Article Contents ::
- 1 CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS COMMON DISEASES DUE TO DM
- 2 HYPERGLYCEMIA AND MICROVASCULAR DISEASE —
- 3 Dyslipidemia —
- 4 Hypertension —
- 5 Microvascular Chronic Long-term Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus
- 6 Complications common from Long-term 10 – 20 years after hyperglycemia.
- 7 Mechanism of Chronic Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus
CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS COMMON DISEASES DUE TO DM
HYPERGLYCEMIA AND MICROVASCULAR DISEASE —
- Hyperglycemia is an important risk factor for the development of microvascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes, as it is in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Chronic Long-term complications result in morbidity and mortality. Children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for associated comorbidities that include:
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
-
Dyslipidemia —
- Dyslipidemia is defined as lipoprotein disorders that promote the development of atherosclerosis and include the following abnormalities: .
- Increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)
- Decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)
- Increased triglycerides (TG)
-
Hypertension —
- However, with the increasing prevalence of obesity, primary hypertension is the most common cause of hypertension in adolescents
- Primary hypertension (also known as essential hypertension) was once considered uncommon in children.
- In diabetics with more than 20 years disease nonproliferative retinopathy is always present.
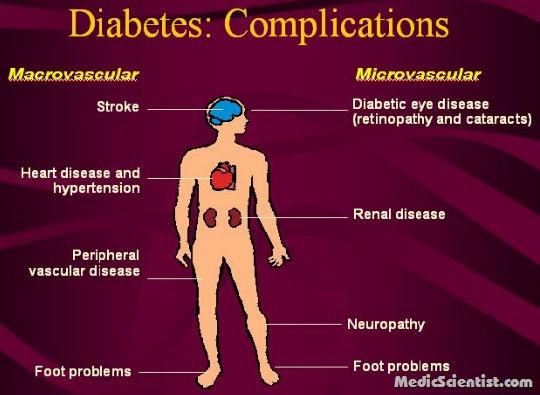
Microvascular Chronic Long-term Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus
- Eye disease:
- · Retinopathy
- ·Macular edema Neuropathy:
- · Sensory and motor
- ·Autonomic Nephropathy
- Macrovascular
- · Coronary artery disease
- · Peripheral vascular disease
- · Cerebrovascular disease
- · Gastrointestinal
- · Genitourinary
- · Dermatologic
- · Infectious
- · Cataracts
- · Glaucoma
Complications common from Long-term 10 – 20 years after hyperglycemia.
- Often complications seen at the time of diagnosis.
- Microvascular complications occur due to hyperglycemia in type 1 and type 2,
- so a reduction in blood sugar levels prevents retinopathy,
- neuropathy
- and nephropathy.
- Genetic factors also responsible for complication of diabetes mellitus.
- In type 2 diabetes mellitus coronary heart disease occurs and mortality is high.
- In Diabetes mellitus risk depends on :
- · Blood sugar
- · Dyslipidemia
- · Hypertension
- · Genetic factors.
Mechanism of Chronic Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus
Intracellular glucose leads to formation of AGE’s (Advanced glycosylation end products) which:
- · Promote atherosclerosis
- · Cause glomerular dysfunction
- · Reduce NO (Nitric OXide) synthesis
- ·Induce endothelial dysfunction.
- Growth factors :
- Play an important role
- VEGF is involved locally in diabetic proliferating retinopathy.
- Hyperglycemia :
- Leads to increased production of reactive oxygen or super oxide which is responsible for the complications of diabetes mellitus.
- Hyperglycemia increases glucose metabolism via sorbitol pathway. This causes generation of reactive oxygen species leading to generalized cellular dysfunction.
Relation of glycemic control and Chronic Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus
- The Diabetes Control and Complication Trial (DCCT) offers proof that controlling blood sugar levels prevent early complications of Diabetes mellitus type 1.
- DCCT demonstrated that control of blood sugar leads to decreased incidence of retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy.
- There is also data to support strict glycemic control to reduce complications in type Il DM.
