air written
- as FiOz
- – Hb content.
- PaOz is arterial oxygen tension.
- SpOz is oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry. SaOz is oxygen saturation by ABG analysis. Hypoxemia: PaOz < 80 mmHg at sea level in an adult breathing room air is hypoxaemia.
- PaOz <40 mmHg indicates severe hypoxemia. Hypoxia: Decreased oxygen saturation of tissues is known as hypoxia.
- Normal Pa02 in adult breathing room air with FiOz of 0.2 is 80 – 100 mmHg.
- Oxygenation ratio PaOz / FiOz is oxygenation ratio.
- Normal PaOz / FiOz is 400 – 500 mmHg or 4 to 5. PaOz / FiOz ratio < 200 indicates shunt greater than 20%.
Acid Base balance —
- – The pH is maintained through lungs, kidneys, and blood buffer.
- HC03, PaCOz‘ and pH are interrelated.
- HC03 is controlled by kidneys and blood buffers
- The lungs control PCOz by volatile acids, carbonic acid in the blood.
- Concentration of carbonic acid depends on dissolved COz‘
- The blood buffer system is carbonic acid / bicarobonate base – HZC03 / HC03-.
- Buffer system acts within a fraction of second to prevent change in pH.
- Respiratory system takes few minutes only, but kidneys take minutes to days to adjust pH.
- PaCOz is the best marker for respiratory acid base disturbance.
- – Rise in PaCOzindicates increased carbonic acid
- and decreased pH.
- – Plasma bicarbonate indicates base status.
- – Normal value of HC03 is 24 ± 2 meq/L.
- – Standard bicarobonate (std HCO -) is plasma
- bicarbonate at 37°C and PaCOz of 40 mmHg.
- – Buffer base is sum of all buffer bases in a liter of blood.
- – It is reported as base excess – negative or positive BB or BE.
- – Normal value of BE is 0 ± 2 meq/L.
Plasma pH and potassium –
- In acidemia, potassium moves out into the plasma leading to hyperkalemia and excess hydrogen ions are transported to intracellular space.
- In alkalemia, potassium moves into cells leading to hypokalemia and hydrogen ions move to extracellular space.
Blood sampling —
- · Arterial blood is taken.
- · Always done in steady state.
- · 0.05 ml heparin is mixed with 1 ml of blood.
- · The sample is placed in ice and tested within 2 hours.
Normal values for ABG
- · pH 7.35 to 7.45
- · PaOz 80 – 100 mmHg
- · PaCOz 35 – 45 mmHg
- · HC03 24 ± 2 meq/L
- · BE = 0 ± 2 meq/L.
- Whenever there is ABG disturbance, there is compensatory response by respiratory system or kidneys.
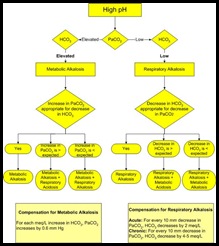
RULES OF COMPENSATION IN ACID-BASE BALANCE —
1. Metabolic acidosis: expected PaCOz decreases by 1 mmHg for every 1 meq/L decrease in HCO-3•
- PaCOz = last 2 digits of pH.
2. Metabolic alkalosis :
- PaCOz increases by 0.5 mmHg for every 1 meq/L increase in HCO-3 or PaCOz = last 2 digits of pH.
3. Respiratory acidosis :
- HC03 increases by 1 meq/ L for every 10 mmHg rise in PaCO in acuteacidosis. z
- HCO-3 increases by 3.5 meq/L for each 10 mm increase in PaCOz in chronic acidosis.
4. Respiratory alkalosis :
- In acute alkalosis HCO decreases by 2 meq/L for every 10 mmHg decrease in PaCOz‘
- In chronic alkalosis HC03 decreases by 5 meq/L for every 10 mmHg decrease in PaCOz‘
Stepwise approach In acidosis & alkalosis —
- 1. Look at pH. — If pH <7.35 it is acidotic and if pH is >7.45, it is alkalotic.
- 2. Look at PaCOz‘ – If >40 mmHg and pH <7.35, it is respiratory acidosis.
- 3 • If more than 25 meq/L and pH more than 7.45, it is metabolic alkalosis.
- 4. pH 7.35 to 7.40 is lower normal range (acidotic side).
- 5. pH 7.40 to 7.45 is higher normal range (alkalotic side).
- 6. If pH<7.35 and PaCOz>45, HC03 and BE normal, it is acute respiratory acidosis due to acute ventilatory failure.
- 7. If pH<7.35, PaCOz>45 mmHg, HCO/BE increased, it is partially compensated respir~tory acidosis.
- 8. If pH<7.35, PaCOz 35-45, HCO/BE decreased, it is acute metabolic acidosis (uncompensated).
- 9. If pH is less than 7.35, PaCOz <35, HCO/BE decreased, it is partially compensated meta bOlic acidosis.
- 10. If pH> 7.45, PaCOz>45, HCO/BE increased, it is partially compensated metabolic alkalosis.
- 11. If pH is>7.45, PaCOz<35 mmHg, HCO/BE normal, it is acute respiratory alkalosis (A3cute alveolar ventilation).
- 12. If pH is> 7.45, PaCOz<35, HC03 decreased, it is partially compensated respiratory alkalosis.
- 13. If pH is 7.35 to 7.4, it is lower normal range acidosis.
- 14. If pH is 7.35 to 7.4, PaCOz>45 mmHg, HCO /BE increased, it is compensated respiratory acid~sis.
- 15. If pH 7.35 to 7.4, PaCOz<35, HCO /BE decreased, It IS compensated metabolic acidosis.
- 16. If pH 7.4 to 7.45 it is higher normal rangealkalosis.
- 17. If pH 7.4 to 7.45, PaCOz <35, HC03 decreased, it is compensataed respiratory alkalosis- chronic alveolar hyperventilation.
- 18. If pH 7.4 to 7.45, PaCOz>45, HC03 increased, it IS compensated metabolic alkalosis.
- These are the main points to remember in ACIDOSIS AND ALKALOSIS .
