Article Contents ::
- 1 All about Tuberculosis , pulmonary or extra-pulmonary.
- 2 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Primary disease:
- 3 Primary pulmonary tuberculosis –
- 4 Progressive primary tuberculosis –
- 5 Post Primary Disease:
- 6 The lung lesions may be —
- 7 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Symptoms are
- 8 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Physical findings:
- 9 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS TREATMENT Case definitions
- 10 History of Tuberculosis treatment – Definitions for diagnosis
- 11 DRUGS – ATT (ANTITUBERCULAR TREATMENT)
- 12 There are 3 main properties of antituberculous drugs:
- 13 The Tuberculosis first line agents consist of
- 14 Tuberculosis Second line drugs have lower efficacy and more toxicity.
All about Tuberculosis , pulmonary or extra-pulmonary.
- Details about PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Diagnosis Signs and Symptoms with Treatment.
 |
| Detail about PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Diagnosis Signs and Symptoms with Treatment |
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Primary disease:
| PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Primary disease |
Primary pulmonary tuberculosis –
- Is due to first infection with the tubercular bacilli. It is seen in children. It involves middle and lower lung zones
- Lesion is peripheral with hilar or paratracheal lymphadenopathy .
- Lesions heal and remain as a calcified nodule called Ghon lesion.
| Primary pulmonary tuberculosis |
Progressive primary tuberculosis –
- In children and persons with low immunity, malnutrition, HIV infection, primary pulmonary tuberculosis progresses to pleural effusion, necrosis of central part, cavity formation, hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, compression of bronchi, segmental or lobar collapse of lung called Progressive Primary Tuberculosis.
- Spread by blood, called haematogenous dissemination, results in severe primary tuberculosis infection.
- Bacilli enter the blood stream from lungs and lymph nodes and spread to various organs where they produce granulomatous lesions.
- Healing may occur, or miliary tuberculosis and meningitis may occur.
| Post Primary PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Disease |
Post Primary Disease:
- It occurs in adults due to reactivation.
- This is called secondary tuberculosis or post primary disease due to endogenous reactivation of infection. It found in apical and posterior segments of upper lobe of lungs.
- This is due to the high oxygen content in these regions favoring growth of bacteria.
- There is infiltration, and cavity formation containing necrotic contents, which can spread to other parts of the lungs. Tubercular pneumonia may occur.
- The disease may be fatal in a few weeks or become chronic in several months.
| Tuberculosis PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS detail |
The lung lesions may be —
- Pneumonia
- Cavity
- Fibrosis
- Calcification Pleural effusion
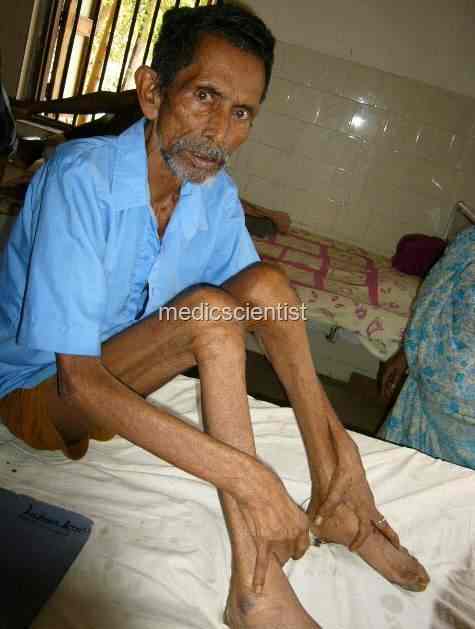
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Symptoms are
- Fever,
- night sweats,
- weight loss,
- anorexia,
- malaise,
- weakness,
- cough,
- purulent sputum or blood stained sputum,
- massive hemoptysis,
- pleuritic chest pain and dyspnoea.
| PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Diagnosis Signs and Symptoms |
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Physical findings:
- There may be no findings.
- Crepts or rales may be present especially after coughing.
- Ronchi may be present due to bronchial obstruction. Amphoric breathing is heard over a cavity communicating with bronchus.
- Fever – low grade, wasting, anaemia, pallor, finger clubbing, leucocytosis;and hyponatraemia are seen.
- Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) may occur. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) may occur rarely.
- Rasmussen’s aneurysm (dilated vessel in a cavity) is rare.
| PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Diagnosis Signs and Symptoms |
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS TREATMENT Case definitions
- 1. Tuberculosis suspect : Any person with symptoms or signs suggestive of tuberculosis like cough more than 2 weeks.
- 2. Case of tuberculosis: A patient in whom tuberculosis is confirmed bacteriologically
- 3. Definite case of tuberculosis : A patient with positive culture for M. tuberculosis complex or patient with 2 sputum smears showing AFB
History of Tuberculosis treatment – Definitions for diagnosis
- 1. New -A patient who has never taken antitubercular treatment or taken for less than a month.
- 2. Relapse -A patient treated for TB and declared cured, or full treatment taken but smear or culture for tuberculosis is positive.
- 3. Treatment after failure – A patient given An again, after failed previous treatment
- 4. Treatment after default – If a patient, bacteriologically positive, interrupts treatment for 2 moths or more and starts An again.
- 5. Transfer in – A patient transferred from another TB centre for continuation of treatment.
- 6. Other – Any other case like chronic case, sputum positive at the end of repeat treatment.
- Sometimes pulmonary and extra pulmonary relapse cases may be smear-negative.
DRUGS – ATT (ANTITUBERCULAR TREATMENT)
There are 3 main properties of antituberculous drugs:
- Bactericidal action
- Sterilizing activity
- To prevent resistance.
The Tuberculosis first line agents consist of
- Isoniazid,
- Rifampin,
- Pyrazinamide,
- Ethambutol.
Tuberculosis Second line drugs have lower efficacy and more toxicity.
- streptomycin,
- kanamycin,
- amikacin,
- capreomycin,
- ethionamide,
- cycloserine, and PAS(Paraamino salicylic acid).
- Complete TUBERCULAR TREATMENT
