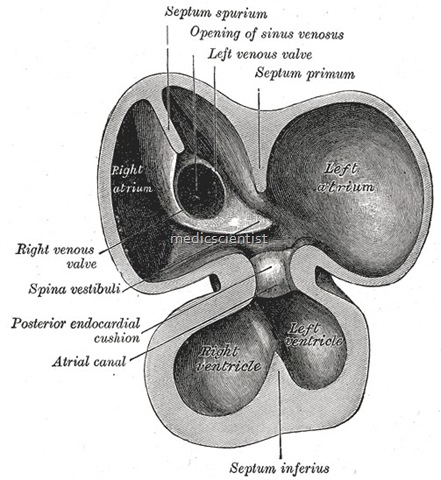
Sinus venosus defect
- AII the features are same as ostium secundum except that P waves are inverted in inferior leads, and right hilum in chest X-ray shows dilatation of lower portion of superior vena cava where it joins the right atrium.
- In the adult, it is incorporated into the wall of the right atrium to form a smooth part called the sinus venarum, also known as the venarum sinus,
- The sinus venosus also forms the SA node and the coronary sinus.
- 2D echo with colour flow and spectral Doppler localizes the ASD.
- In humans, it exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart, where it is found between the two venae cavae.
SD with reversal of shunt (Eisenmengern)
- Occurs in < 10% of cases
- Cyanosis develops after 3rd decade only Dyspnoea and fatigue occur
- There may be syncope
- JVP shows big ‘a’ waves
- There is parasternal heave and P2 is loud and palpable.
- There are signs of pulmonary hypertension, fourth
- heart sound, pulmonary ejection sound, soft short pulmonary ejection systolic murmur narrow split of or single second heart sound with loud P2 and Graham steell murmur (early diastolic murmur in left parasternal area of pulmonary regurgitation due to pulmonary hypertension).
ECG:
- shows RSR pattern in V1 or rR pattern or dominant R wave with deeply inverted T waves.
X-ray:
- shows clear peripheral lung fields, large pulmonary trunk and its branches and small aorta.