Article Contents ::
Diagnosis of Megaloblastic Anaemia and Treatment —
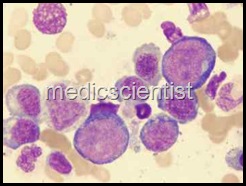 |
Megaloblastic Anaemia |
- The megaloblastic anaemias are disorders caused by impaired synthesis of DNA.
- Due to slow cell division, the cells are large, called megaloblastic cells, with more RNA than DNA.
- There may also be ineffective erythropoiesis.
- Most megaloblastic anaemias are due to deficiency of cobalamin j vitamin B12 and deficiency of folic acid.
- Normal range of cobalamin in blood is 300 – 900 pgj ml. Less than 200 pgjml gives rise to significant deficiency features.
- Normal serum concentration of folic acid ranges from 6 – 20 ngjml. Less than 4 ngjml is significant folate deficiency.
Types of megaloblastic anaemia’s —
- 1. Gastric achlorhydria
- 2. Inadequate intake especially in pure vegetarians
- 3. Pernicious anaemia
- 4. ‘Congenital absence of intrinsic factor
- 5. Tropical sprue
- 6. Regional enteritis
- 7. Non-tropical sprue
- 8. Drugs like colchicine, neomycin, methotrexate, azathioprine, pyrimethamine, triamterene diuretic.
- 9. Alcoholics
- 10. Pregnancy
- 11. Malignancy
- 12. Hemodialysis
- 13. Dihydrofolate reductase deficiency.
Clinical features symptoms of megaloblastic anaemia —
- Weakness, giddiness, vertigo, palpitations, angina, anorexia, weight loss, diarrhoea, peripheral nerve disease, demyelination of posterior and lateral columns-numbness, paraesthesia, weakness, ataxias; sphincter disturbances, dementia, psychosis.
- Neurological disease may occur even with normal hematocrit and normal RBC indices.
- In pernicious anaemia, the above features are seen along with other diseases of similar immunologic origin, like Grave’s disease, vitiligo, and hypothyroidism.
- Pernicious anaemia is more common in elderly and rare below 30 years.
Treatment of Magloblastic Anaemia —
- Intramuscular cyanocobalamin – 100 IJg j week for 8 wks followed by 1000 IJgm intramuscular every month.
- For practically whole life, 2 mg crystalline B12 may be given orally daily.
- Reticulocytosis occurs 5 days after therapy and patients improve within a week.
- For severe cases-blood transfusion, packed RBCs, exchange transfusions may be given.
- Folates and cobalamin both must be given because the neurologic manifestations may be aggravated by giving folate alone.
- Cobalamin and folate deficiency may present without anaemia with neurologic manifestations only.
- Folic acid 1 – 5 mgjday orally is given.
- The patient must be advised to take balanced diet.
This is the short description of magloblastic anaemia.
