Article Contents ::
- 1 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
- 2 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
- 3 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA
- 4 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Etiology —
- 5 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Classification —
- 6 Clinical presentation Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
- 7 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Symptoms —
- 8 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Treatment
- 9 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Hematological findings
- 10 Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Treatment
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
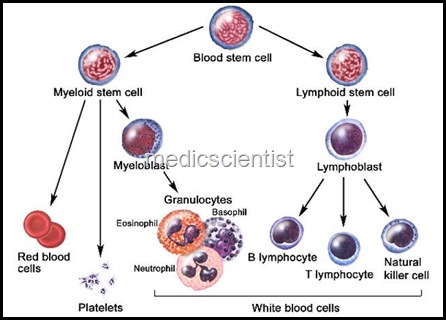
- Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias neoplastic cells of the hemopoietic system
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias ,The myeloid leukemias are a group of diseases with infiltration of blood, bone-marrow and other tissues by neoplastic cells of the hemopoietic system
 |
| Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias |
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
- The myeloid leukemias are a group of diseases with infiltration of blood, bone-marrow and other tissues by neoplastic cells of the hemopoietic system.
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA
- Incidence is higher in men than in women. Incidence increases with age.
 |
| Etiolog |
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Etiology —
- Heredity, radiation, chemical and occupational exposure, drugs, virus.
- Certain syndromes are associated with leukemias like Down’s syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Patau syndrome, Fanconi anemia, Ataxia telangiectasia, Kostmann syndrome.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Classification —
- Acute leukemias are classified on basis of morphology, cytochemistry, cytogenetics and molecular techniques.
Clinical presentation Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias
- Patients with AML(acute myeloid leukemia) present with non-specific symptoms, gradually or abruptly.
- Presentation may be due to anaemia, leukocytosis, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Symptoms —
- are fatigue, weakness, anorexia, weight loss, fever, bleeding, easy bruising, bone pains, lymphadenopathy, cough, headache, diaphoresis.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Physical findings —
- are fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy, sternal tenderness, infection, haemorrhage, GI (gastrointestinal) bleeding, intracranial haemorrhage, retinal hemorrhages.
- There may be infiltration of gums, skin, soft tissues, meninges, granulocytic sarcoma in GIT, lung, uterus, breast, prostate, mediastinum, and bone.
- Other systems
- which are involved are cardiovascular, hepatic and renal systems.
- The most severe and fatal presentation is in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) or monocytic AML.
Hematological findings
 |
| Hematological findings |
- Anaemia – usually normocytic, normochromic. Reduced reticulocyte count.
- Leukocyte count may be 15,000 to 100,000 or sometimes more than even 100,000/1J1.
- 20 – 40 per cent of patients have leucocyte count less than 5000/1J1.
FAB (French-American-British) classification of AML
- MO M1 M2 M3 M4 M4Eo
- Minimally differentiated leukemia Myeloblastic leukemia without maturation Myeloblastic leukemia with maturation Hypergranular promyelocytic leukemia Myelomonocytic leukemia
- Variant: Increase in abnormal marrow eosinophils
- Monocytic leukemia
- Erythroleukemia (DiGuglielmo’s disease) Megakaryoblastic leukemia
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Treatment
- The treatment is divided into 2 phases:
- Induction phase
- Post remission management
- The goal is to quickly induce CR (complete remission).
Complete remission (CR)
- CR is defined as absence of blast cells in circulation. Blood neutrophil count must be more than 1500/1J1. Platelet count must be more than 100,000/ IJI. Bone-marrow should contain less than 5% blast cells. Auer rods should be absent.
- Standard therapy is 7-day continuous infusion of Cytarabine 100 – 200 mg /sq m / day.
- Patients who achieve CR must be given consolidation therapy with sequential courses of Cytarabine in high doses and allogenic stem cell transplant.
- Patients with APL (acute promyeiocytic leukemia) should receive Tretinoin with anthracycline chemotherapy (Daunorubicin), and then consolidation chemotherapy with Daunorubicin and Cytarabine, followed by maintenance with tretinoin.
- Clinical trials with recombinant hemopoietic growth factors are going on.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Supportive care
- with blood transfusion, platelet transfusion, broad-spectrum antibacterials, and antifungals are given.
CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS I MYELOID LEUKEMIA
- The diagnosis ofCML(chronicmyeloid leukemia) is by presence of haematopoietic stem cell with reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22.
- The disease is characterized by elevated white blood cell counts with a majority of immature granulocytes, which progresses to an accelerated phase and a blast crisis.
- The incidence of CML increases after the age of 40.
Etiology is same as AML
- Clinical presentation Onset is slow, with patients often asymptomatic at diagnosis.
- There is fatigue, malaise, weight loss, splenomegaly, infections, thrombosis, bleeding, cerebrovascular accidents, MI, venous thrombosis, bone and joint pains, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Hematological findings
- White blood cells counts are grossly elevated, immature granulocytes are seen in circulating blood, but small in number i.e. less than 5% blasts and less than 10% promyelocytes are seen in circulating blood.
- Platelet counts may be elevated
- There is increased bone marrow cellularity, of myeloid and megakaryocytic types.
- Disease acceleration is defined as increasing anaemia, blood or marrow blasts between 10 and 20%, blood or marrow basophils >20%, platelet count less than 100,000/1-11.
- Blast crisis is defined as acute leukemia with blood or marrow blasts more than 20%.
Acute & Chronic Myeloid Leukemias Treatment
- Allogenic stem cell transplant or treatment with ImatinibInterferon
- Chemotherapy with hydroxyurea, 1-4 g/day, halved when leucocyte count reduces by 50%
- Busulphan : alkylating agent, with serious sideeffects and therefore not used nowadays
- HHT — Homoharringtonine is a plant alkaloid from Cephalotaxus tree
- Leukapheresis and splenectomy
