RUBELLA OR GERMAN MEASLES and CHICKENPOX and SMALLPOX Causative agents Diagnosis Clinical Signs and Symptoms With Treatment
 |
| RUBELLA OR GERMAN MEASLES |
- Acute mild infection of children.
- There is low grade fever, lymphadenopathy, maculopapular rash, and arthritis in adults.
- In early pregnancy, rubella infection results in congenital defects and even death of the fetus.
RUBELLA Causative agent
- RNA toga virus.
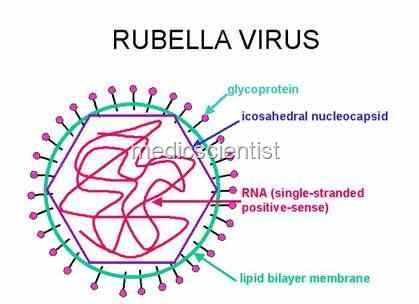 |
| RUBELLA VIRUS OR GERMAN MEASLES virus |
RUBELLA Source of infection
- · Clinical and subclinical cases of rubella.
- · Virus is transmitted from nose, throat secretion one week before rash to one week after rash.
- · The virus can cross the placenta leading to congenital rubella in the baby.
RUBELLA Period of infectivity
- A week before symptoms to a week after rash.
- One attack gives life-long immunity. Second attacks are rare.
RUBELLA Incubation period
- 10-20 days. Age: 3 to 15 years.
RUBELLA Rash
- · It is seen on the face within 24 hours.
- · Rashes are small, discrete, macular, spread to
- the trunk, arms and legs.
- · Disappears on third day.
RUBELLA Complications
- Arthralgia,
- encephalitis,
- thrombocytopenic purpura.
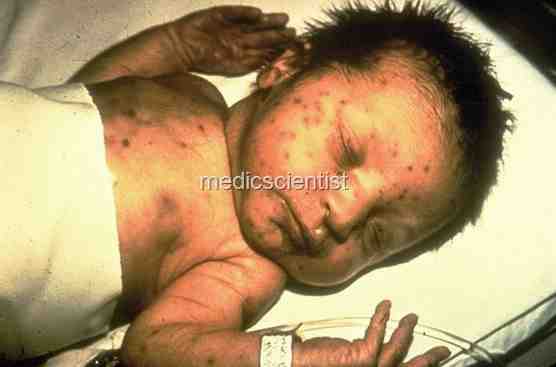
CONGENITAL RUBELLA
- Infants born to mothers with rubella in pregnancy suffer from congenital rubella syndrome.
- Congenital defects are deafness, low birth weight, cardiac defects, cataracts, glaucoma, retinopathy, microcephaly, mental retardation.
- In first trimester of pregnancy abortion can occur.
RUBELLA Vaccination
- · Active immunization with live attenuated vaccine.
- · MMR vaccine consists of measles, mumps, rubella vaccine.
- · All children aged 1 to 14 years or preferably all i-year old children should be vaccinated.
- · All women of child bearing age (15 to 39 years) should be vaccinated if not already vaccinated.
 |
| CHICKENPOX Diagnosis Clinical Signs and Symptoms |
CHICKENPOX Caused by
- Varicella zoster virus.
- Characterized by vesicular rash, fever, malaise Chickenpox and Herpes zoster have same etiology.
 |
| CHICKENPOX VIRUS Clinical Signs and Symptoms |
CHICKENPOX Source of infection –
- A case of chickenpox.
CHICKENPOX Infection occurs from
- skin lesions
- oropharyngeal secretions.
- Vesicular fluid spreads the virus during the first 3 days.
- Scabs are not infective
CHICKENPOX Period of infectivity –
- 2 days before rash to 4 days after rash.
CHICKENPOX Age
- Children under 10 years. Second attack is rare.
 |
| CHICKENPOXCongenital varicella |
CHICKENPOX Congenital varicella
- Virus crosses placental barrier,
- infects the fetus called congenital varicella.
CHICKENPOX Incubation period –
- 14 days.
CHICKENPOX Clinical features –
- sudden onset fever,
- pain in the back,
- shivering,
- malaise.
