Article Contents ::
Polycythemia Vera Diagnosis Type And Treatment
 |
| Polycythemia Vera Diagnosis |
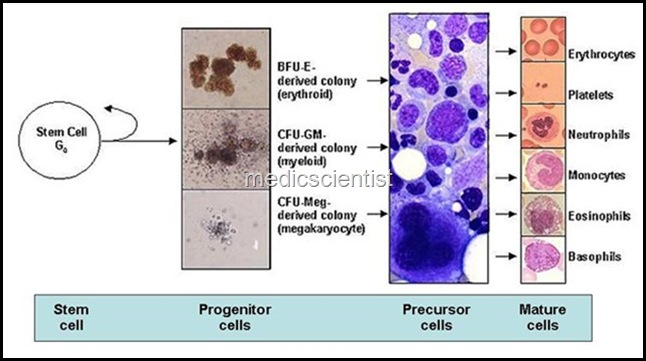
- Chronic myeloproliferative disorders are due to overproduction of one or more of the formed elements of blood.
- These are polycythemia vera, chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, essential thrombocytosis, chronic myeloid leukemia.
Definition Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis
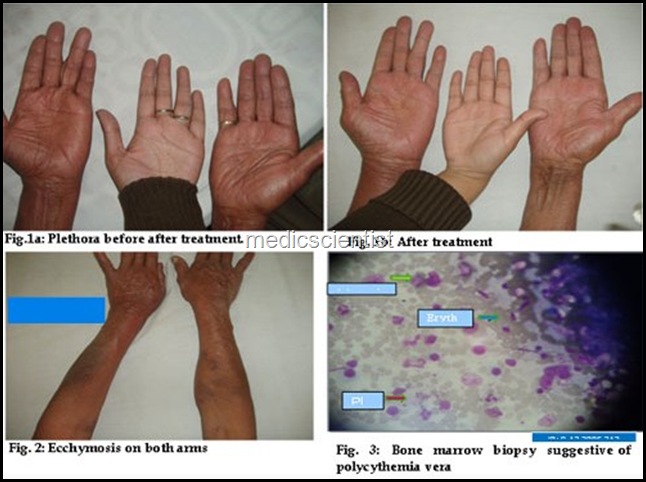
Polycythemia vera is a clonal disorder with accumulation of phenotypically normal red cells, granulocytes and platelets without any known physiologic stimulus.
- There is a genetic basis for the disorder. There is massive splenomegaly.
- There is high hemoglobin or hematocrit. There is uncontrolled erythrocytosis.
- There is vertigo, tinnitus, headache and visual disturbances.
- There is systolic hypertension.
- There is venous or arterial thrombosis, particularly intraabdominal venous thrombosis.
- Patients of polycythemia vera develop Budd Chiari syndrome.
- There is ischemia of digits.
- There is easy bruising, epistaxis, GI (gastrointestinal) haemorrhage.
- There is hyperuricaemia, with secondary gout, and uric acid stones.
- Acid peptic disease is very common.
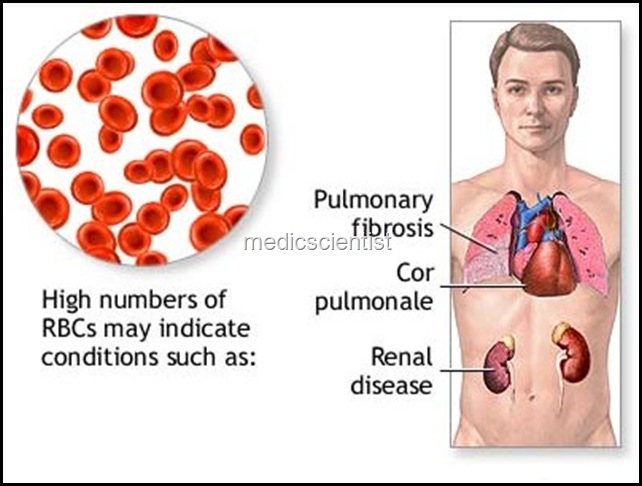
Causes of polycythemia
 |
| Causes of polycythemia |
- Polycythemia vera
- Carbon mono-oxide poisoning High altitude
- Pulmonary diseases
- Sleep apnea syndrome
- Right to left cardiac shunts
- Renal diseases like renal artery stenosis, cysts, transplantation
- Hypernephroma, hepatoma Pheochromocytoma.
Diagnosis Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis
 |
| Diagnosis |
- Polycythemia is diagnosed by presence of elevated red cell mass, normal arterial oxygen saturation, splenomegaly, and in absence of splenomegaly there is leukocytosis.
Treatment Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis
- Hemoglobin level should be less than 14 g/dl in men and less than 12 g/dl in women to avoid thrombotic complications.
- Periodic phlebotomy (section of vein to drain blood to reduce red cell mass and hyperviscosity) is done at 3-month intervals till iron deficiency occurs.
- Chemotherapy is not indicated.
