Article Contents ::
Cushing’s Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Cushing’s disease is a hormone disorder caused by high levels of cortisol in the blood disease in which there is excess ACTH secretion, by pituitary adenomas.
- Cushing’s syndrome is the signs and symptoms that result from prolonged exposure to excessive glucocorticoid hormones.
Cushing’s disease:
- Cushing’s syndrome hormone disorder caused by excessive production of adrenocorticotropic hormone in the body.
- It is more common in women.
- There is hypercortisolemia.
- On giving glucocorticoids, the cortisol levels are suppressed indicating a pituitary origin.
- Cushing’s disease is hypercortisolemia due to pituitary adenomas.
- Cushing’s syndrome is excess cortisol due to any cause like exogenous ACTH tumor, adrenal tumor, pituitary ACTH secreting tumor, excess glucocorticoid therapy.
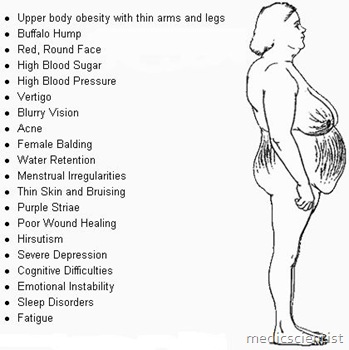
Cushing’s Syndrome Symptoms
Clinical features:
- most common feature of patients with Cushing’s syndrome hormone disorder is progressive central (centripetal) obesity
- thin, brittle skin, purple striae, gonadal dysfunction, osteoporosis, central obesity, hypertension, moon facies, diabetes mellitus / glucose intolerance,depression, mania, osteoporosis.
- proximal muscle weakness, acne, hirsutism,
- Menstrual irregularities are common in women with Cushing’s syndrome
- There is leukocytosis, lymphopenia, delayed hypersensitivity.
- In patients on steroids there is hyperpigmentation, myopathy,
- hypertension, hypokalemic alkalosis, edema, glucose intolerance.
Cushing’s Syndrome Lab Diagnosis
- Estimation of 24-hour free cortisol in urine (UFC).
- Failure to suppress plasma cortisol after 1 mg dexamethasone given at night.
- Increased midnight levels of cortisol are found in Cushing’s syndrome (in normal persons the level of cortisol is low at midnight).
Cushing’s Syndrome Treatment
- Transsphenoidal resection Pituitary irradiation
- Ketoconazole, an antimycotic agent, lowers cortisol in Cushing’s disease, in doses of 600- 1200 mg/day.
- Other drugs are metyrapone, mitotane
- Adrenalectomy – Removal of both adrenal glands corrects hypercortisolism but results in Nelson’s syndrome i.e. pituitary tumor with high ACTH levels.
