Ischemia Types Effects of Ischemia, Myocardial ischemia(MI) ECG ,vertebrobasilar ischemia and other metabolic changes
- A temporary deficiency of blood flow to an organ or tissue,
- Normal muscle contraction and relaxation affected
- Angina pectoris has been considered the cardinal symptom of myocardial ischemia for more than two centuries.

- LVF (left ventricular failure)
- Papillary muscle dysfunction ~MR ~LV dilata-
- LVF
- Angina pectoris
- Myocardial necrosis and scarring
- MI
- Akinesis
- Dyskinesis.
- between 25 and 45 percent of patients with acute and chronic ischemic syndromes have evidence of myocardial ischemia during daily life,
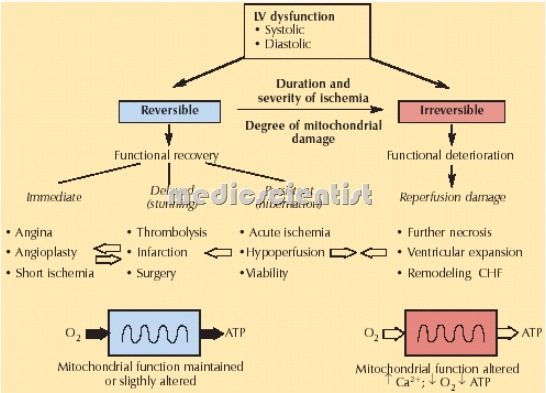
Types of Ischemia —
myocardial ischemia (MI):
- evidence of myocardial ischemia in the absence of chest discomfort or other anginal equivalents.
- An inadequate supply of blood and oxygen to meet the metabolic demands of the heart muscle.
- Exercise testing or ambulatory monitoring shows transient ST segment changes
vertebrobasilar ischemia:
- Inadequate blood flow through the arteries that supply nutrients and oxygen to the structures at the base of the brain (esp. the brain stem and cerebellum).
lower limb ischemia:
- An inadequate blood flow to one or both legs due either to chronic arterial obstruction caused by atherosclerosis or to acute obstruction caused by embolism.
Metabolic Changes
- Accumulation of lactic acid, depletion (wash out) of high energy phosphates, oxygen and creatine phosphate.
- In the presence of oxygen, fatty acid and glucose are metabolized to carbon dioxide and water.
- Fatty acids, glucose O2 co2 —–> and H20.
- In absence of oxygen fatty acids and glucose are metabolized to lactic acid which promotes coronary spasm,
- Changes are reversible up to 10 minutes .
- after 20 minutes changes are irreversible.
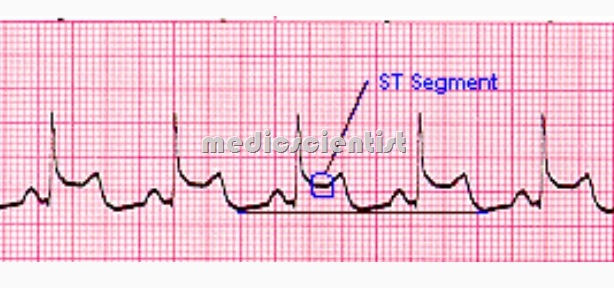
ECG Changes
- typical changes of angina / IHD are:
- ST depression
- T inversion
- These are seen in contiguous leads like 2, 3, AVF, ferior wa or I, L, V5,V6 (lateral wall).
- severe ischemia, ST elevation is seen and indi:c~es transmural ischemia; it may evolve into ‘: myocardial infarction).
- eIedrical instabilit~ads to arrhythmias – VT-(ven:-icular tachycardia) -.and VF-(ventricular fibril~ation).
- death occurs due to pump failure or ventricular :tachyarrhythymias.
