Article Contents ::
- 1 Iron Deficiency Anaemia symptoms , iron deficiency Causes and treatment —
- 2 Anaemia
- 3 Hypoproliferative anaemias —
- 4 Functions of Iron in body —
- 5 Causes of Iron Deficiency anaemia —
- 6 Stages of iron deficiency in patient —
- 7 Clinical presentation of iron deficiency in patient —
- 8 Lab Diagnosis of anaemia —
- 9 TREATMENT OF IRON DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA —
- 10 OTHER HYPOPROLIFERATIVE ANAEMIAS Types –
Iron Deficiency Anaemia symptoms , iron deficiency Causes and treatment —
 |
Anaemia |
Hypoproliferative anaemias —
- are anaemias with normocytic and normochromic red cells and low reticulocyte index <2.5.
- Hypoproliferative anaemias are
- · Iron deficiency anaemia (there is microcytic hypochromic anaemia)
- · Acute and chronic inflammation with anaemia
- · Anaemias in malignancy
- · Anaemia associated with renal disease
- · Anaemia in protein malnutrition
- · Anaemia in endocrine deficiencies.
- The most common type of anaemia is iron deficiency anaemia and anaemia in acute and chronic inflammation.
- Iron is a critical element in the function of all cells of the body.
- Free iron is highly toxic as it generates free radicals.
Functions of Iron in body —
- · Iron is an important constituent of haemoglobin which carries oxygen for metabolism of cells.
- · Oxygen is also bound by myoglobin in muscles, which is also a heme compound.
- · The cytochrome system in mitochondria has iron containing enzymes.
- · Iron is important for electron transport and energy metabolism.
- Average life span of red cell is 120 days.
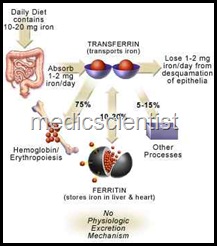
- Iron absorbed from diet circulates in the blood, bound to a protein called transferrin.
- Daily requirement of elemental iron for adult male is 1 mg.
- The daily requirement for adult child-bearing age female is 1.4 mg.
- In iron deficiency states, the bone marrow’s proliferative response is diminished and normal hemoglobin synthesis is impaired. This leads to typical microcytic hypochromic anaemia with hypoproliferative bone marrow.
 |
| Causes of Iron Deficiency anaemi |
Causes of Iron Deficiency anaemia —
- · Decreased intake
- · Blood loss via GIT, menstruation, other sites
- · Increased demand
- · Decreased absorption of iron.
- There is on an average, about 6 mg of elemental iron per 1000 calories of intake.
- Vegetarians suffer from iron deficiency more commonly because phytates and phosphates in vegetables reduce iron absorption by 50%.
- Moreover, iron in vegetables is absorbed in the ferrous form in a ratio of 20% only.
- Infants, children, pregnant females have an increased demand of iron due to increased demand of body for growth. Adding iron salts to food stuffs is not recommended because of risk of iron overload.
- Iron absorption occurs in the small intestine facilitated by acid of the stomach.
- Iron absorption is facilitated by erythroid hyperplasia, as occurs in iron deficiency.
- When a large number of iron tablets are accidentally consumed, the amount of iron absorbed exceeds the transferrin binding capacity of the plasma, resulting in free iron that results in dysfunction of cells e.g. cardiac muscle cells.
Stages of iron deficiency in patient —
- The first stage is negative iron balance where the demand for iron is high e.g. blood loss, pregnancy, rapid growth in children, inadequate intake.
- Blood loss > 10 – 20 ml red cells/day exceeds the limit of absorption from the gut. This results in mobilization of iron from reticulo-endothelial storage sites. The serum ferritin level decreases because serum ferritin reflects the iron stores.
- The serum iron, total iron binding capacity, red cell protoporphyrin levels remain normal.
- In the next stage, iron stores become depleted, serum iron falls, but TIBC (total iron binding capacity) increases.
- The transferrin saturation which reflects the circulating iron falls to 15 – 20% and hemoglobin synthesis becomes impaired. Erythropoiesis is decreased.
