Article Contents ::
Disorders of Anterior PituitaryHormones
The anterior pituitary is called the master gland be , it regulates the function of most other endocrine organs. The anterior pituitary gla’nd produces 6 major hormones.
- 1, Prolactin (PRL)
- 2. Growth hormone (GH)
- 3. Adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
- 4. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- 5. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- 6. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
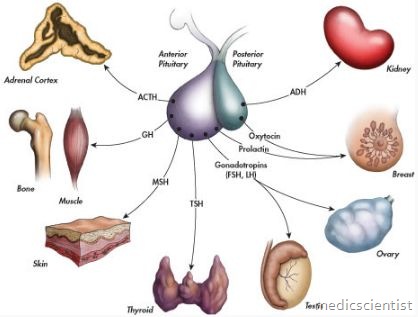
- All the pituitary hormones are secreted in a pulsatile manner by the corresponding specific hypothalamic releasing factors.
- Each pituitary hormone causes specific response from the target organ / issues.
- Pituitary diseases can cause acquired or inherited hormone deficiency.
- Pituitary tumors cause hormone excess syndrome or they cause a mass effect by pressing on adjacent structures like cavernous sinuses, optic chiasma and ._ cranial nerves, and blood vessels.
- The pituitary gland has 2 lobes-anterior and posterior lobes.
- The posterior pituitary is also called neurohypophysis,
- These target organs / glands release hormones which exert a feedback inhibition on the hypothalamus and pituitary to control the bjood level of the hormones.
ANTERIOR PITUITARY INSUFFICIENCY
- · Hypopituitarism is due to decreased levels of anterior pituitary trophic hormones released from the hypothalamus.
- · It can also occur due to inherited diseases.
- · Acquired deficiency can result from tumors, inflammation or vascular damage of pituitary or hypothalamus.
Developmental and genetic causes: Pituitary dysplasia –
- This is due to hypoplastic or ectopic pituitary gland.
- It can also be due to birth trauma, asphyxia and breech delivery.
Examples are:
- · Septo-optic dysplasia (hypothalamic dysfunction, cleft palate, syndactyly, ear deformity, optic atrophy, microgenitals, anosmia).
- · Kallmann syndrome (isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, associated with defects of smell, X-linked).
- · Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Bidel Syndrome (autosomal recessive, mental retardation, obesity, hexadactyly, syndactyly, diabetes insipidus, retinal degeneration).
- · Frohlich syndrome (Hypothalamic lesions, obesity, hyperphagia-Ieptin deficiency, hypogonadism).
- · Prader-Willi Syndrome (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, obesity, hypotonia, mental retardation, diabetes mellitus).
Acquired Hypopituitarism
- Acquired causes are accidental, or neurosurgical trauma.
- Vascular causes like pituitary apoplexy. Neoplasms like pituitary adenoma, craniopharyngioma, metastatic tumors.
- Inflammatory diseases like sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, tuberculosis, and irradiation.
Pituitary apoplexy
- Acute haemorrhagic damage of pituitary may occur spontaneously in a pre-existing adenoma, or postpartum as in Sheehan’s syndrome, or in diabetes, hypertension, sickle cell anaemia, or acute shock.
- During pregnancy there is enlargement of the pituitary, sometimes resulting in haemorrhage. Apoplexy is an emergency with hypotension, hypoglycemia, brain haemorrhage and death.
- There is severe headache, meningeal irritation, visual defects, cardiovascular collapse, coma and death. CT or MRI is used for diagnosis.
Treatment of Pituitary apoplexy
- High dose glucocorticoids.
- Surgical decompression is required in patients with visual loss and coma.
