Chikungunya Virus Infection
An alphavirus, typically found inSoutheast Asia, or Africa that can be transmitted to humans by the bite of Aedes mosquitoes. After an incubation period of about a week, headache, nausea, vomiting, the virus produces high fevers, and severe joint pain, usually in the wrists or ankles.
 |
| Chikungunya Virus Infection |
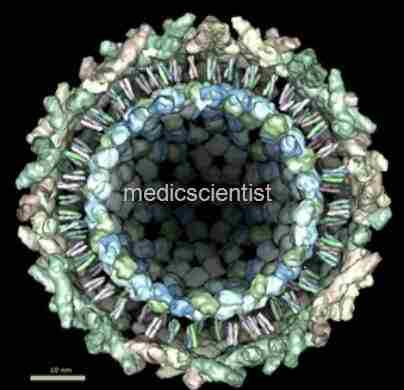 |
| Chikungunya Virus |
pathogenesis of Chikungunya —
- The pathogenesis of the severe and persistent joint symptoms that characterize chikungunya virus infections is uncertain.
- Chikungunya is a single-stranded RNA virus of the genus Alphavirus (Togaviridae family).
- Some data suggest that macrophage-derived products such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma, and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 may play important roles in the joint tissue damage
The name chikungunya is derived from a local language of Tanzania meaning “that which bends up” or “stooped walk” because of the incapacitating arthralgia caused by the disease.
- Chikungunya is an arthropod-borne virus (arbovirus) endemic to West Africa that causes acute febrile polyarthralgia and arthritis.
- Chikungunya had traditionally been perceived as a tropical disease until an outbreak in Italy in 2007,
- Chikungunya Virus infection is a disease transmitted by the Aedes and Culex mosquito similar to dengue viral infection.
- he major chikungunya virus mosquito vectors are Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, they also capable of transmitting dengue virus, which, like chikungunya virus.
 |
| ChikungunyaVirus infection is a disease transmitted by the Aedes and Culex mosquito |
 |
| ChikungunyaVirus infection is a disease transmitted by the Aedes and Culex mosquito |
- Chikungunya means ‘that which bends up’ (patient doubles up with joint pains).
- Rapid spread of chikungunya virus has been observed in outbreaks involving the Indian Ocean islands, where attack rates have been extremely high in previously unexposed populations
- Chikungunya virus is endemic in parts of West Africa where it appears to be maintained in a cycle involving humans, Aedes mosquitoes, primates and perhaps other animals.
- The disease is found in Africa and Asia.
The appearance and spread of chikungunya virus in India was observed after a hiatus of almost 32 years In India, nearly 1.4 million cases of chikungunya fever were reported in 2006, and outbreaks have continued to occur.
- Chikungunya virus spreads by means of travel of infected individuals between regions where competent mosquitoes exist for perpetuation of local transmission.
- In India the disease is found in Kolkata, Chennai and Karnatak.
- The disease is common in adults. Incubation period is 2-3 days.
 |
| Clinical features of Chikungunya |
Clinical features of Chikungunya
- Following acute illness (usually lasting 7 to 10 days),
- There is fever, severe arthralgia, chills, headache, photophobia, conjunctival injection, anorexia, nausea, abdominal pain.
- some patients may experience persistent rheumatologic signs and symptoms including arthritis/arthralgia,
- morning pain and stiffness edematous polyarthritis of fingers and toes, and severe tenosynovitis ( of hands and ankles)
- There is migratory polyarthritis of hands, wrists, ankles and feet and sometimes larger joints also.
- Rashes appear within one or two days on the trunk and limbs.
- There may be petechiae and epistaxis. There is recovery in a few weeks.
- There may be persistent stiffness and joint pains, especially in HLA-B27 patients.
 |
| Clinical features of Chikungunya |
Lab findings of Chikungunya
- There may be leukopenia,
- increased AST,
- C-reactive protein,
- decreased platelet count.
Chikungunya Treatment
- Treatment of chikungunya infection consists of supportive care including anti-inflammatory agents that relieve symptoms in many patients and analgesic agents
- Cefixime and Fluoroquinolones like Ofloxacin may be given.
- A live attenuated vaccine has been developed for prevention.
- Prevention consists of minimizing mosquito exposure
