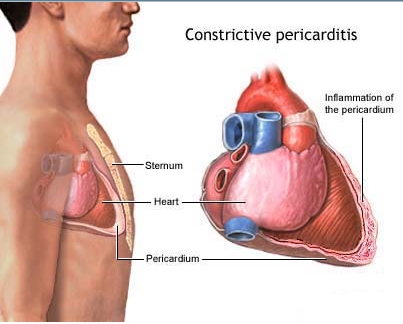
CHRONIC CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITIS
Constrictive pericarditis —
Constrictive pericarditis is the result of scarring and consequent loss of elasticity of the pericardial sac. The normal pericardium is a fibroelastic sac containing a thin layer of fluid that surrounds the heart.
- After the absorption of ericardial fluid thereis organization of fibrin, serous fluid and granulation tissue In t e pericardium.
- This results in a thickening, scar formation, hardening and constriction of pericardium.
- Causes are – tuberculosis, trauma, irradiation, tu~ors, SLE, uraemia.
CHRONIC CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITIS Physical findings :
- JVP is raised – x and y descent are prominent
- Ascites, Edema, Anasarca and Hepatomegaly
- Pulsus parodoxus
- Kussmaul’s sign – increased JVP during inspira-
- tion i.e. rise of venouscolumn in the neck during inspiration instead of a fall is called Russmaul’SSi n
- Pericardial knock -is an extra sound after second heart sound
- Atrial fibrillation may be present.
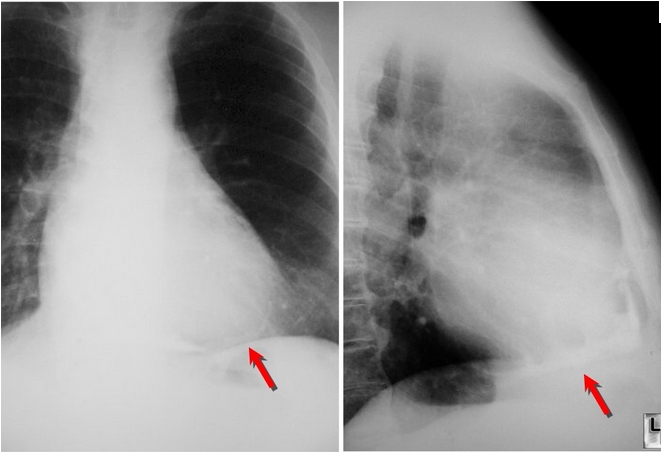
X-ray I echocardiogram I CT scan I MRI
- Thickening, calcification, scarring of pericardium is seen.
CHRONIC CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITIS Treatment
- Resection of pericardium. Mortality may be high depending on myocardial atrophy.
- Treatment of etiology.
