Article Contents ::
Cardiac Arrhythmias Types and Definitions Mechanisms with Methods for Diagnosis Arrhythmias
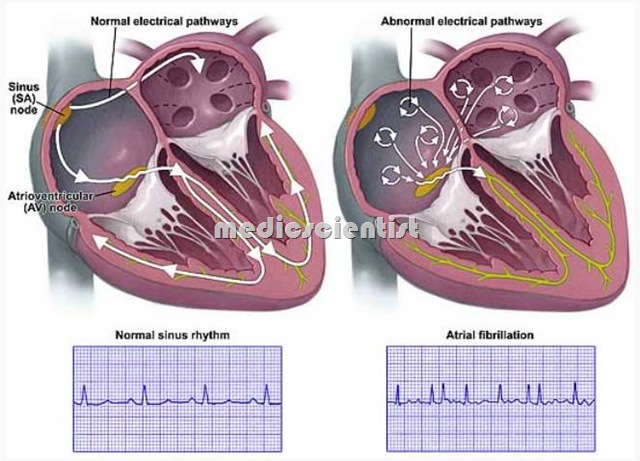
Mechanisms of arrhythmias
- Problems of impulse formation i.e. automaticity.
- Problems of impulse conduction i.e. Block I Reentry.
Methods for Detecting Arrhythmias
- Is to monitor the ECG, Transtelephonic monitoring, Holter monitoring, invasive ECG recordings.
Transtelephonic monitoring
- Cardiac monitoring in which the patient uses a pocket sized transmitter to send a cardiac rhythm strip over the telephone when cardiac symptoms occur.
Dynamic (Holter) Monitoring:
- Holter monitoring means monitoring of ECG over long periods of time even while the patient is ambulant. The ECG recording is then analyzed by a computer for arrhythmias.
Sinus arrhythmia
- Sinus arrhythmia is a variation of heart rate with respiration. The heart rate increases during inspiration and decreases during expiration. .
Definitions
- Automaticity : Ability of certain specialized cells to achieve spontaneous depolarization and act as pacemakers i.e. generate impulses.
AV Dissociation:
- Independent beating of atria and ventricles caused by block of atrial impulse in the AV junction or by interference in conduction by a ventricular impulse.
- · Delay or partial failure or total failure of impulse conduction.
- · Delay of conduction – First degree block.
- · Partial failure – Second degree block.
- · Total failure – Third degree block.
Isorhythmic dissociation:
- AV dissociation with atria and ventricles beating at nearly the same rate .
Junction:
- AV node, common. His bundle and sometimes accessory conduction bundle (KENT). –
Premature beat:
- A beat that occurs before time or prior to the next expected beat.
Relative refractory:
- A term referring to cells that have only partly recovered from their previous activation and are therefore capable of slow conduction of another impulse.
Spontaneous depolarization:
- The ability of a specialized cardiac cell to activate by altering the permeability of its membrane to a sufficient degree to attain threshold potential without any external stimulation.
Accelerated atrial rhythm (AAR) :
- A tachyarrhythmia that is caused by an increase of automaticity in Atrial pacemaking cells.
Accelerated junctional rhythm (AJR) :
- A tachyarrhythmia that is caused by an increase of automaticity in the pacemaking cells of the His bundle.
Accelerated rhythm:
- An increase in a particular cardiac rhythm above its normal limit .
Accelerated ventricular rhythm (AVR) :
- A tachyarrythmia that is caused by an increase of automaticity in pacemaking cells of the bundle branches & their fascicles.
Carotid sinus massage:
- Manual stimulation of the area of the neck that overlies the bifurcation of the carotid artery, to increase parasympathetic nervous activity, and thereby decrease the heart rate.
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) :
- A rapid rhythm produced by increased automaticity in pacemaking cells located at multiple sites within the atria.
Escape rhythms:
- Rhythms that originate from sites in the pacemaking and conduction system other than the sinus node, after a pause created by the failure of either normal sinus impulse formation or atrioventricular impulse conduction.
Junctional rythum —
- A rythum with a rate of less than 100 beats/minut, with an inverted p wave direction visible in the frontal plane leads, and normaly appearing QRS complexes.
- P wave may be obscured if they occur during the QRS complexes.
Sic Sinus Syndrome:
- Inadequate function of cardiac cells with pace making capability, resulting in continuous or intermittent slowing of the heart rate at rest and an inability to appropriately increase the rate with exercise.
Vasovagal reaction (Reflex) :
- Sudden slowing of the heart rate either from decreased impulse formation (sinus pause) or decreased impulse conduction (AV block) resulting from increased activity of the parasympathetic or decreased activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
Ventricular rhythm:
- A rhythm with a rate of less than 100 beats/min. with abnormally wide There may be either retrograde conduction to the atria or AV dissociation.
Recognition of a ventricular premature beat:
- A ventricular premature beat is recognized by wide and bizarre QRS complex, and it is not preceded by a premature P wave. It IS followed by a fully compensatory pause because of its’ inability to conduct retrogradely through the AV node to reset the SA node.
