DIAGNOSIS OF SECONDARY HYPERTENSION with Investigations
- nursing diagnosis for high blood pressure
- secondary hypertension differential diagnosis
- diagnosis high blood pressure
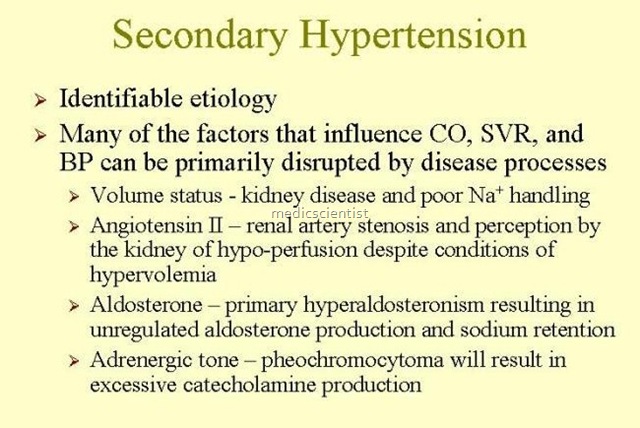
- Age of patients of secondary hypertension may be <25 or >50 years.
- Phaeochromoc toma and renovascular hypertensiof.l are t e likel causes.
- In phaeochromocytoma there is anxiety, headache, weight loss, hyperglycemia, palpitations and sweating.
- In Renovascular hypertension there is abdominal bruit. In polycystic renal disease abdominal masses can be palpated bilaterally along with hypertension.
- Ultrasound, IVP, serum creatinine (increased), blood urea (increased), proteinuria, hematuria.
Pheochromocytoma – c
- atecholamine and its metabolites are seen in 24 hours urine sample.
- Measurement of plasma catecholamines is done.
Cushing‘s syndrome –
- 24 hours urine for cortisol and creatinine.
- 1 mg dexamethasone is given at bed time and plasma cortisol measured at 7 am.
- A urine cortisol of less than 100 IJg or suppression to less than 5 IJg / dl rules out Cushing’s.
Renovascular hypertension
- Rapid sequence IVP.
- Captopril enhanced radionuclide renal scan.
- Duplex doppler flow study.
- agnetic resonance angiography.
- CT scan with IV contrast agent.
- For surgically treatable patients evaluate by renal angiogram and renal vein renin determination.
- renal angiogram is done for location and type of lesion which may be atheromatous, or fibrous dysplasia.
- renal artery stenosis is a frequent finding in normal individuals and at post mortem.
- essential hypertension may occur in presence of renal artery stenosis.
- right and left renal vein catheterization and PRA from each side with reveal if ischemic kidney is producing “ore renin.
- he ischemic kidney has venous PRA more than 1.5 more compared to normal kidney.
- on normal kidney PRA is same as inferior vena cava lood before entrance of renal veins.
- before this test restrict sodium intake, given ACE in-ibitors, stop beta blockers (beta blockers suppress renin formation).
- Primary aldosteronism – ere is hypokalemia.
- Idosterone concentration is increased.
- aldosterone : renin ratio is high. is decreased.
- disease is unilateral surgical removal of lesion may _ e hypertension.
Tests for Evaluation of Hypertension
- Urine for sugar,
- albumnuria,
- hematuria,
- microscopic examination
- Hematocrit
- Total cholesterol/lipid profile ECG
- TSH
- WBC count
- Serum sodium potassium
- Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen Fasting glucose
- Serum calcium and phosphate Chest X-ray
- Echocardiogram.
HYPERTENSION from JNC – EXPRESS
- systolic blood pressure of more than 140 mmHg in persons older than 50 years is an important cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor.
- The risk of CVD after 115 / 75 mmHg doubles with each rise of 20 / 10 mmHg.
The JNC-7 classifies hypertension into 4 classes:
- Normal –
- Blood pressure < 120/80 mmHg
- Pre hypertension
- – BP 120 – 139 / 80-89 mmHg
- Stage 1 hypertension
- – 140 ·159/90-99 mmHg
- Stage 2 hypertension
- – BP > 160/ > 100 mmHg
Drug treatment can be started with thiazide-like diuretics and other drugs like angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers and calcium channel blockers added as required.
- Patients of diabetes and chronic kidney disease must maintain a BP of < 130/80 mmHg.
Blood pressure measurement :
- Patient should be seated quietly for 5 minutes on a chair with feet on the floor and arm supported at heart level on a table.
- In case of postural hypotension the BP should be measured in the standing position also.
- The cuff of the BP instrument should encircle at least 80% of the arm. SBP (systolic blood pressure) is the point at which 1st 2 sounds are heard and DBP (diastolic blood pressure) is the point of the disappearance of sounds.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is done for patients with white coat hypertension (raised blood pressure in the presence of the doctor), hypotensive symptoms, labile hypertension, and autonomic dysfunction.
Identifiable causes of hypertension must be detected and treated like:
- · Sleep apnoea
- · Drug induced hypertension (Oral contraceptives, NSAIDs, cyclosporin, erythropoietin, decongestants, cocaine etc.)
- · Chronic kidney disease
- · ECG
- · Urinalysis
- · Blood glucose
- · Serum Na, K
- · Serum creatinine
- · Serum calcium
- · Chronic steroid therapy
- · Pheochromocytoma
- · Primary aldosteronism
- · Renovascular disease
- · Coarctation of aorta
- ·Thyroid or parathyroid disease Advise tests:
- · Lipid profile after 9-12 hrs fast – TC, HDL, LDL, TG.
