Article Contents ::
- 1 Alcoholic Cirrhosis Clinical features Physical findings Treatment
- 2 ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS
- 3 Alcoholic Cirrhosis Clinical features
- 4 Physical findings in alcohol abuse
- 5 Abnormality Diagnostic characteristics
- 6 Lab findings
- 7 ACG guideline for the diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease
- 8 Alcoholic Cirrhosis Treatment
Alcoholic Cirrhosis Clinical features Physical findings Treatment
ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS
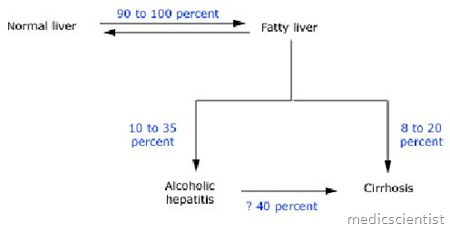
- This results from chronic alcohol ingestion and may follow alcoholic fatty liver and alcoholic hepatitis.
- It is also called Laennec‘s cirrhosis, and micronodular cirrhosis.
- Chronic hepatitis C infection worsens alcoholic hepatitis leading to alcoholic cirrhosis.
Alcoholic Cirrhosis Clinical features
- · It may be symptomless
- · There is slow onset of symptoms after about 10 years of alcohol intake, progressive in weeks and months.
- · There is progressive liver dysfunction and portal hypertension i.e. jaundice, bleeding from gastrooesophageal varices, ascites and encephalopathy.
- • The liver is firm, nodular, may be enlarged or shrunken (decreased in size).
- · There is jaundice, palmar erythema (red palm), spider angiomas or spider nevi (spider-like dilatation of capillaries seen on the skin), splenomegaly, clubbing, muscle wasting (loss of skeletal muscle mass), ascites, and peripheral oedema.
- · There is anorexia, weight loss.
- · There is weakness, fatigue, easy bruising.
- · Men may have gynaecomastia, testicular atrophy.
- · Women may have menstrual irregularity.
- · There is Dupuytren’s contracture due to palmar fascia fibrosis (claw hand).
- · Patient may go into hepatic coma and die.
- · There may be renal dysfunction and failure also.
Physical findings in alcohol abuse
- Abdominal wall collaterals (caput medusa)
- Ascites
- Cutaneous telangiectasias
- Digital clubbing
- Disheveled appearance
- Dupuytren’s contractures
- Gynecomastia
- Jaundice
- Malnutrition
- Palmar erythema
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Splenomegaly
- Testicular atrophy
Abnormality Diagnostic characteristics
- Serum AST>ALT (ratio usually >2.0, both usually <300 IU/L, and almost never >500 IU/L) Sensitivity and specificity have not been well studied, but may vary with the magnitude of the ratio
- Elevated serum AST Sensitivity 50 percent
- Specificity 82 percent
- Elevated serum ALT Sensitivity 35 percent
- Specificity 86 percent
- Elevated serum GGT Sensitivity approximately 70 percent
- Specificity approximately 60 to 80 percent
Lab findings
- · Anaemia, hemolytic anaemia
- · Hypercholesterolemia
- · Hyperbilirubinaemia
- · Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase
- · Elevated AST (Aspartate aminotransferase)
- · AST / ALT ratio is more than 2
- · Serum prothrombin time is prolonged
- · Serum albumin is decreased
- · Insulin resistance occurs leading to glucose in- tolerance
- · Respiratory alkalosis, hypokalemia
- · Hypomagnesemia, hypophosphatemia
- · Pre-renal azotemia.
- Ultrasound
- • Hepatomegaly or shrunken liver.
ACG guideline for the diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease
- All patients should be screened for alcoholic liver disease. A thorough history of alcohol use should be obtained. The CAGE questionnaire is a useful screening method for alcohol abuse or dependency.
- A detailed physical examination should be done, searching for signs of chronic liver disease and staging its severity.
- A liver chemistry profile (including serum albumin, bilirubin and transaminases [AST/ALT]). A complete blood count and prothrombin time or INR should be obtained to support a clinical suspicion of alcoholic liver disease and to assess its severity.
- However, both laboratory abnormalities and physical findings may be minimal or absent even in patients with established alcoholic liver disease. When evaluating a patient for alcoholic liver disease, the clinician must remember that the toxic daily threshold dose of 80 g of alcohol is not absolute. Elevations in serum ALT may develop at much lower doses, especially in women and patients with hepatitis C infection.
- It may be necessary to perform a liver biopsy in patients with suspected alcoholic liver disease when the diagnosis is unclear because of atypical features or possible concomitant disease.
Alcoholic Cirrhosis Treatment
- Supportive treatment
- Specific treatment for bleeding Glucocortioids may be helpful
- S-adenosyl methionine may increase survival by decreasing inflammatory cytokines
- Counselling
- Diuretics, Aspirin, Paracetamol should be avoided.