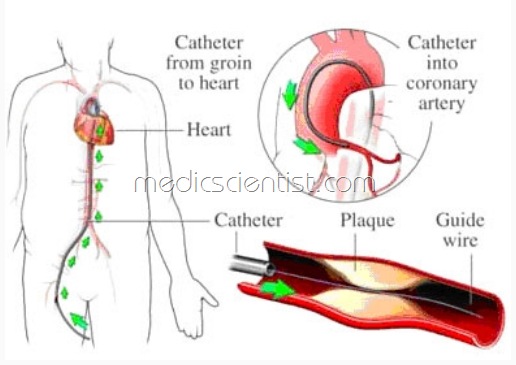
Coronary Arteriography (Angiography)
- Radio-opaque dye is injected into a peripheral artery and coronary arteries are visualized for any obstructive atherosclerotic lesions.
- cardiac catheterization was primarily a diagnostic procedure that was used to evaluate ventricular function, and coronary anatomy hemodynamics,.
- diagnostic catheterization and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are done by skin puncture ,under local anesthesia,
MAJOR COMPLICATIONS —
- The risk of producing a major complication (death, myocardial infarction, or major embolization)
- potentially fatal or lifestyle-limiting cardiac disease
- the risk-to-benefit ratio still favors performing this procedure
- The death during diagnostic cardiac catheterization is generally well below 1 percent.
Indications of Coronary Angiogrpahy :
- Severe symptoms despite optimal medical therapy.
- intracardiac tumor, mass or thrombus (6 to 8 percent each),
- native valvular disease, aortic dissection or aneurysm,
- and congenital heart disease (4 percent)
- r cardiac sources of embolism (36 percent),
- endocarditis (14 percent), prosthetic heart valve function (12 percent),
- Patients for PC! (percutaneous coronary intervention) or CABG (Coronary artery bypass surgery)
- Diagnostic test for troublesome symptoms Patients with CAD who have been resuscitated. Signs of severe ischemia on noninvasive testing.
- Aortic Stenosis or HOCM -hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy with angina to rule out cause, or before valve replacement in AS
- High-risk patients after acute MI
- Other causes of Myocardial Ischemia, suspeCted Kawasaki or coronary artery anomaly.
