Article Contents ::
Management of APH (Antepartum haemorrhage) and ManagementPlacenta previa (PP)
- Management
- } b. Standard management of symptomatic patients with PP
- ◦ hospitalization with hemodynamic stabilization and continuous maternal and fetal monitoring.
- ◦ Laboratory studies should be ordered
- ◦ Steroids should be given to promote lung maturity for gestations between 24 and 34 weeks.
- ◦ Rho(D) immunoglobulin should be administered to Rh-neg-ative mothers.
- } is then based on
- } gestational age,
- } severity of the bleeding, and
- } fetal condition and presentation.
- } d. Management of complications, such as
- } placenta accreta or one of its variants
Management of Placenta previa (PP)
- } In patients with PP and a previous history of cesarean section, cesarean hysterectomy-may be required.
- } in cases where uterine preservation is highly desired and no bladder invasion has occurred,
- } bleeding has been successfully controlled with selective arterial embolization or
- } packing of the lower uterine segment, with subsequent removal of the pack through the vagina in 24 hours.
- } 2. Term Gestation, Maternal and Fetal Hemodynamic Stability.
- } At this point, management depends on placental location.
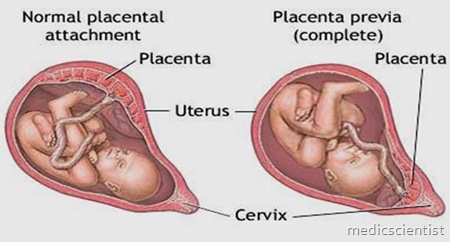
- } a. Complete Previa.
- } Patients with complete previa at term require cesarean section.
- } b. Partial, Marginal Previa.
- } These patients may deliver vaginally;
- } a double setup in the operating room is recommended.
- } The patient should be prepared and draped for cesarean section.
- } An anesthesiologist and the operating room team should be present.
- } If at any point maternal or fetal stability is compromised, urgent cesarean section is indicated.
- } 3. Term Gestation,
- } Maternal and Fetal Hemodynamic Instability.
- } The first priority is to stabilize the mother with
- } fluid resuscitation and
- } administration of blood products, if necessary.
- } a. Delivery is indicated with
- } evidence of nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing,
- } life-threatening maternal hemorrhage,
- } or any bleeding after 34 weeks with known fetal lung maturity.
- } b. Delivery should then occur via cs.
- } If the mother is hemody-namically stable and fetal loss has occurred or the fetus is less than 24 weeks,
- } then vaginal delivery can be considered.
- } 4. Preterm Gestation, Maternal and Fetal Hemodynamic Stability
- } a. Labor Absent.
- } Patients at 24 to 37 weeks’ gestation with PP who are hemo-dynamically stable can be
- } managed expectantly until fetal lung maturity has occurred.
- } Hospitalization until stabilized
- } Bed rest with
- } periodic assessment of maternal hematocrit
- } Blood transfusions to keep hematocrit above 30% in patients with a
- } low-grade continuous bleed
- } steroids for fetal lung maturity
- } Fetal testing, and serial ultrasounds
- } Tocolysis is used for
- } the administration of antenatal steroids in an otherwise stable patient.
- } After initial hospital management,
- } care as an outpatient
- } if the bleeding has stopped for more than 1 week,
- } no other complications exist,
- } and the following criteria are met:
- } ■ The patient can maintain bed rest at home.
- } The patient has a responsible adult present at all times who can assist
- } in an emergency situation.
- } The patient lives near the hospital with
- } available transportation to the
- } hospital and is adherent to medical care.
- } once a patient has been hospitalized
- } for three separate episodes of bleeding,
- } she remains in the hospital until delivery
- } b. Labor Present.
- } Twenty percent of patients with PP show evidence of uterine contractions.
- } If the patient and fetus are stable,
- } tocolysis may be considered
- } with magnesium sulfate.
- } Preterm Gestation,
- } Maternal and Fetal Hemodynamic Instability.
- } maternal stabilization with
- } resuscitative measures is the priority.
- } Once stable,
- } the patient should be delivered by urgent cesarean section.
- } This is a very rare condition in which
- } the umbilical vessels in the membranes are passing opposite the internal cervical in case of velamentous insertion of the cord.
- } Rupture of these vessels will lead to
- } bleeding of fetal origin which is very dangerous
- } a. Labor Absent.
RUPTURE VASA PRAEVIA
- } It should be suspected when
- } fetal distress is marked with mild vaginal bleeding and good general condition of the mother
- } . Examination of the blood will show fetal RBCs.
- } Treatment is by immediate caesarean section
- } It is one form of ante partum haemorrhage in which the bleeding occurs due to the premature separation of normally situated placentae .
- } It occurs in three forms—
- 1.Concealed type
- 2.Revealed type
- 3.Mixed type
Abruptio Placentae
- } History of trauma
- } High birth order of pregnancies
- } Low socio economic status
- } Advancing age of mother
- } Sudden decompression
- } Pregnancy induced hypertension
- } External version
Etiology
- } GRADE 0—
- } No clinical features
- } Grade 1—
- } Slight external bleeding and tenderness
- } Fetal distress may occur
- } Grade 2—
- } External bleeding mild to moderate
- } Shock absent
Grading of ABP
- } Grade 3—
- } Bleeding moderate to severe May be concealed
- } Marked uterine tenderness
- } Fetal death is a rule
- } Shock present
- } Depending upon the degree of separation, speed at which separation occurs and amount of blood concealed inside the uterine cavity , the features of ABP can be studied comparatively under following headings
- } Symptoms
- } General condition
- } Pallor
- } Toxemia
CLINICAL FEATURES
- } Hight of utrus
- } Uterine feel
- } Fetal parts
- } FHS
- } Coagulation profile
Management
- Management Comparison of PP and AP
- } Feature of Bleeding
- ◦ Painless
- ◦ Causeless
- ◦ Recurrent
- } Character of bleeding
- ◦ Bright red
- } General condition & anemia
- ◦ Proportionate to visible blood loss
- ◦ Painfull bleeding with h/o trauma
- ◦ Bright red
- ◦ Out of proportion to visible blood loss
- } Abdominal examination
- ◦ Height of the uterus is proportional to gestational age
- } Feel
- ◦ Uterus feelsvsoft and relaxed
- } Malpresentation
- ◦ It is common in pp
- ◦ Painful bleeding with h/o trauma
- ◦ May be disproportionate rarely enlarge
- ◦ Tender and hard
- ◦ unrelated
- } F.H.S.
- ◦ Usualy present
- } Placenta in lower segment
- } Engagement
- ◦ High floating
- ◦ Absent/feeble
- ◦ Upper segment
- ◦ Tender and hard
- ◦ Normal engagement