Management of UA / NSTEMI ,with Anti-ischemic treatment -,uses of Nitrates and Beta adrenergic blockers .
Risk stratification and Prognosis
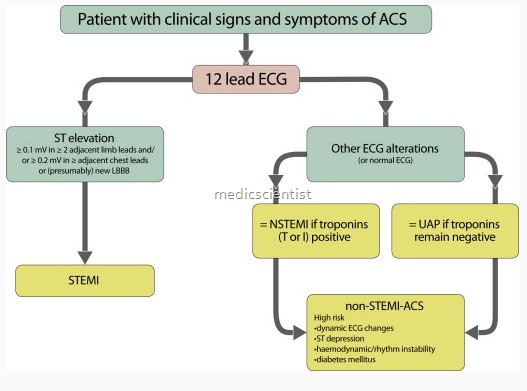
- Early risk within 30 days for death and new infarction is about 10%. Patients at high risk are age more than 65 years, 3 or more risk factors for CAD, documented CAD, angina inspite of aspirin, more than 2 episodes of angina in preceeding 24 hours, ST deviation more than 0.5 mm, and elevated cardiac marker.
Management of UA / NSTEMI
- Bed rest
- ECG monitoring f(x ST changes and rhythm y After 12 – 24 hours if the patient is pain free, has no new ECG changes, cardiac marker is not elevated then ambulation is allowed.
Anti-ischemic treatment –
Nitrates –
- Nitrates are given sublingually or . by buccal spray (0.3 – 0.6 mg) for pain. 3 doses are given at 5 minute intervals and then IV nitroglycerine started at 5 – 10 micro gm/minute using non-absorbing tubing if pain is not rel1eved.
- Nitrates are not given if systolic blood pressure is less than 100 mmHg. If patient has used Sildenafil in past 24 hours or if patient has hypotension then nitrates are not used.
- Nitrates may be discontinued or shifted to oral tablets when ischemic pain has subsided for 24 hours.
Beta adrenergic blockers –
- IV beta blockers followed by oral beta blockers should be given to all the patients where there is no contraindication.
Contraindications to beta blockers
- are heart rate less than 60/ minute, bronchial asthma, peripheral vascular disease.
- In such cases diltiazem or verapamil may be sed. –
- ACE inhibitors may be given especially in patients with history of MI, hypertension, CHF, AR, MR to reduce afterload.
- HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) may be given for long term secondary prevention.
- Morphine sulphate 1-5 mg IV every 5 minutes upto 15 mg may be given for severe persistent pain.
Antithrombotic therapy –
- Aspirin is Platelet aggregation inhibitor.
- Clopidogrel the platelet adenosine receptor blocker (CURE trial)
- Aspirin plus clopidogrel
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH) or low molecular weight heparin (lMW ) especially enoxaparin, improves survival.
- e/ GPIIb / IIIa inhibitors are also beneficial and can be given IV.
- Invasive treatment: In patients with multiple risk factors, coronary arteriography is done within 48 hours of admission followed by coronary revascularization by PeI (percutaneous coronary intervention) or CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting).
Indications for early invasive treatment like PCI (Percutaneous coronary intervention) or CABG (Coronary artery bypass grafting) are:
- a. Recurrent angina inspite of full treatment
- b. Elevated TnT (Troponin T), or TnI (TroponinI)
- c. Fresh ST changes
- d. Angina with CHF, rales, MR
- e. Positive stress test
- f. Ejection fraction less than 40%
- g. Low blood pressure
- h. Sustained VT (ventricular tachycardia) i. PeI or CABG already done
- Invasive treatment should not be offered to lowrisk patients.
Long term management:
- Stoppage of smoking, weight reduction, daily exercise, diet control, lipid control, blood sugar control, life style changes and stress management.
- Beta blockers, statins, ACE inhibitors, anti platelets may be continued for a long time and even lifelong.