- Now macrocytic and hypochromic cells start appearing.
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit, and transferrin saturation fall.
- When the hemoglobin is about 10, the bone marrow is hypoproliferative but when hemoglobin is 7- 8 mg/ dl i.e severe anaemia there is hypochromia and macrocytosis with poikilocytes-misshapen cells, cigarshaped cells and target cells in peripheral blood. This result in iron deficiency anaemia with erythyroid hyperplasia i.e. hyperproliferative anaemia.
Clinical presentation of iron deficiency in patient —
- Common in pregnancy, adolescence, growing children, and patients with history of blood loss.
- In adult males, commonest cause of iron deficiency is gastrointestinal blood loss.
- There is fatigue, pallor, reduced exercise capacity, dyspnoea. There may be cheilosis (fissures at corners of mouth). There is koilonychia (spooning offinger nails).
Lab Diagnosis of anaemia —
- Normal serum iron is 50 – 150 IJg /dl. Normal TIBC is 300 – 360 IJg/dl. Normal transferrin saturation is 25 – 50%.
- Serum ferritin level correlates with total iron body stores.
- Adult males have serum ferritin 100 IJg/L. Adult females have 30 IJg/L.
- Low serum ferritin i.e. < 15 indicates absent body iron stores.
- In thalassemias, the serum iron and transferrin saturation levels are normal or increased.
- In chronic inflammatory disease, the anaemia is normocytic normochromic, ferritin levels is increased and TIBC is low.
TREATMENT OF IRON DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA —
- Patients with severe anaemia and cardiovascular instability require red cell transfusion.
- Young and asymptomatic patients may be treated with oral iron. Pregnant women, and growing children may be given oral iron.
- For excessive blood loss, red cell transfusion is given. 300 mg of elemental iron per day is given as 50 mg tablets – 3-4/ day.
- Oral iron should be taken on empty stomach as food inhibits absorption.
- Iron syrups may be given for patients with gastric disease.
- A dose of 300 mg elemental iron / day results in absorption of 50 mg /day of elemental iron.
- Sustained treatment for 6 – 12 months is given even after correction of anaemia.
- Oral iron may cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
- Reticulocyte count begins to increase in one week. If iron deficiency persists, then parenteral iron therapy is given.
- Intravenous iron is given to patients unable to tolerate oral iron.
- For continuing blood loss, parenteral iron should be given.
- In patients with erythropoietin deficiency as in renal disease, parenteral iron is given along with recombinant erythropoietin therapy.
- Intravenous sodium ferric gluconate and iron sucrose are some parenteral preparations in use.
- Iron dextran which was previously used, has serious toxic effects.
- Parenteral iron may be given as a total dose or in small doses over a period. Iron dextran can give rise to anaphylaxis.
- After several days of iron infusion, arthralgias, skin rash, and low grade fever can occur.
- Iron is given in 5% dextrose or 0.9% sodium chloride solution over a 90 minute period. Iron is tested by a slow infusion.
- If chest pain, wheezing, or hypotension occur, then therapy is stopped.
- In dialysis patients, 100 mg of elemental iron is given weekly for 10 weeks in addition to recombinant erythropoietin therapy.
Amount of iron needed —
- Body weight in kg X 2.3 X (15 – patient’s haemoglobin) + 500 mg for store. .
OTHER HYPOPROLIFERATIVE ANAEMIAS Types –
- Chronic inflammation / infection – There is low serum iron, hypoproliferative marrow, increased serum ferritin.
- Renal disease – Reticulocytes are decreased, and there is normocytic, normochromic anaemia, or hypoproliferative anaemia.
- Endocrine and nutritional – Testosterone and anabolic steroids increase erythropoiesis.
- Patients with hypothyroidism, on estrogen therapy, hypopituitarism have anaemia.
- Anaemia in Addison’s disease may be severe. In hyperparathyroidism, there is decreased erythropoietin production due to renal damage, leading to anaemia.
- Marrow damage leads to hypo proliferative anaemia.
- This is about anaemia due to iron deficiency , in next post i will describe about other types of anaemia, for updates subscribe free email updates.
