Article Contents ::
- 1 INTRACATH / INTRAVENOUS CANNULA It is used for giving IV fluids and drugs—
- 2 CANNULA
- 3 Indications —
- 4 The LP needle —
- 5 LP needle
- 6 Lumber puncture Method —
- 7 Lumber puncture Method
- 8 Complications —-
- 9 Contraindications —
- 10 BONE MARROW BIOPSY —
- 11 Bone marrow biopsy needle —-
- 12 Site of Puncture
- 13 Technique
- 14 Indications—
INTRACATH / INTRAVENOUS CANNULA It is used for giving IV fluids and drugs—
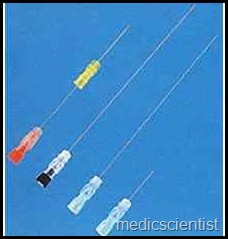 |
CANNULA |
- It consists of a long metallic: needle and a plastic cannula or sheath over it.
- The bevelled tip of the needle goes inside the vein and at the other end the blood leaking out can be seen.
- The needle may then be withdrawn and the plastic cannula or sheath left in place for many days.
Indications —
- · To withdraw CSF in cases of meningitis for diagnosis of etiology.
- · Subarachnoid haemorrhage.
- · GB syndrome – albumin cytological dissociation.
- · Queckenstedt test for CSF block.
- · For myelogram – for diagnosis of spinal tumors, disc prolapsed etc.
- · Therapeutic use – Intrathecal administration of steroids, immunoglobulin’s, methotrexate etc.
- · For Spinal anaesthesia.
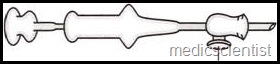
The LP needle —
 |
LP needle |
- · It is a sharp needle with a short bevel (slanting tip), with a stilette fitting inside the needle.
- · It is made of steel.
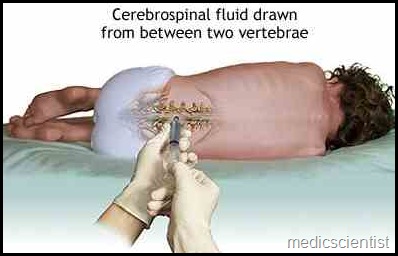
Lumber puncture Method —
 |
Lumber puncture Method |
- · The patient may sit up and bend forwards or lie in a lateral decubitus position with the knees drawn up on the abdomen and head fully flexed.
- · In this position the back arches backwards and the intervertebral spaces are increased.
- · The LP need Ie is inserted between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebra i.e. on a line joining the highest points of the two iliac crests.
- · The patient is sedated, positioned, cleaned, draped and local anaesthetic xylocaine is injected subcutaneously at the site. LP needle is inserted with the stilette with the bevel of needle pointing upwards, direct into the space till loss of resistance is felt when the needle passes through the dura. The stillete is removed and CSF is seen to trickle out. CSF is collected in 3 bottles about 2 ml each for biochemical test, culture sensitivity and cytological examination.
- · The needle is taken out after replacing the stilette and the site is sealed with tincture benzoin.
- · The head end is lowered by raising the foot end.
Complications —-
- · Dry tap – no CSF comes out.
- · Traumatic LP
- · Hypotension
- · Headache
- · Brain stem herniation
- · Introduction of infection
- · Backache.
Contraindications —
- · Raised intracranial tension and papilledema
- · Skin infection at the site of puncture
- · Spinal cord compression
- · Bleeding disorders
- · Septicemia.
BONE MARROW BIOPSY —
- Aspiration biopsy is done with a wide bore needle.
Indications —-
- · Anaemias
- · Pancytopenia
- · Purpuras
- · Myeloid metaplasia
- · Leukemias
- · Multiple myeloma
- · Lymphomas
- · Kala azar
- · Prog nostic.
Bone marrow biopsy needle —-
- It is also called a sternal puncture needle.
- The Salah’s needle consists of stout wide bore short bevelled needle With a stilette. On the side it has a screw guard which can be tightened at a particular distance from the tip to avoid over- penetration.
Site of Puncture
- · The first part of body of sternum.
- · Posterior Iliac crest.
Technique
- · Sternal puncture
- · Patient is mildly sedated. The sternum is cleaned and punctured opposite the second and third
- intercostal spaces and ~ocal anaesthetic Xylocaig.e injected so as to infiltrate the periosteum whiCh is very sensitive to pain.
- >· The aspiration needle is inserted vertically half cm. into the sternum. On entering the bone marrow loss of resistance is felt, stilette is removed and suction applied with a syringe to draw out 0.2 ml of marrow. The needle is withdrawn and puncture site is pressed and sealed with tincture ben?:oin.
- · Films are prepared from aspirate immediately.
- · For posterior iliac crest puncture, the patient is in lateral decubitus position and the needle is introduced perpendicularly into the ilium at the posterior superior iliac spine.
- Cutting fork
Indications—
- · For diagnosis of liver disease in jaundice
- · Hepatitis
- · Chronic hepatitis
- · Cirrhosis and portal hypertension
- · Unexplained hepatomegaly
- · Abnormal LFT
- · PUO
- · Malignancies and lymphomas
- · Metabolic diseases.
This is short description about some spatial processors’ in medical field, general practice.