Article Contents ::
- 1 Biliary Cirrhosis (Primary and Secondary) Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
- 2 BILIARY CIRRHOSIS
- 3 PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Etiology
- 4 Manifestations of PBC
- 5 PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Pathology
- 6 PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Symptoms
- 7 Physical examination:
- 8 PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Diagnosis
- 9 PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Treatment
- 10 SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS
- 11 SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Symptoms
- 12 SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Diagnosis
- 13 SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Treatment
Biliary Cirrhosis (Primary and Secondary) Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
BILIARY CIRRHOSIS
- Biliary cirrhosis occurs due to injury or prolonged obstruction of intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary system. There is destruction of liver cells and progressive fibrosis with biliary obstruction.
- In primary biliary cirrhosis there is intrahepatic bile ductules obstruction.
- progressive jaundice, consequences of impaired bile excretion, and ultimately cirrhosis and liver failure.
- Presents as asymptomatic elevation in alkaline phosphatase (better prognosis) or with pruritus,
- Secondary biliary cirrhosis is due to long-standing obstruction, of larger extrahepatic ducts.
PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Etiology
- May be associated with:
- · CREST syndrome – (Calcinosis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia)
- · Diabetes type I
- · Sicca syndrome.
- Cause is unknown. It may be autoimmune.
- IgG mitochondrial antibody (AMA) is detected. Serum levels of IgM is elevated
- Liver biopsy most important in AMA-negative PBC.
- Biopsies identify 4 stages:
- stage 1—destruction of interlobular bile ducts, granulomas;
- stage 2—ductular proliferation;
- stage 3—fibrosis; stage 4—cirrhosis.
Manifestations of PBC
- Specific to PBC
- Fatigue
- Pruritus
- Portal hypertension
- Metabolic bone disease
- Xanthomata
- Fat soluble vitamin malabsorption
- Urinary tract infection
- Malignancy
- Associated disorders
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Sicca syndrome
- CREST
- Raynaud’s syndrome
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease
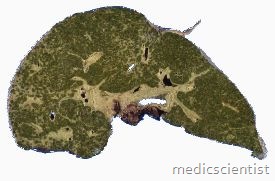
PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Pathology
- · There is chronic non-suppurative destructive cholangitis.
- · Cirrhosis may be micronodular or macronodular.
PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Symptoms
- PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Clinical features
- 90% of patients are females of age 35 – 60 years. May be asymptomatic and detected on routine screening with elevated serum alkaline phosphatase.
- There is progressive liver injury.
- There is pruritus, especially of palms and soles. There is fatigue, jaundice, and darkening of the exposed areas of skin (melanosis).
- There is steatorrhoea and malabsorption offat solu’ble vitamins due to impaired bile excretion.
- Xanthelasma can be seen over eyes, joints, tendons. There is portal hypertension-ascites, variceal haemorrhage.
- Death occurs due to hepatic insufficiency in 5 – 10 years.
Physical examination:
- May be normal (no finding) Jaundice
- Melanosis
- Xanthomas
- Hepatomegaly Splenomegaly
- Clubbing
- Bone tenderness
- Sicca syndrome (drying up of mucus membranes) CREST syndrome.
PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Diagnosis
- Lab findings
- · Serum alkaline phosphatase is elevated
- · Serum 5 nucleotidase activity and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GTT) levels are elevated
- · Serum bilirubin is normal.
- · ALT and AST are increased
- · Positive AMA test
- · Hyperlipidemia
- · Steatorrhea
- · Hypoprothrombinemia
- · Liver biopsy confirms the diagnosis.
PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Treatment
- No specific treatment for PBC Liver transplantation
- Ursodiol – 13 to 15 mg/kg/day single dose Colchicine
- Methotrexate
- Cholestyramine orally helps to relieve pruritus For steatorrhoea-Iow fat diet
- Vitamin A, 0, E, K
- Zinc and calcium supplementation Biphosphonate (Alendronate) for osteoporosis.
SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS
- Etiology:
- · Partial or total obstruction of common bile duct
- · Cause of obstruction may be strictures, gall stones, chronic pancreatitis
- · Autoimmune causes
- · Congenital biliary atresia
- · Cystic fibrosis.
SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Symptoms
- Clinical features
- · Jaundice
- · Pruritus
- · Biliary colics.
SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Diagnosis
- Investigation
- · Cholangiography
- · Liver biopsy.
SECONDARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS Treatment
- Relief of obstruction by surgery or endoscopy Antibiotics.