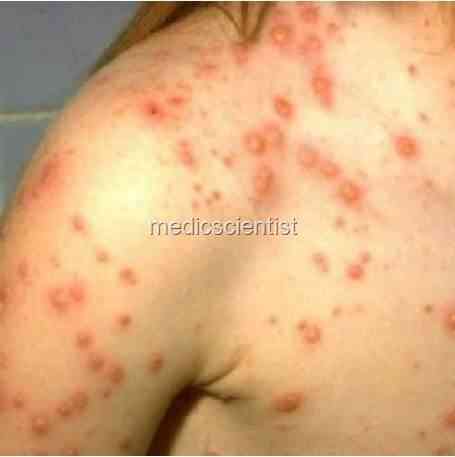
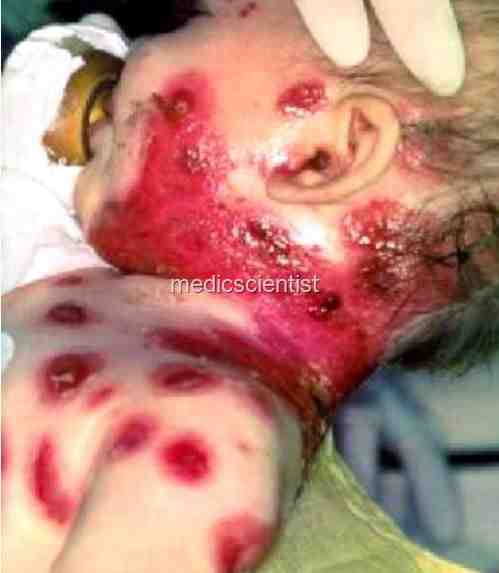
CHICKENPOX Rash
- after 1 to 2 days.
- Rash is symmetrical, on trunk, face, arms, legs, mouth Palms and soles not affected.
- Vesicles have clear fluid and look like dew drops. Scabbing after 4 days.
- There is pleomorphism – all stages of rash seen together.
- There are several crops of rash each time with fever.
CHICKENPOX Complications
- Haemorrhages,
- Pneumonia,
- Encephalitis.
CHICKENPOX Vaccine
- There is no need of vaccine as the disease does not occur after first attack and it is a mild illness.
 |
| SMALLPOX |
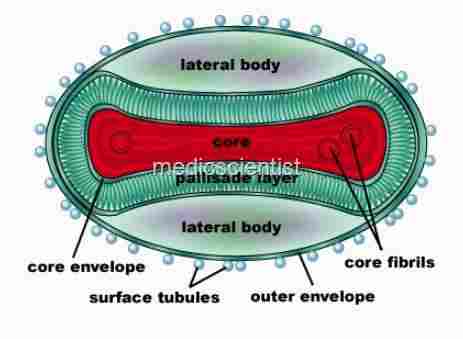
SMALLPOX Caused by
- Variola virus
 |
| Variola virus SMALLPOX |
SMALLPOX Characterized by :
- · Fever of sudden onset
- · Headache, Backache
- · Vomiting
- · Convulsions
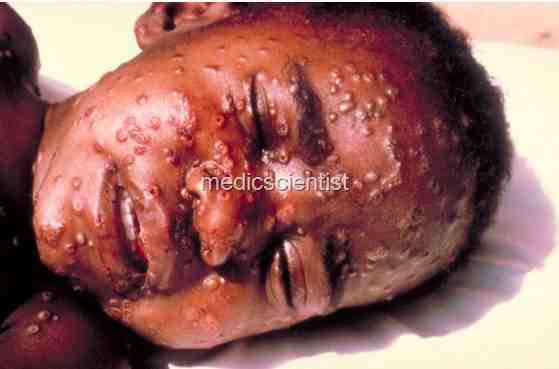
- On 3rd day of fever – typical centrifugal rash, i.e. more peripherally, appears.
Stages of SMALLPOX –
- macules,
- papules,
- vesicle,
- pustule,
- scab,
- scarring.
- Smallpox has been eradicated globally.
