Article Contents ::
- 1 Chronic pancreatitis Diseases Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
- 2 Chronic pancreatitis Pregentation
- 3 Chronic pancreatitis Causes
- 4 Chronic pancreatitis Clinical Features
- 5 Diagnostic Tests and Interpretation
- 6 Chronic pancreatitis Diagnosis
- 7 Chronic pancreatitis Complications
- 8 Chronic pancreatitis Prognosis
- 9 Chronic pancreatitis Treatment
- 10 Chronic pancreatitis:
- 11 Diet
Chronic pancreatitis Diseases Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
Chronic pancreatitis Pregentation
- · Abdominal pain
- · Steatorrhea.
A form of pancreatitis that results from repeated or massive pancreatic injury, marked by the formation of scar tissue, which leads to malfunction of the pancreas
- Irreversible:
- Progressive destruction of the pancreas
- Results in both exocrine and endocrine deficiencies
- Pain, maldigestion, and diabetes mellitus (DM) are the major features.
Chronic pancreatitis Causes
- · Alcoholism
- · Cystic fibrosis
- · Genetic disease
- · Autoimmune.
Chronic pancreatitis Clinical Features
- Chronic pancreatitis typically presents as chronic unrelenting pain with episodic flares,
- Pain in abdomen may be continuous, intermittent or absent
- · Atypical pain, back pain, diffuse pain, chest pain or flank pain.
- · Persistent, deep-seated pain.
- · Pain after alcohol or heavy meal.
- · Weight loss.
- · Stools abnormal like malabsorption.
- · Abdominal tenderness.
- · Fever.
Diagnostic Tests and Interpretation
- Chronic pancreatitis:
- Tests sometimes normal
- Hyperglycemia
- Steatorrhea
- Flare-ups may mimic acute pancreatitis.
- Elevated alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin
- Hereditary pancreatitis: Mutations in PRSSI gene and SPINKI gene
- Autoimmune pancreatitis: Elevated serum IgI, autoantibodies to lactoferrin and carbonic anhydrase
- Chronic pancreatitis Differential Diagnosis :
- Pancreatic cancer
- Other malabsorptive processes
- •Other cause of biliary obstruction
- Disorders that may alter results:
- Biliary tract disease
- Penetrating peptic ulcer
- Intestinal obstruction
- Intestinal ischemia/infarction
- Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
- Renal insufficiency
- Burns
- Macroamylasemia, macrolipasemia
Chronic pancreatitis Diagnosis
- · Serum amylase and lipase may not be elevated.
- · Alkaline phosphatase levels increased.
- · Fasting hyperglycemia.
- · Triad of pancreatic calcification, steatorrhea and diabetes mellitus.
- · Decreased serum trypsinogen less than 20 ng/ ml, fecal elastase less than 100 I-lg/mg of stool.
- · X-ray – scattered calcification.
- · Ultrasound, CT and ERCP.
- Radiograph of abdomen: Pancreatic calcification
- Ultrasound and/or CT scan of abdomen: Pseudocyst formation/calcification
- ERCP/MRCP: Ductal deformity, retained common bile duct stone, pancreatic duct stones, and strictures
- Endoscopic ultrasound
Chronic pancreatitis Complications
- · Cobalamin malabsorption (812 deficiency) in alcoholic and cystic fibrosis.
- · It is corrected by giving pancreatic enzymes.
- · Diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis
- · Pleural effusion
- · Pericardial effusion
- · GI bleeding
- · Portal vein thrombosis
- · Jaundice
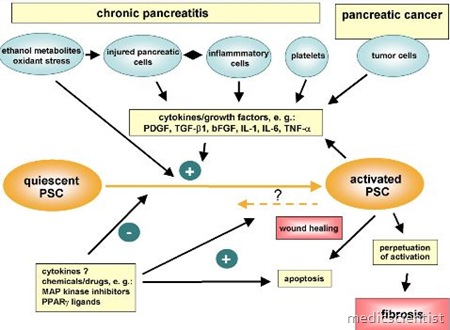
- · Incidence of pancreatic carcinoma is increased.
Chronic pancreatitis Prognosis
- Acute pancreatitis: 85–90% resolve spontaneously; 3–5% mortality (17% in necrotizing pancreatitis). APACHE II scoring is most accurate but difficult to apply
- Ranson criteria (see below) have a sensitivity of ~40%.
- On admission: Age >55 years, WBCs >16,000/mm, blood glucose >200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L), serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) >350 IU/L, AST >250 IU/L.
- Within 48 h: hematocrit decreases >10%, serum calcium <8 mg/dL, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) increase >8 mg/dL, arterial PO2 <60 mmHg, base deficit >4 mEq/L, fluid retention >6 L
Chronic pancreatitis Treatment
- Ensure alcohol abstinence.
- Persistent elevation of amylase weeks after acute pancreatitis suggests possibility of pseudocyst; perform imaging study.
- Avoid alcohol No fats
- Pain killers – narcotics
- Surgical interference – resection of pancreas Nerve blocks
Chronic pancreatitis:
- Analgesics
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements (Pancrease MT, Creon)
- H2 blockers (reducing gastric acid, increases availability of pancreatic enzymes)
- Pancreatic enzymes
- H2 receptor antagonist Sodium bicarbonate Proton pump inhibitors
- Antacids – Calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide
- Supportive measures.
- Chronic pancreatitis—pain: Pseudocyst drainage
-
Diet
- Acute pancreatitis: Begin diet after pain, tenderness, and ileus have resolved; small amounts of high-carbohydrate, low-fat, and low-protein foods; advance as tolerated; NPO or nasogastric tube if patient is vomiting
- Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) if oral is not tolerated (no lipids if triglycerides are increased)
- Enteral nutrition preferable to TPN if tolerated (less infection, decreased organ failure)
- Give oral pancreatic enzymes if necrotizing pancreatitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis: Small meals high in protein; adjust if DM is present.